37款传感器与执行器的提法,在网络上广泛流传,其实Arduino能够兼容的传感器模块肯定是不止这37种的。鉴于本人手头积累了一些传感器和执行器模块,依照实践出真知(一定要动手做)的理念,以学习和交流为目的,这里准备逐一动手尝试系列实验,不管成功(程序走通)与否,都会记录下来—小小的进步或是搞不掂的问题,希望能够抛砖引玉。
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
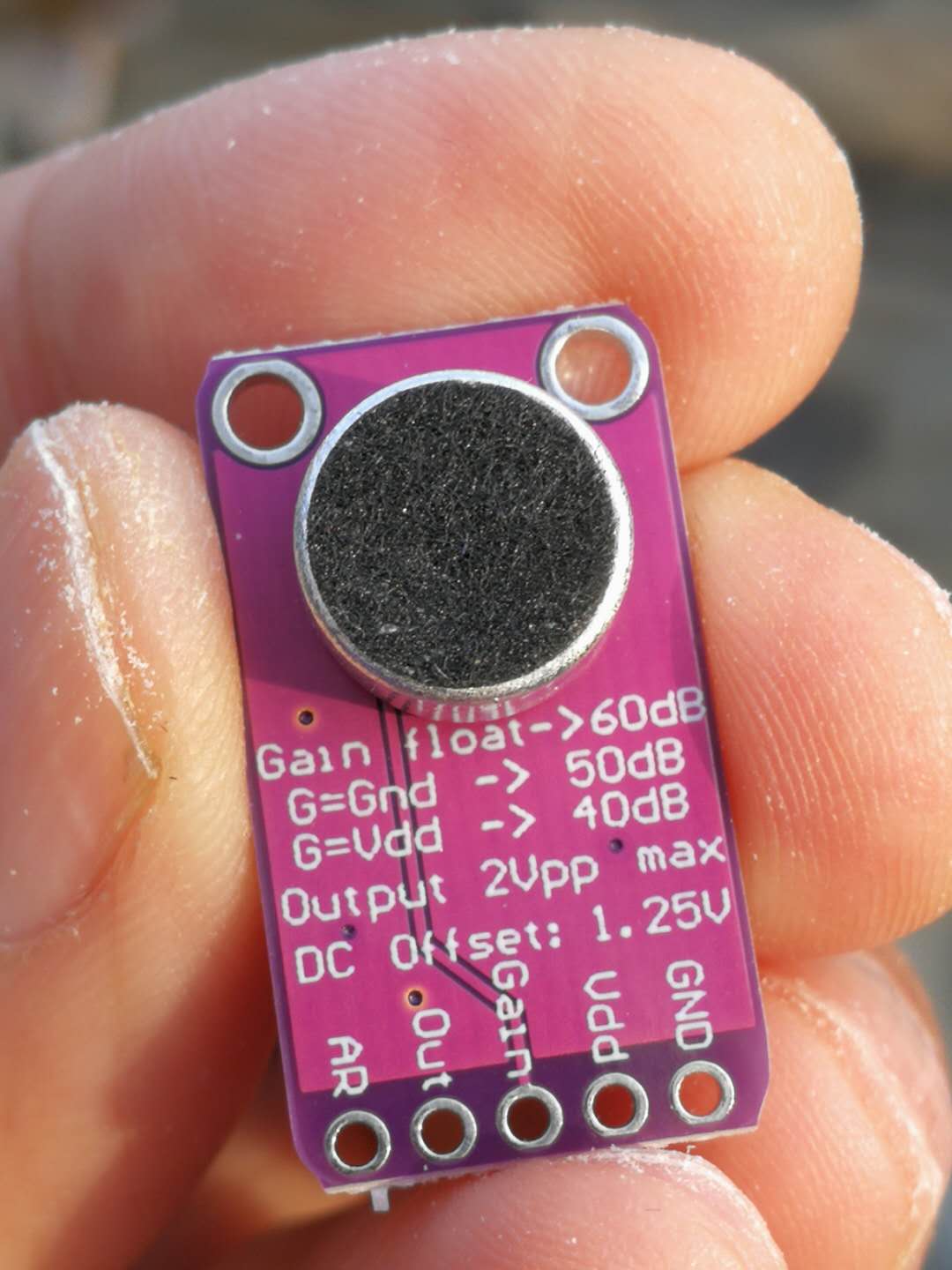
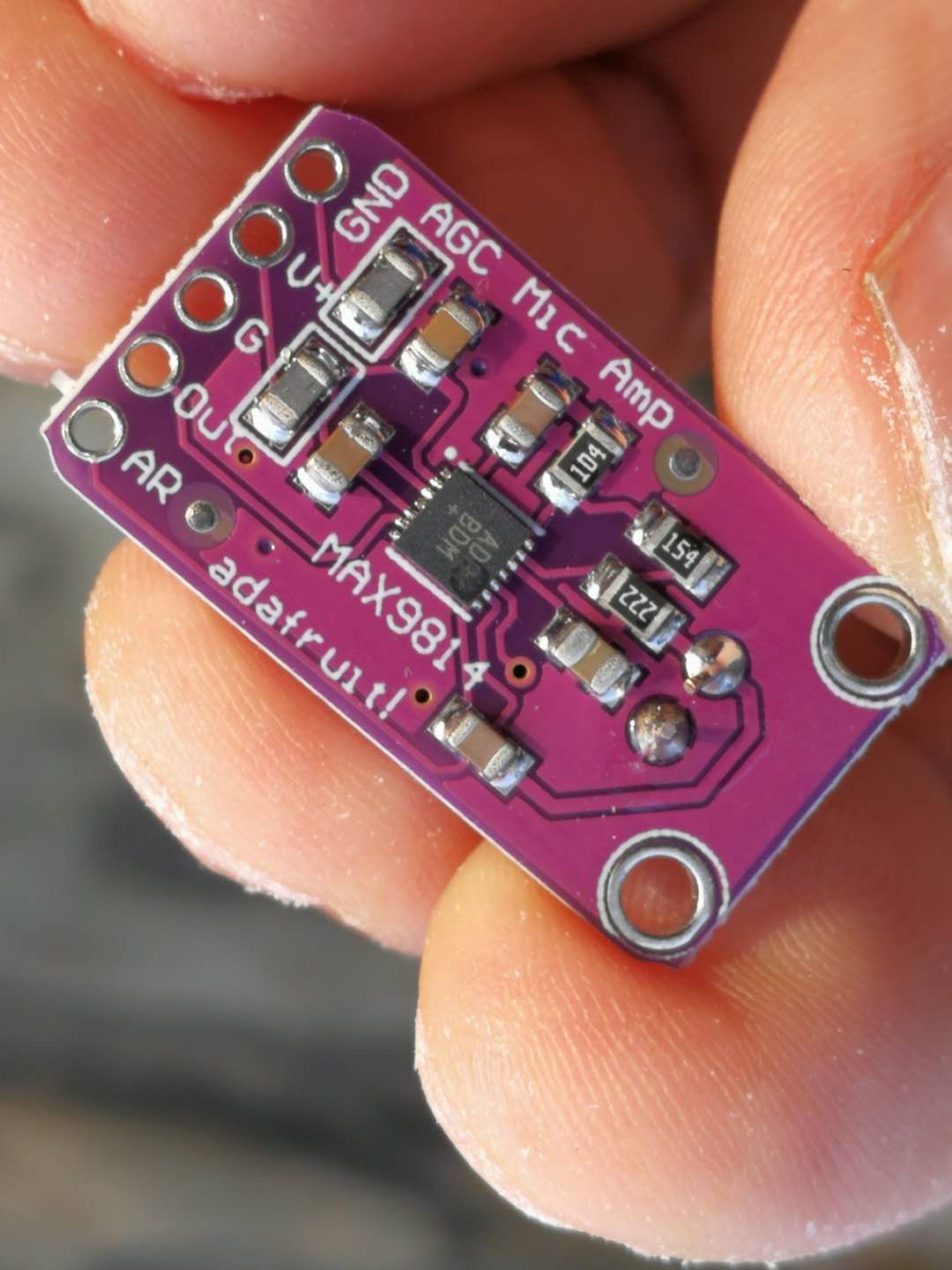
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十一:六十四位音乐频谱灯十六位音乐反应动态频谱灯
Arduino实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码 +图形编程 +仿真编程)
实验一百四十六:64位WS2812B 8 * 8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目四十一:六十四位音乐频谱灯十六位音乐反应动态频谱灯
*/
#include "FastLED.h"
#define OCTAVE 1 // // Group buckets into octaves (use the log output function LOG_OUT 1)
#define OCT_NORM 0 // Don't normalise octave intensities by number of bins
#define FHT_N 256 // set to 256 point fht
#include <FHT.h> // include the library
//int noise[] = {204,188,68,73,150,98,88,68}; // noise level determined by playing pink noise and seeing levels [trial and error]{204,188,68,73,150,98,88,68}
// int noise[] = {204,190,108,85,65,65,55,60}; // noise for mega adk
int noise[] = {204, 195, 100, 90, 85, 80, 75, 75}; // noise for NANO
//int noise[] = {204,198,100,85,85,80,80,80};
float noise_fact[] = {15, 7, 1.5, 1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.7, 3}; // noise level determined by playing pink noise and seeing levels [trial and error]{204,188,68,73,150,98,88,68}
float noise_fact_adj[] = {15, 7, 1.5, 1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.7, 3}; // noise level determined by playing pink noise and seeing levels [trial and error]{204,188,68,73,150,98,88,68}
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_TYPE WS2812
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
// Params for width and height
const uint8_t kMatrixWidth = 8;
const uint8_t kMatrixHeight = 8;//----------was 27
//#define NUM_LEDS (kMatrixWidth * kMatrixHeight)
#define NUM_LEDS 64
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
int counter2 = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(1000);
FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection( TypicalLEDStrip );
FastLED.setBrightness (33);
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Black);
FastLED.show();
// TIMSK0 = 0; // turn off timer0 for lower jitter
ADCSRA = 0xe5; // set the adc to free running mode
ADMUX = 0x40; // use adc0
DIDR0 = 0x01; // turn off the digital input for adc0
}
void loop() {
int prev_j[8];
int beat = 0;
int prev_oct_j;
int counter = 0;
int prev_beat = 0;
int led_index = 0;
int saturation = 0;
int saturation_prev = 0;
int brightness = 0;
int brightness_prev = 0;
while (1) { // reduces jitter
cli(); // UDRE interrupt slows this way down on arduino1.0
for (int i = 0 ; i < FHT_N ; i++) { // save 256 samples
while (!(ADCSRA & 0x10)); // wait for adc to be ready
ADCSRA = 0xf5; // restart adc
byte m = ADCL; // fetch adc data
byte j = ADCH;
int k = (j << 8) | m; // form into an int
k -= 0x0200; // form into a signed int
k <<= 6; // form into a 16b signed int
fht_input[i] = k; // put real data into bins
}
fht_window(); // window the data for better frequency response
fht_reorder(); // reorder the data before doing the fht
fht_run(); // process the data in the fht
fht_mag_octave(); // take the output of the fht fht_mag_log()
// every 50th loop, adjust the volume accourding to the value on A2 (Pot)
if (counter >= 50) {
ADMUX = 0x40 | (1 & 0x07); // set admux to look at Analogpin A1 - Master Volume
while (!(ADCSRA & 0x10)); // wait for adc to be ready
ADCSRA = 0xf5; // restart adc
delay(10);
while (!(ADCSRA & 0x10)); // wait for adc to be ready
ADCSRA = 0xf5; // restart adc
byte m = ADCL; // fetch adc data
byte j = ADCH;
int k = (j << 8) | m; // form into an int
float master_volume = (k + 0.1) / 1000 + .75; // so the valu will be between ~0.5 and 1.---------------------+.75 was .5
Serial.println (master_volume);
for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++) {
noise_fact_adj[i] = noise_fact[i] * master_volume;
}
ADMUX = 0x40 | (0 & 0x07); // set admux back to look at A0 analog pin (to read the microphone input
counter = 0;
}
sei();
counter++;
// End of Fourier Transform code - output is stored in fht_oct_out[i].
// i=0-7 frequency (octave) bins (don't use 0 or 1), fht_oct_out[1]= amplitude of frequency for bin 1
// for loop a) removes background noise average and takes absolute value b) low / high pass filter as still very noisy
// c) maps amplitude of octave to a colour between blue and red d) sets pixel colour to amplitude of each frequency (octave)
for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++) { // goes through each octave. skip the first 1, which is not useful
int j;
j = (fht_oct_out[i] - noise[i]); // take the pink noise average level out, take the asbolute value to avoid negative numbers
if (j < 10) {
j = 0;
}
j = j * noise_fact_adj[i];
if (j < 10) {
j = 0;
}
else {
j = j * noise_fact_adj[i];
if (j > 180) {
if (i >= 7) {
beat += 2;
}
else {
beat += 1;
}
}
j = j / 30;
j = j * 30; // (force it to more discrete values)
}
prev_j[i] = j;
// Serial.print(j);
// Serial.print(" ");
// this fills in 11 LED's with interpolated values between each of the 8 OCT values
if (i >= 2) {
led_index = 2 * i - 3;
prev_oct_j = (j + prev_j[i - 1]) / 2;
saturation = constrain(j + 50, 0, 255); //-----------50 was 30
saturation_prev = constrain(prev_oct_j + 50, 0, 255);
brightness = constrain(j, 0, 255);
brightness_prev = constrain(prev_oct_j, 0, 255);
if (brightness == 255) {
saturation = 50;
brightness = 200;
}
if (brightness_prev == 255) {
saturation_prev = 50;
brightness_prev = 200;
}
for (uint8_t y = 0; y < kMatrixHeight; y++) {
leds[XY(led_index - 1, y)] = CHSV(j + y * 30, saturation, brightness);
if (i > 2) {
prev_oct_j = (j + prev_j[i - 1]) / 2;
leds[ XY(led_index - 2, y)] = CHSV(prev_oct_j + y * 30, saturation_prev, brightness_prev);
}
}
}
}
if (beat >= 7) {
fill_solid(leds, NUM_LEDS, CRGB::Gray);
FastLED.setBrightness(200);
}
else {
if (prev_beat != beat) {
FastLED.setBrightness(40 + beat * beat * 5);
prev_beat = beat;
}
}
FastLED.show();
if (beat) {
counter2 += ((beat + 4) / 2 - 2);
if (counter2 < 0) {
counter2 = 1000;
}
if (beat > 3 && beat < 7) {
FastLED.delay (20);
}
beat = 0;
}
// Serial.println();
}
}
// Param for different pixel layouts
const bool kMatrixSerpentineLayout = false;
// Set 'kMatrixSerpentineLayout' to false if your pixels are
// laid out all running the same way, like this:
// Set 'kMatrixSerpentineLayout' to true if your pixels are
// laid out back-and-forth, like this:
uint16_t XY( uint8_t x, uint8_t y)
{
uint16_t i;
if ( kMatrixSerpentineLayout == false) {
i = (y * kMatrixWidth) + x;
}
if ( kMatrixSerpentineLayout == true) {
if ( y & 0x01) {
// Odd rows run backwards
uint8_t reverseX = (kMatrixWidth - 1) - x;
i = (y * kMatrixWidth) + reverseX;
} else {
// Even rows run forwards
i = (y * kMatrixWidth) + x;
}
}
i = (i + counter2) % NUM_LEDS;
return i;
}Arduino实验场景图
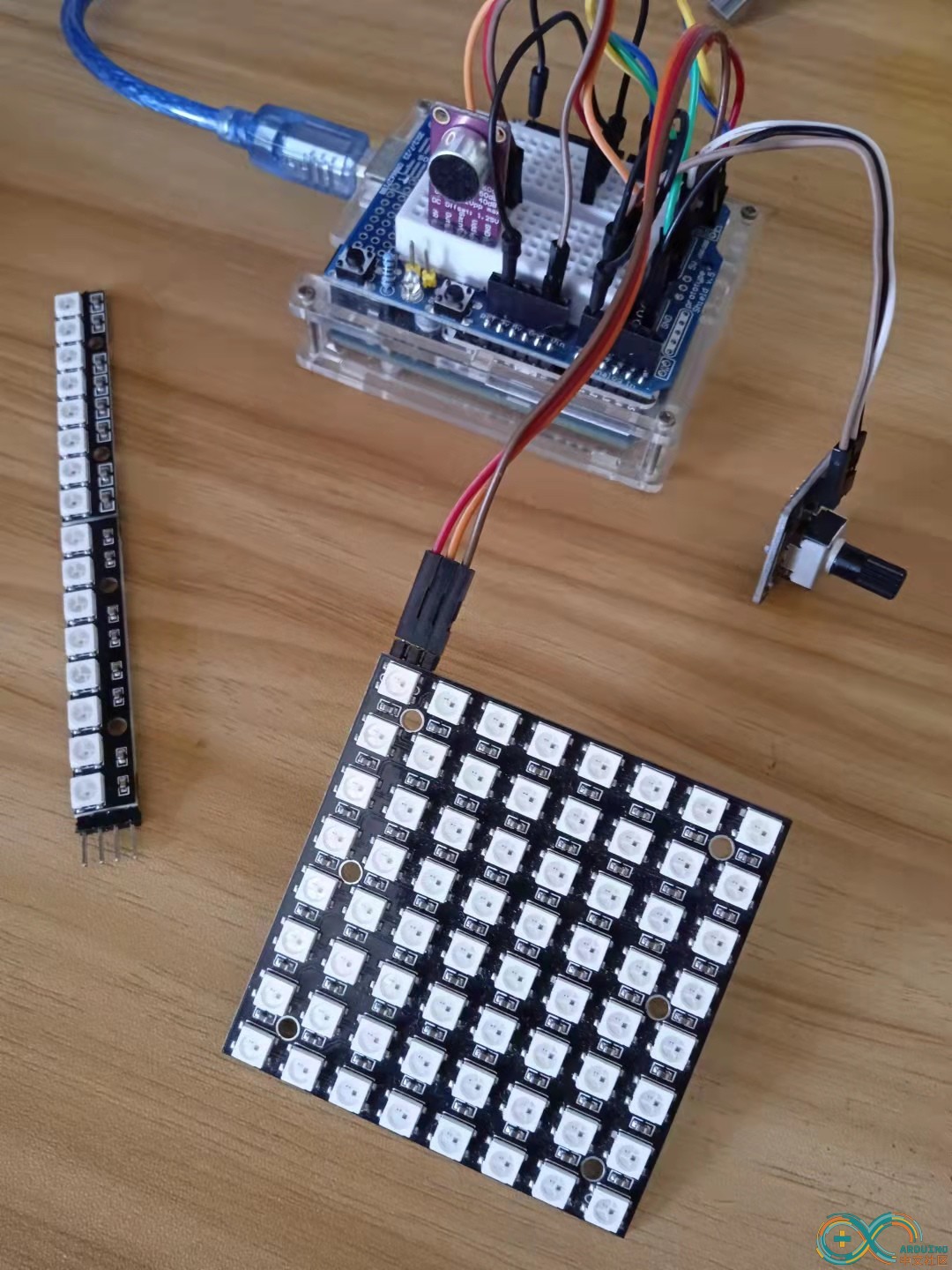
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十二:快速哈特利变换FHT音乐反应灯条
Arduino实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十二:快速哈特利变换FHT音乐反应灯条
*/
/*
这是带有 FastLED 的 FHT 库的项目
FHT 库位于 http://wiki.openmusiclabs.com/wiki/ArduinoFHT
开始的例子是:
https://github.com/TJC/arduino/blob/master/fhttest/fhttest.cpp
注意:如果您使用的是由 3.3V 信号供电的麦克风,例如 Sparkfun MEMS 麦克风,则将 3.3V 连接到 AREF 引脚。
还要确保取消对 analogReference(EXTERNAL); 的注释。 在设置()中。
在线频率发生器 测试:http://onlinetonegenerator.com/frequency-sweep-generator.html
*/
#define qsubd(x, b) ((x>b)?wavebright:0) // A digital unsigned subtraction macro. if result <0, then => 0. Otherwise, take on fixed value.
#define qsuba(x, b) ((x>b)?x-b:0) // Unsigned subtraction macro. if result <0, then => 0.
#define wavebright 128 // qsubd result will be this value if subtraction is >0.
#include "FastLED.h" // FastLED library. Preferably the latest copy of FastLED 2.1.
#if FASTLED_VERSION < 3001000
#error "Requires FastLED 3.1 or later; check github for latest code."
#endif
// Fixed definitions cannot change on the fly.
#define LED_DT 6 // Data pin to connect to the strip.
//#define LED_CK 11 // Clock pin for APA102 or WS2801
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB // It's GRB for WS2812
#define LED_TYPE WS2812B // What kind of strip are you using (APA102, WS2801 or WS2812B)
#define NUM_LEDS 16 // Number of LED's.
// Initialize changeable global variables.
uint8_t max_bright = 255; // Overall brightness definition. It can be changed on the fly.
struct CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS]; // Initialize our LED array.
#define LOG_OUT 1
#define FHT_N 256 // Set to 256 point fht.
#define inputPin A0
//#define potPin A4
#include <FHT.h> // FHT library
uint8_t hueinc = 0; // A hue increment value to make it rotate a bit.
uint8_t micmult = 25;
uint8_t fadetime = 900;
uint8_t noiseval = 25; // Increase this to reduce sensitivity. 30 seems best for quiet
void setup() {
analogReference(EXTERNAL); // Connect 3.3V to AREF pin for any microphones using 3.3V
Serial.begin(9600); // use the serial port
LEDS.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_DT, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
// LEDS.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_DT, LED_CK, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
FastLED.setBrightness(max_bright);
set_max_power_in_volts_and_milliamps(5, 500); // FastLED Power management set at 5V, 500mA.
}
void loop() {
// noiseval = map(analogRead(potPin), 0, 1023, 16, 48); // Adjust sensitivity of cutoff.
EVERY_N_MILLISECONDS(13) {
fhtsound();
}
show_at_max_brightness_for_power();
Serial.println(LEDS.getFPS(), DEC); // Display frames per second on the serial monitor.
Serial.println(" "); // Display frames per second on the serial monitor.
Serial.println(analogRead(inputPin)); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal */
}
void fhtsound() {
// hueinc++; // A cute little hue incrementer.
GetFHT(); // Let's take FHT_N samples and crunch 'em.
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) { // Run through the LED array.
int tmp = qsuba(fht_log_out[2 * i + 2], noiseval); // Get the sample and subtract the 'quiet' normalized values, but don't go < 0.
if (tmp > (leds[i].r + leds[i].g + leds[i].b) / 2) // Refresh an LED only when the intensity is low
leds[i] = CHSV((i * 4) + tmp * micmult, 255, tmp * micmult); // Note how we really cranked up the tmp value to get BRIGHT LED's. Also increment the hue for fun.
leds[i].nscale8(fadetime); // Let's fade the whole thing over time as well.
}
} // fhtsound()
void GetFHT() {
cli();
for (int i = 0 ; i < FHT_N ; i++) fht_input[i] = analogRead(inputPin);
sei();
fht_window(); // Window the data for better frequency response.
fht_reorder(); // Reorder the data before doing the fht.
fht_run(); // Process the data in the fht.
fht_mag_log();
} // GetFHT()【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十二:快速哈特利变换FHT音乐反应灯条
实验视频剪辑
https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNTgwODY0ODEyOA==.html?firsttime=0
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十三:快速哈特利变换FHT音乐反应64位灯板
Arduino实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十三:快速哈特利变换FHT音乐反应64位灯板
*/
/*
这是带有 FastLED 的 FHT 库的项目
FHT 库位于 http://wiki.openmusiclabs.com/wiki/ArduinoFHT
开始的例子是:
https://github.com/TJC/arduino/blob/master/fhttest/fhttest.cpp
注意:如果您使用的是由 3.3V 信号供电的麦克风,例如 Sparkfun MEMS 麦克风,则将 3.3V 连接到 AREF 引脚。
还要确保取消对 analogReference(EXTERNAL); 的注释。 在设置()中。
在线频率发生器 测试:http://onlinetonegenerator.com/frequency-sweep-generator.html
*/
#define qsubd(x, b) ((x>b)?wavebright:0) // A digital unsigned subtraction macro. if result <0, then => 0. Otherwise, take on fixed value.
#define qsuba(x, b) ((x>b)?x-b:0) // Unsigned subtraction macro. if result <0, then => 0.
#define wavebright 128 // qsubd result will be this value if subtraction is >0.
#include "FastLED.h" // FastLED library. Preferably the latest copy of FastLED 2.1.
#if FASTLED_VERSION < 3001000
#error "Requires FastLED 3.1 or later; check github for latest code."
#endif
// Fixed definitions cannot change on the fly.
#define LED_DT 6 // Data pin to connect to the strip.
//#define LED_CK 11 // Clock pin for APA102 or WS2801
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB // It's GRB for WS2812
#define LED_TYPE WS2812B // What kind of strip are you using (APA102, WS2801 or WS2812B)
#define NUM_LEDS 64 // Number of LED's.
// Initialize changeable global variables.
uint8_t max_bright = 255; // Overall brightness definition. It can be changed on the fly.
struct CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS]; // Initialize our LED array.
#define LOG_OUT 1
#define FHT_N 256 // Set to 256 point fht.
#define inputPin A0
//#define potPin A4
#include <FHT.h> // FHT library
uint8_t hueinc = 0; // A hue increment value to make it rotate a bit.
uint8_t micmult = 25;
uint8_t fadetime = 900;
uint8_t noiseval = 25; // Increase this to reduce sensitivity. 30 seems best for quiet
void setup() {
analogReference(EXTERNAL); // Connect 3.3V to AREF pin for any microphones using 3.3V
Serial.begin(9600); // use the serial port
LEDS.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_DT, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
// LEDS.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_DT, LED_CK, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS);
FastLED.setBrightness(max_bright);
set_max_power_in_volts_and_milliamps(5, 500); // FastLED Power management set at 5V, 500mA.
}
void loop() {
// noiseval = map(analogRead(potPin), 0, 1023, 16, 48); // Adjust sensitivity of cutoff.
EVERY_N_MILLISECONDS(13) {
fhtsound();
}
show_at_max_brightness_for_power();
Serial.println(LEDS.getFPS(), DEC); // Display frames per second on the serial monitor.
Serial.println(" "); // Display frames per second on the serial monitor.
Serial.println(analogRead(inputPin)); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal */
}
void fhtsound() {
// hueinc++; // A cute little hue incrementer.
GetFHT(); // Let's take FHT_N samples and crunch 'em.
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) { // Run through the LED array.
int tmp = qsuba(fht_log_out[2 * i + 2], noiseval); // Get the sample and subtract the 'quiet' normalized values, but don't go < 0.
if (tmp > (leds[i].r + leds[i].g + leds[i].b) / 2) // Refresh an LED only when the intensity is low
leds[i] = CHSV((i * 4) + tmp * micmult, 255, tmp * micmult); // Note how we really cranked up the tmp value to get BRIGHT LED's. Also increment the hue for fun.
leds[i].nscale8(fadetime); // Let's fade the whole thing over time as well.
}
} // fhtsound()
void GetFHT() {
cli();
for (int i = 0 ; i < FHT_N ; i++) fht_input[i] = analogRead(inputPin);
sei();
fht_window(); // Window the data for better frequency response.
fht_reorder(); // Reorder the data before doing the fht.
fht_run(); // Process the data in the fht.
fht_mag_log();
} // GetFHT()项目四十三:快速哈特利变换FHT音乐反应64位灯板
实验视频剪辑
https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNTgwODY2NzkzMg==.html?spm=a2hcb.playlsit.page.1
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十四:Adafruit_NeoPixel音乐节奏灯板
Arduino实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十四:Adafruit_NeoPixel音乐节奏灯板
*/
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N_PIXELS 64
#define MIC_PIN A0
#define LED_PIN 6
#define SAMPLE_WINDOW 5
#define PEAK_HANG 24
#define PEAK_FALL 4
#define INPUT_FLOOR 10
#define INPUT_CEILING 50
byte peak = 16;
unsigned int sample;
byte Count = 0;
byte HangCount = 0;
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(N_PIXELS, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
analogReference(EXTERNAL);
strip.setBrightness(22);
strip.show();
strip.begin();
}
float fscale( float originalMin, float originalMax, float newBegin, float newEnd, float inputValue, float curve) {
float OriginalRange = 0;
float NewRange = 0;
float zeroRefCurVal = 0;
float normalizedCurVal = 0;
float rangedValue = 0;
boolean invFlag = 0;
if (curve > 10) curve = 10;
if (curve < -10) curve = -10;
curve = (curve * -.1) ;
curve = pow(10, curve);
if (inputValue < originalMin) {
inputValue = originalMin;
}
if (inputValue > originalMax) {
inputValue = originalMax;
}
OriginalRange = originalMax - originalMin;
if (newEnd > newBegin) {
NewRange = newEnd - newBegin;
}
else
{
NewRange = newBegin - newEnd;
invFlag = 1;
}
zeroRefCurVal = inputValue - originalMin;
normalizedCurVal = zeroRefCurVal / OriginalRange; // normalize to 0 - 1 float
Serial.print(OriginalRange, DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(NewRange, DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(zeroRefCurVal, DEC);
Serial.println();
delay(10);
if (originalMin > originalMax ) {
return 0;
}
if (invFlag == 0) {
rangedValue = (pow(normalizedCurVal, curve) * NewRange) + newBegin;
}
else
{
rangedValue = newBegin - (pow(normalizedCurVal, curve) * NewRange);
}
return rangedValue;
}
void loop() {
unsigned long startMillis = millis();
float peakToPeak = 0;
unsigned int signalMax = 0;
unsigned int signalMin = 1023;
unsigned int c, y;
while (millis() - startMillis < SAMPLE_WINDOW)
{
sample = analogRead(MIC_PIN);
if (sample < 1024)
{
if (sample > signalMax)
{
signalMax = sample;
}
else if (sample < signalMin)
{
signalMin = sample;
}
}
}
peakToPeak = signalMax - signalMin;
for (int i = 0; i <= strip.numPixels() - 1; i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(map(i, 0, strip.numPixels() - 1, 30, 150)));
}
c = fscale(INPUT_FLOOR, INPUT_CEILING, strip.numPixels(), 0, peakToPeak, 2);
if (c < peak) {
peak = c;
HangCount = 0;
}
if (c <= strip.numPixels()) {
drawLine(strip.numPixels(), strip.numPixels() - c, strip.Color(0, 0, 0));
}
y = strip.numPixels() - peak;
strip.setPixelColor(y - 1, Wheel(map(y, 0, strip.numPixels() - 1, 30, 150)));
strip.show();
if (HangCount > PEAK_HANG) {
if (++Count >= PEAK_FALL) {
peak++;
Count = 0;
}
}
else {
HangCount++;
}
}
void drawLine(uint8_t from, uint8_t to, uint32_t c) {
uint8_t fromTemp;
if (from > to) {
fromTemp = from;
from = to;
to = fromTemp;
}
for (int i = from; i <= to; i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
}
}
uint32_t Wheel(byte WheelPos) {
if (WheelPos < 85) {
return strip.Color(WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3, 0);
}
else if (WheelPos < 170) {
WheelPos -= 85;
return strip.Color(255 - WheelPos * 3, 0, WheelPos * 3);
}
else {
WheelPos -= 170;
return strip.Color(0, WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3);
}
}Arduino实验场景图
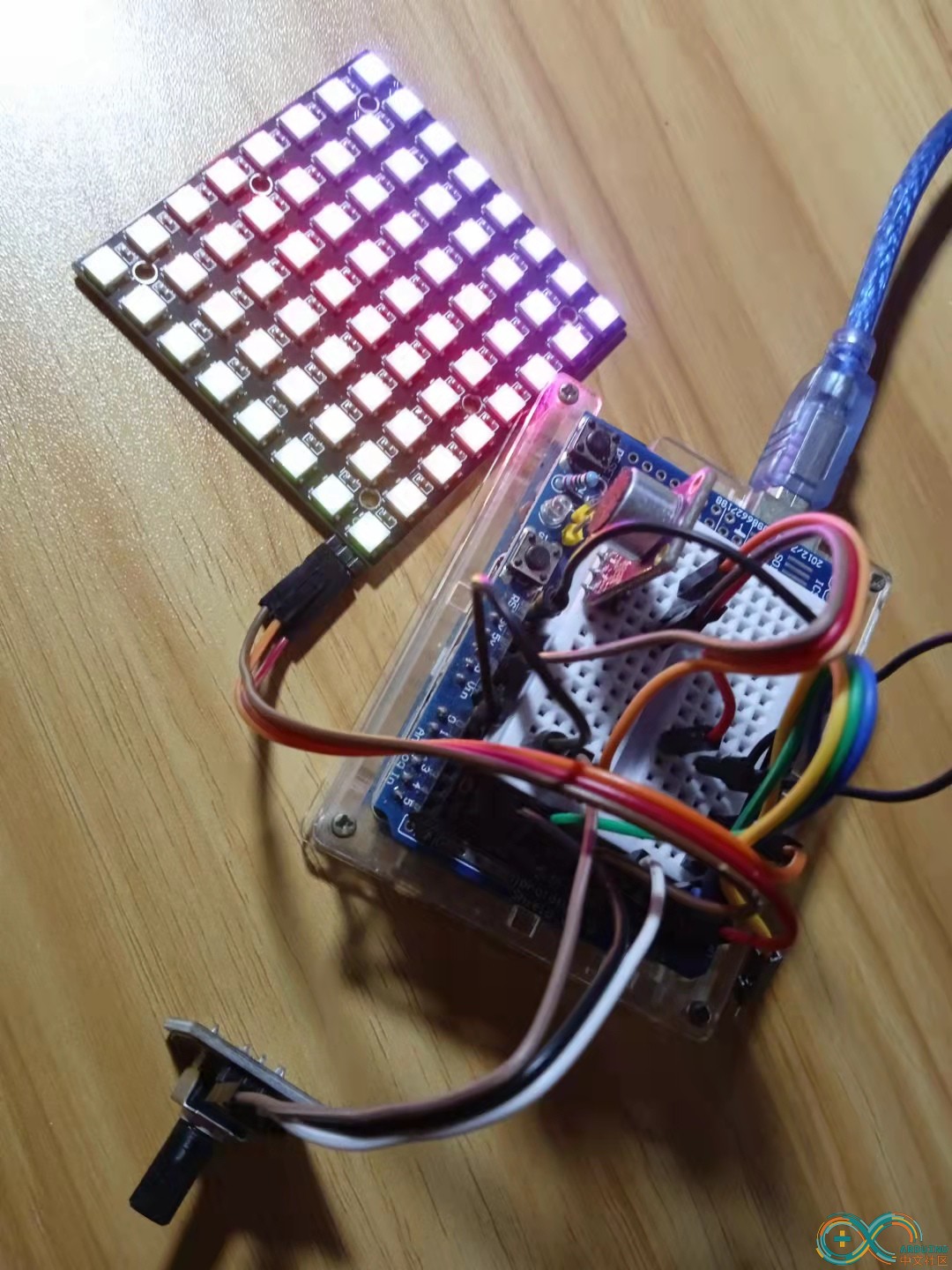
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十四:Adafruit_NeoPixel音乐节奏灯板
实验视频剪辑
https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNTgwODgwMzk5Ng==.html?spm=a2hcb.playlsit.page.1
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十五:动态音乐频谱仪
Arduino实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十五:动态音乐频谱仪
接脚连线:
MAX7219 UNO
VCC →→→→→ 5V
GND →→→→→ GND
DIN →→→→→ D12(数据,数据接收引脚)
CS →→→→→ D11(负载,命令接收引脚)
CLK →→→→→ D10(时钟,时钟引脚)
*/
#include "LedControl.h"
/* Led matrix - Max7219 Declared */
LedControl lc = LedControl(12, 11, 10, 1);
const int maxScale = 11;
/* Sensor - Max9812 Declared */
const int sensorPin = A4;
const int sampleWindow = 50; // 50ms = 20Hz
unsigned int sample;
unsigned long startMillis;
unsigned long timeCycle;
unsigned int signalMax = 0;
unsigned int signalMin = 1024;
unsigned char index = 0;
unsigned int peakToPeak[8];
unsigned int displayPeak[8];
unsigned int temp[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
unsigned int signalMaxBuff[8];
unsigned int signalMinBuff[8];
void setup() {
// Led matrix
lc.shutdown(0, false); // bật hiện thị
lc.setIntensity(0, 1); // chỉnh độ sáng
lc.clearDisplay(0); // tắt tất cả led
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
startMillis = millis();
//peakToPeak = 0;
signalMax = 0;
signalMin = 1024;
// Get data in 50ms
while (millis() - startMillis < sampleWindow) {
sample = analogRead(sensorPin);
if (sample < 1024) {
if (sample > signalMax) {
signalMax = sample;
}
if (sample < signalMin) {
signalMin = sample;
}
}
// 20Hz - 64Hz - 125Hz - 250Hz - 500Hz - 1kHz (timeCycle = 1/F)(ms)
timeCycle = millis() - startMillis;
if (timeCycle == 1 || timeCycle == 2 || timeCycle == 4 || timeCycle == 8
|| timeCycle == 16 || timeCycle == 32 || timeCycle == 40 || timeCycle == 50) {
signalMaxBuff[index] = signalMax;
signalMinBuff[index] = signalMin;
index = (index + 1) % 8;
delay(1);
//Serial.println(timeCycle);
}
}
// Delete pointer to array
index = 0;
// Calculation after get samples
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { // i = row (led matrix)
// sound level
peakToPeak[i] = signalMaxBuff[i] - signalMinBuff[i];
// Map 1v p-p level to the max scale of the display
displayPeak[i] = map(peakToPeak[i], 0, 1023, 0, maxScale);
// Show to led matrix
displayLed(displayPeak[i], i);
// Led drop down
if (displayPeak[i] >= temp[i]) {
temp[i] = displayPeak[i];
}
else {
temp[i]--;
}
lc.setLed(0, i, temp[i], true);
delayMicroseconds(250);
}
}
void displayLed(int displayPeak, int row) {
switch (displayPeak) {
case 0 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0x80); break;
case 1 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0xC0); break;
case 2 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0xE0); break;
case 3 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0xF0); break;
case 4 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0xF8); break;
case 5 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0xFC); break;
case 6 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0xFE); break;
case 7 : lc.setRow(0, row, 0xFF); break;
}
}Arduino实验场景图

【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百四十九:MAX9814麦克风放大器模块 MIC话筒声音放大/咪头传感器
项目四十五:动态音乐频谱仪
实验视频剪辑
https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNTgxMDQ1Mjk4NA==.html?spm=a2hcb.playlsit.page.1

 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部

评论