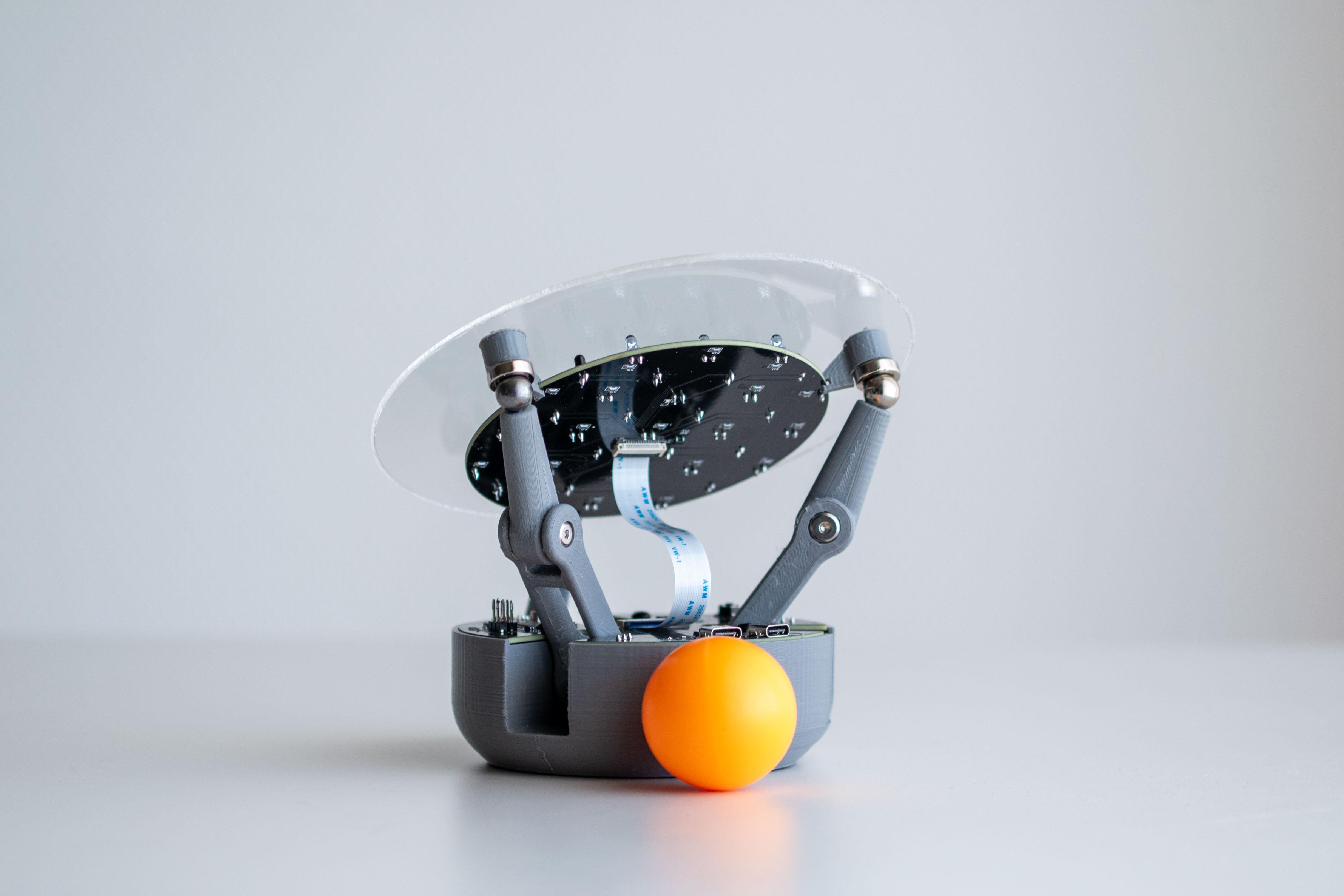
BaBot 是一款紧凑型开源机器人,它使用红外 (IR) 传感器和 ATmega32U4 微控制器实时平衡球体,将控制理论变为现实。无论您是学生、教育工作者还是业余爱好者,BaBot 都能为您提供一种探索 PID 控制、传感器集成和机器人技术的有趣方式。
BaBot 始于 2018 年的一个高中项目,最初使用电脑和高架摄像头来追踪球。经过多次迭代,包括使用树莓派在透明板下方安装摄像头的版本,我开发出了一种更高效的设计。当前版本采用红外传感器和 ATmega32U4 微控制器,打造出一款更紧凑、更经济、更易于使用的机器人。

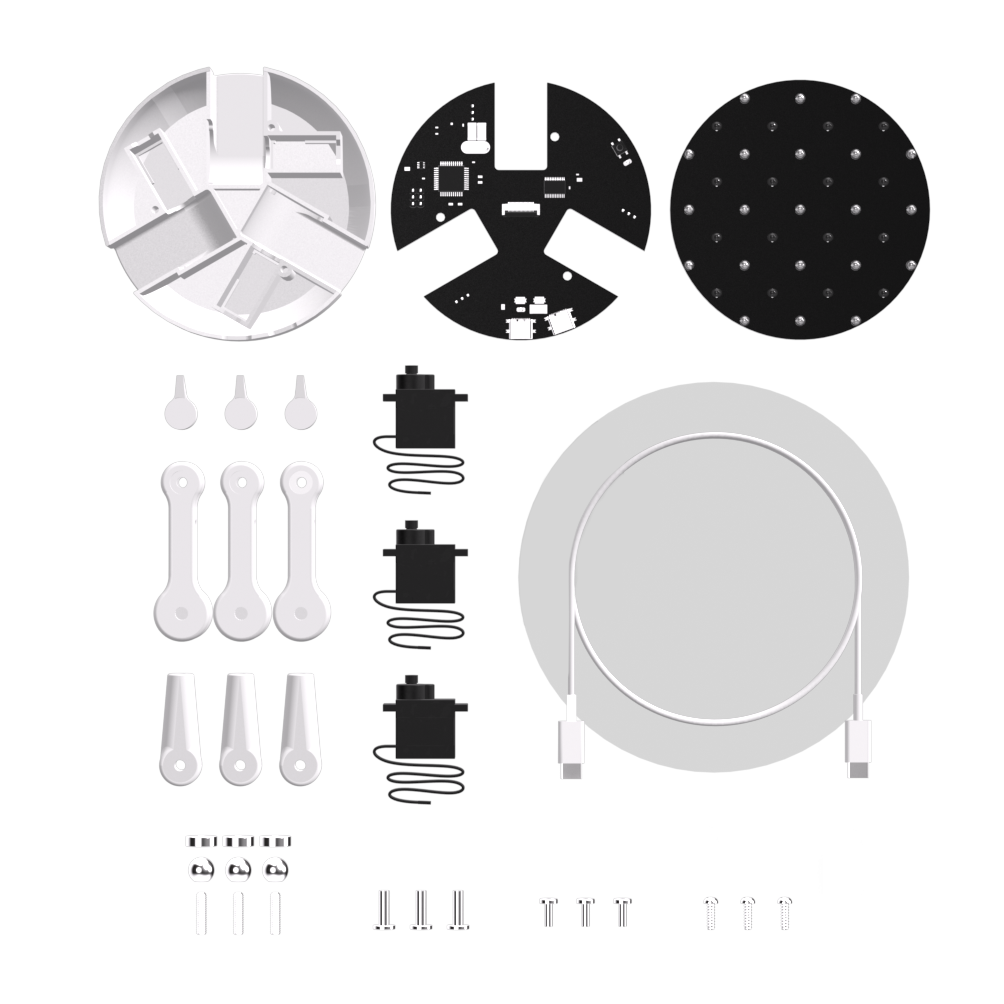
材料:
1x 亚克力板(用于平台)2mm PMMA
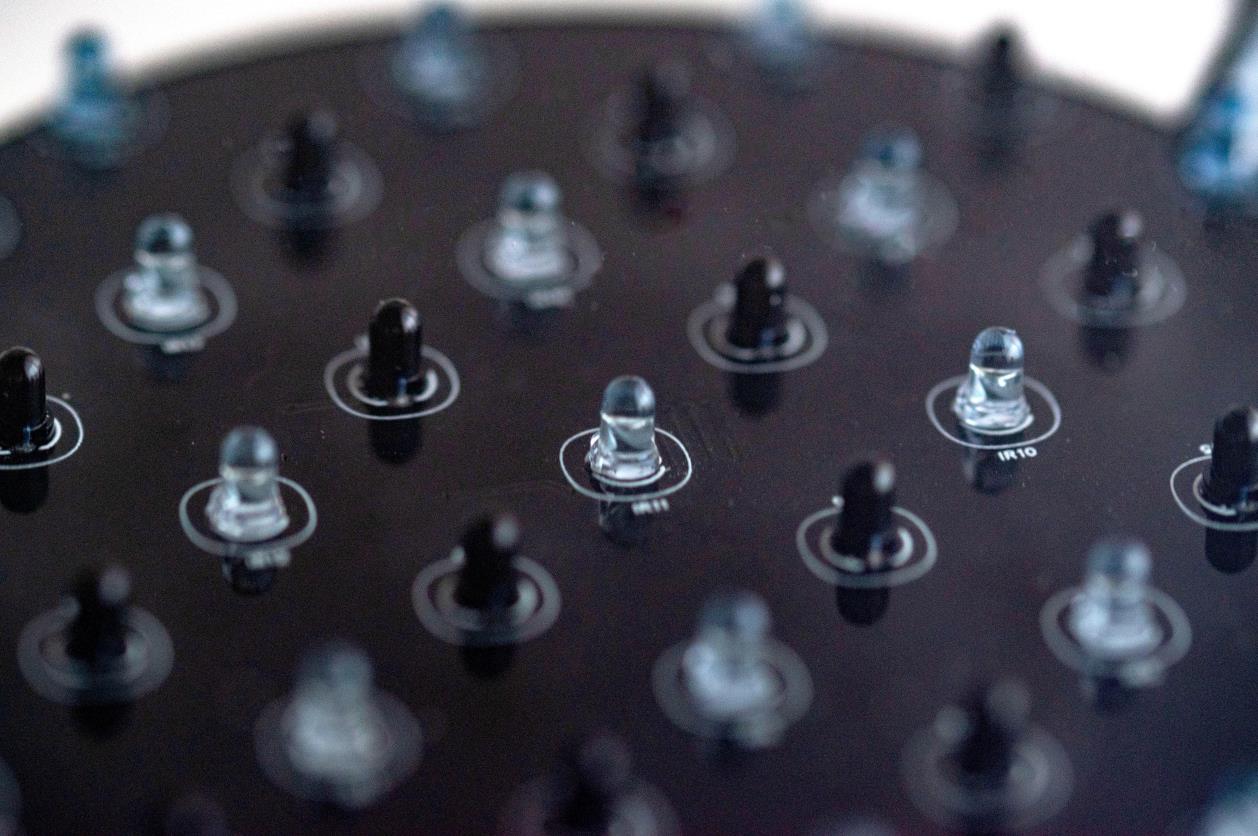
16个红外光电晶体管
16 个广角红外 LED
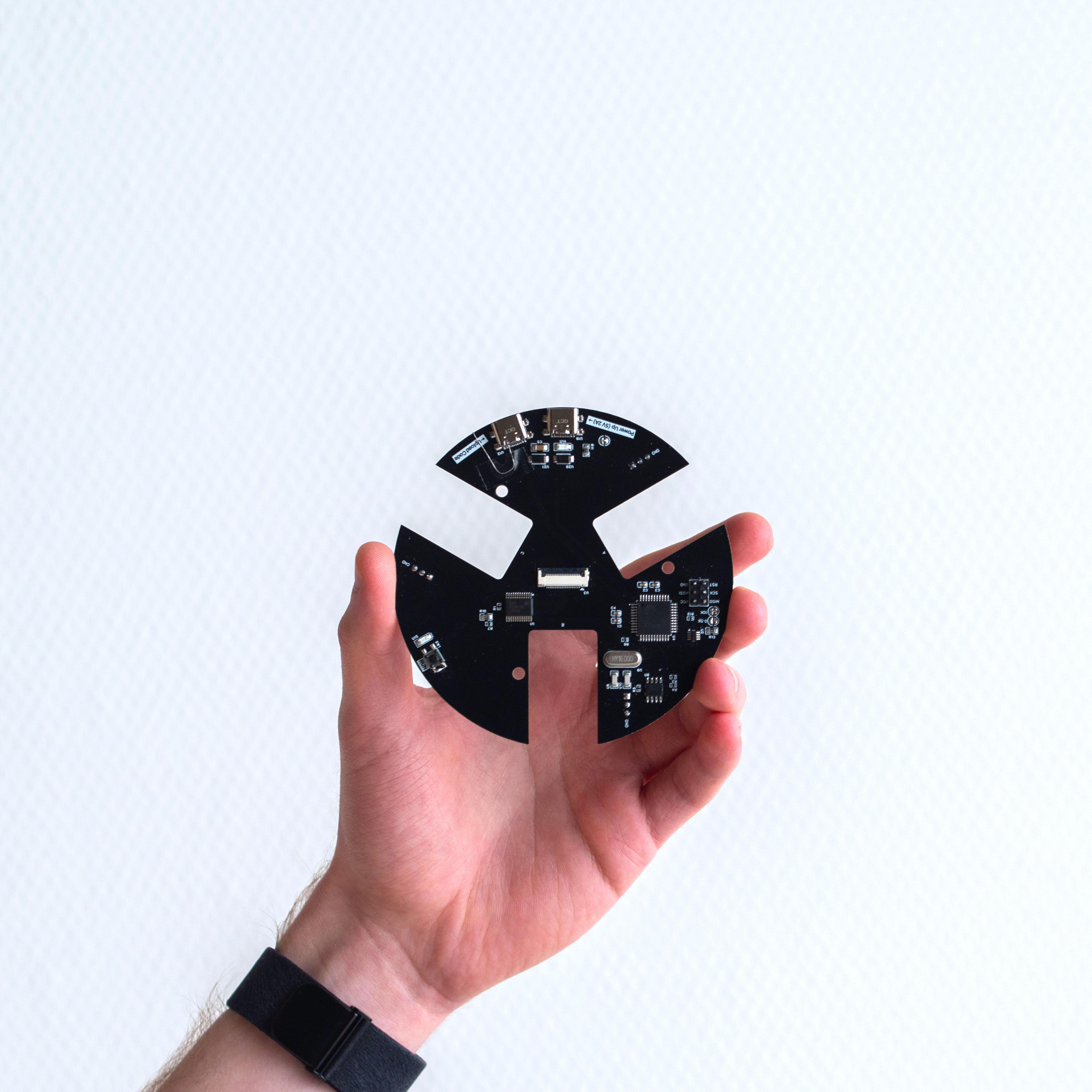
1x 定制 PCB(可通过 PCBWay 获取)
1个ATmega32U4微控制器
1x CD74HC4067 16通道模拟/数字多路复用器
1个5V 10A直流电源
3个MG90微型伺服器
工具:
激光切割机(用于亚克力部件)
3D打印机
软件:
Arduino IDE 2.0
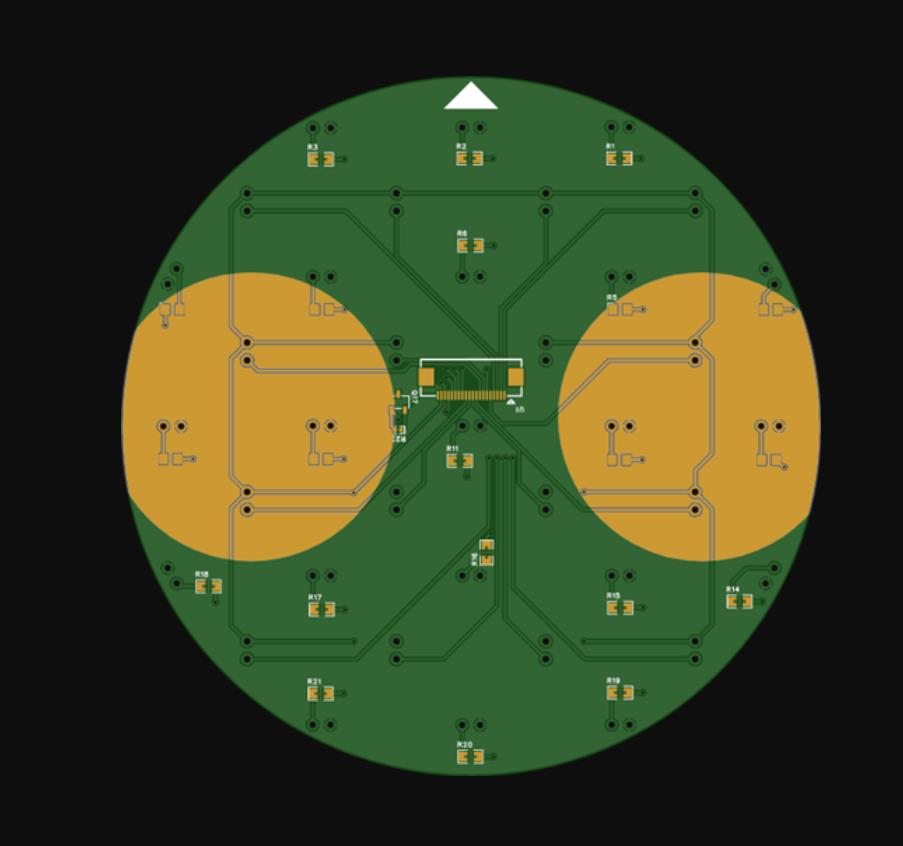
步骤 1:订购 PCB
订购您的 PCB
为了使事情变得更容易和更可靠,我强烈建议订购预先组装的 PCB,特别是因为它们包含许多 SMD 组件。
👉 您可以直接从PCBWay订购组装好的 PCB 。
或者,如果您想要最流畅的体验,您可以从ba-bot.com购买完整的 BaBot 套件(包含所有组件) 。这样,您就省去了采购单个零件的麻烦,可以全身心地投入到构建和享受机器人的乐趣中。
附件
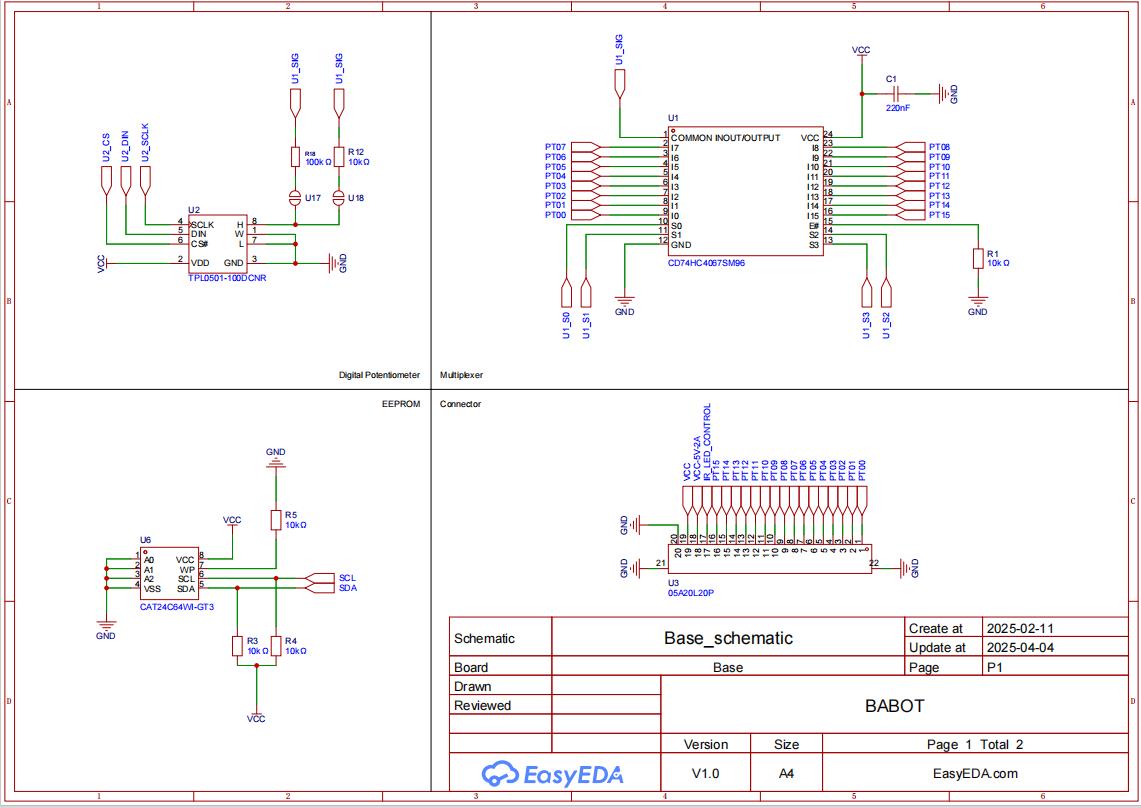
下载 {{ file.name }}原理图_iNWgbALrz5.pdf下载



步骤2:3D打印零件
BaBot 的所有结构部件均可 3D 打印。请务必使用精度高的打印机,尤其是与伺服器直接连接的部件。所有部件均可在Thingiverse 上找到。
附件
下载 {{ file.name }}所有.stl下载3D视图
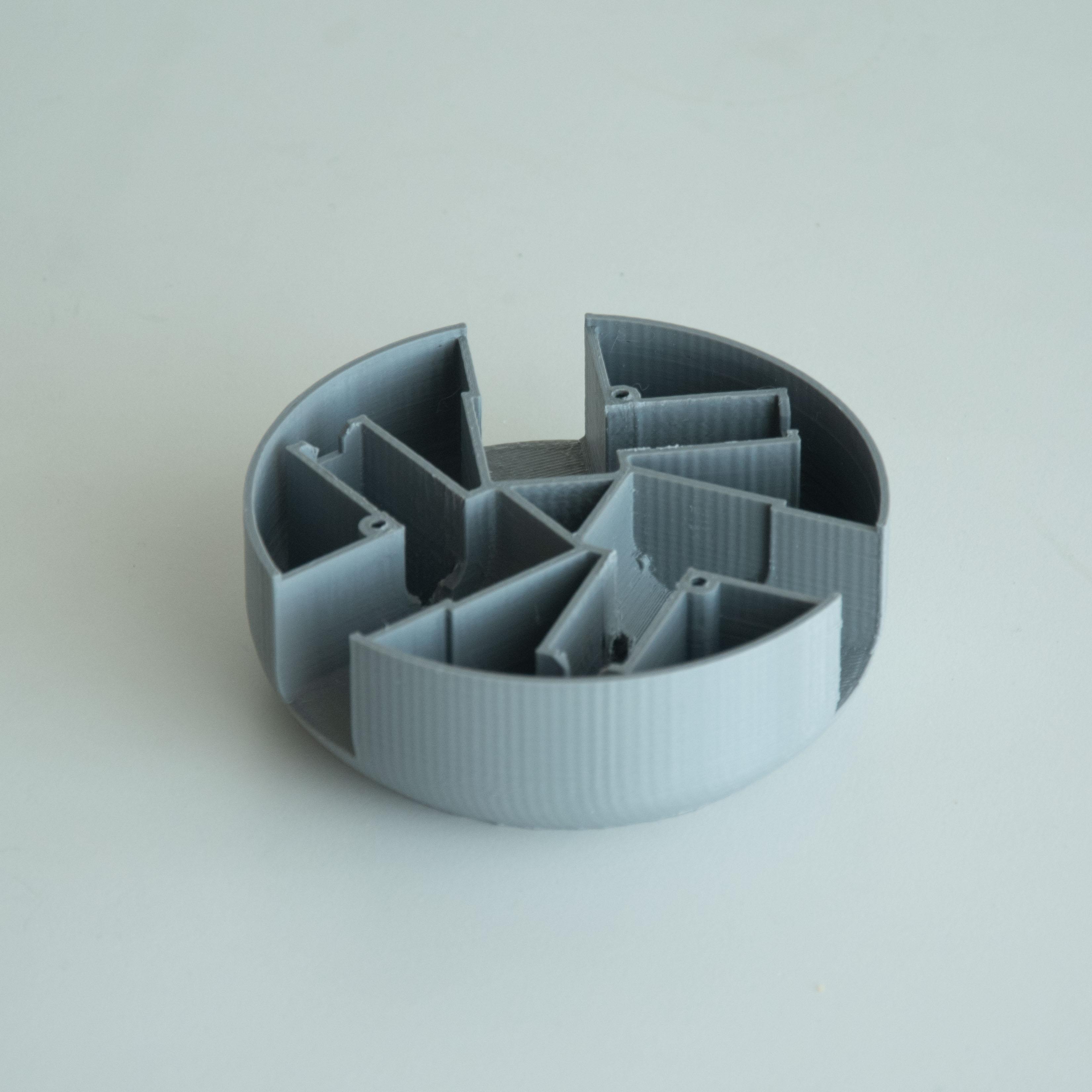
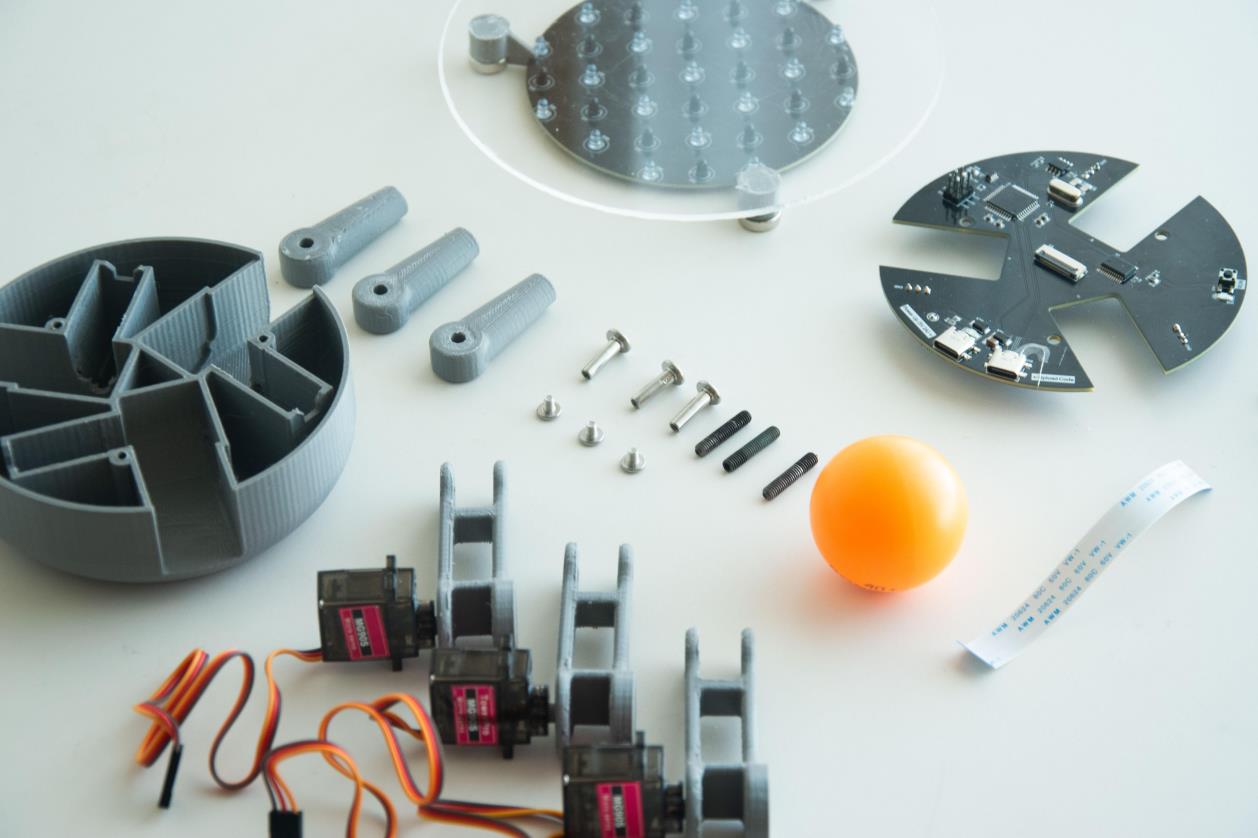

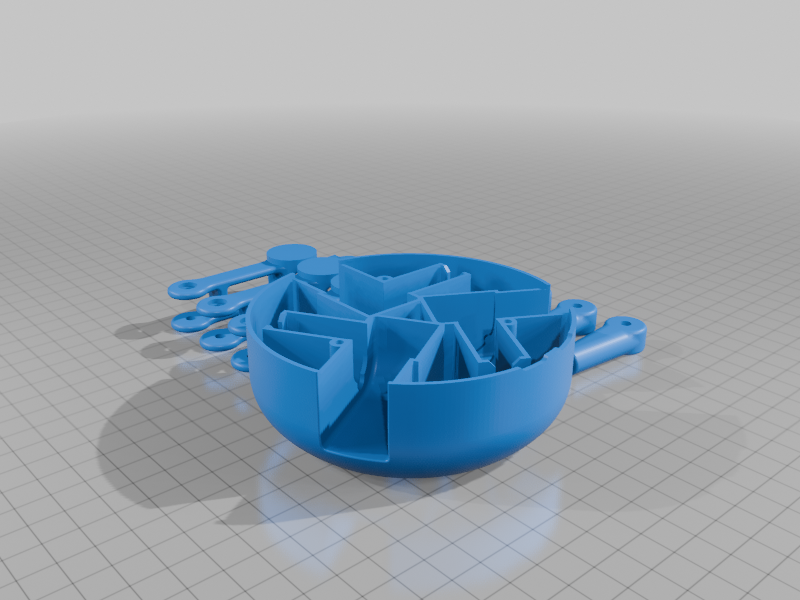
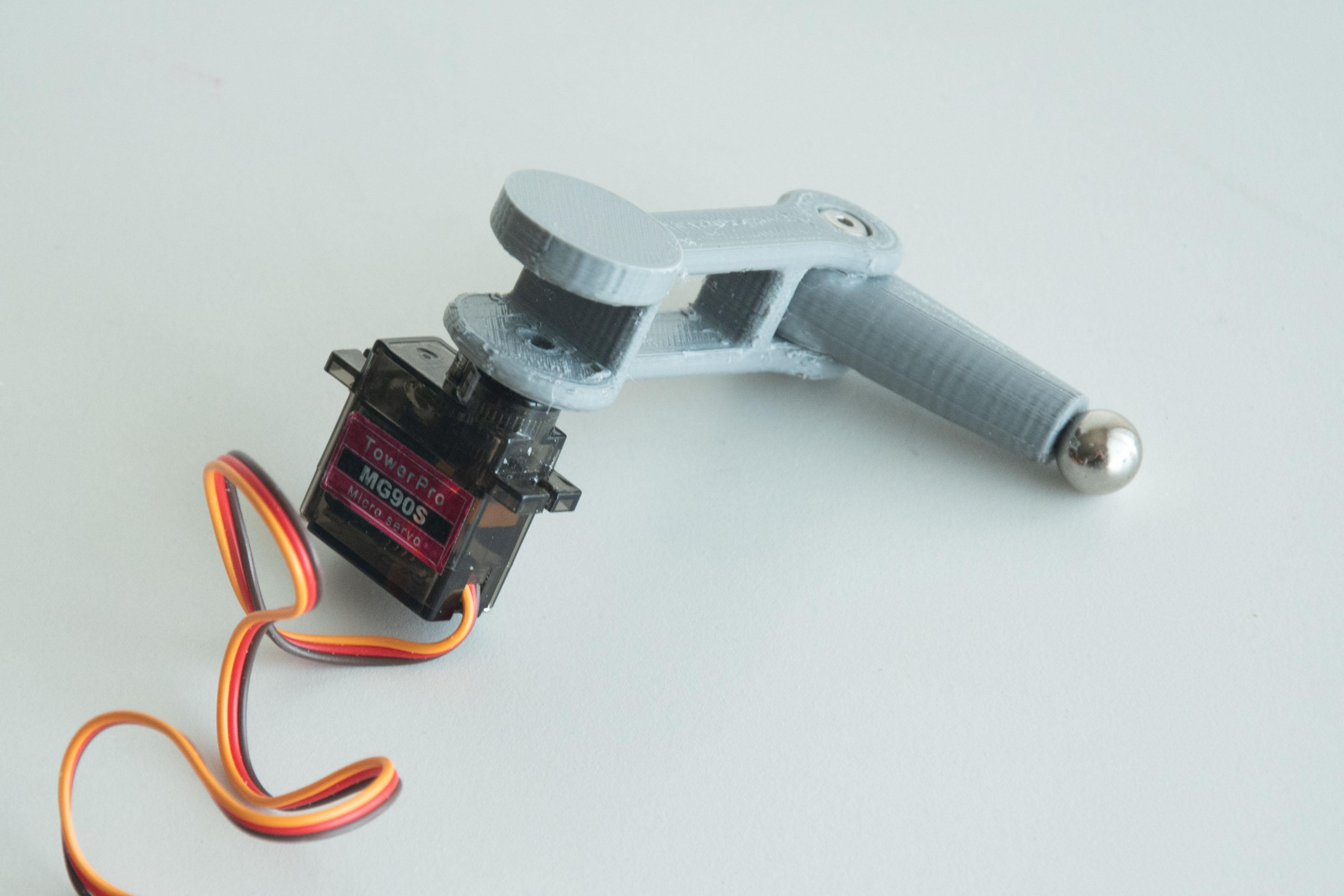
步骤 3:组装机械臂和伺服装置
组装机械臂和伺服器
3D 打印部件准备就绪后,首先组装三个臂并将它们连接到 MG90S 伺服器上。

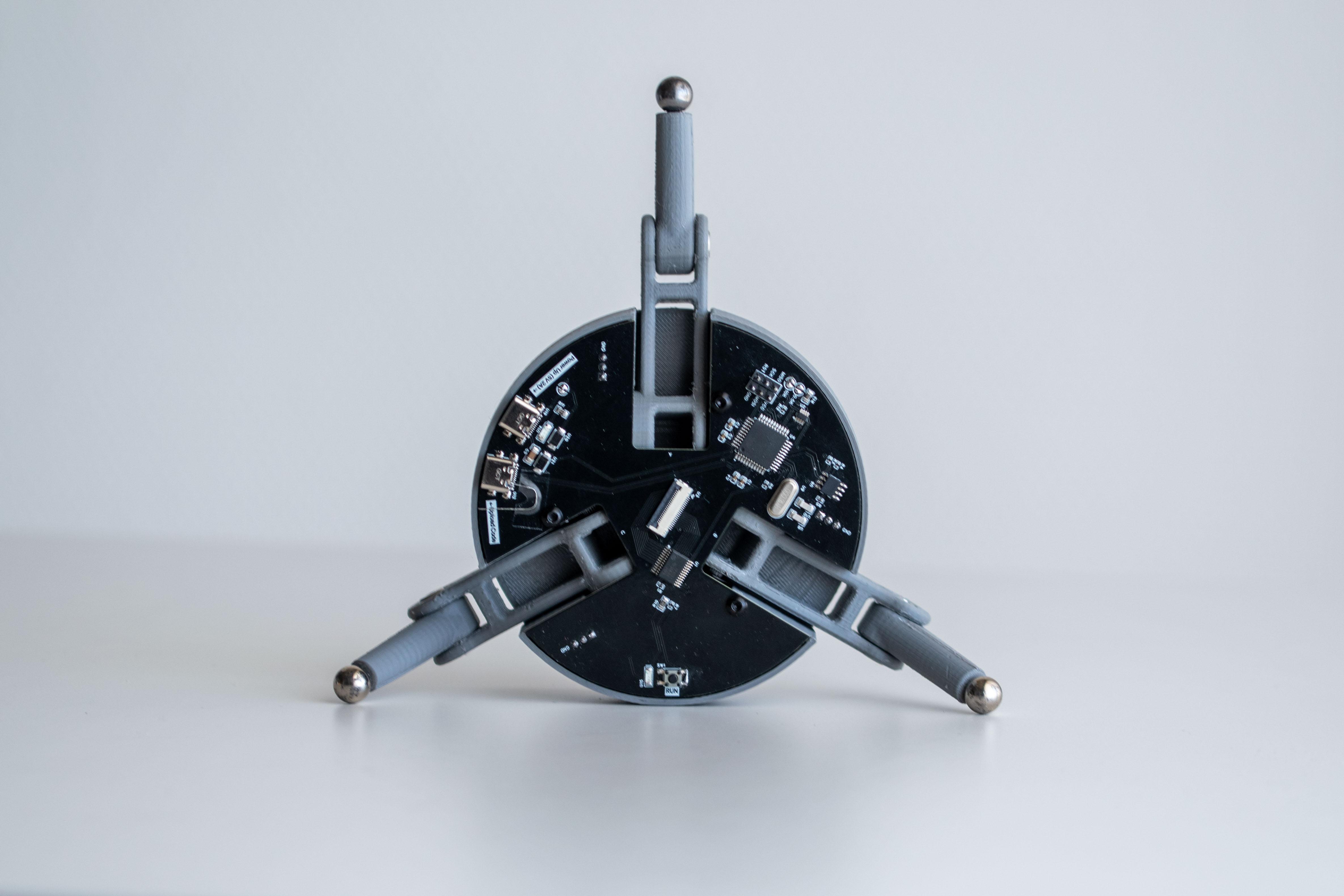
步骤4:组装底座
接下来,将伺服臂安装到底座上。该结构作为 BaBot 的基础,支撑电子设备并控制平衡机制。

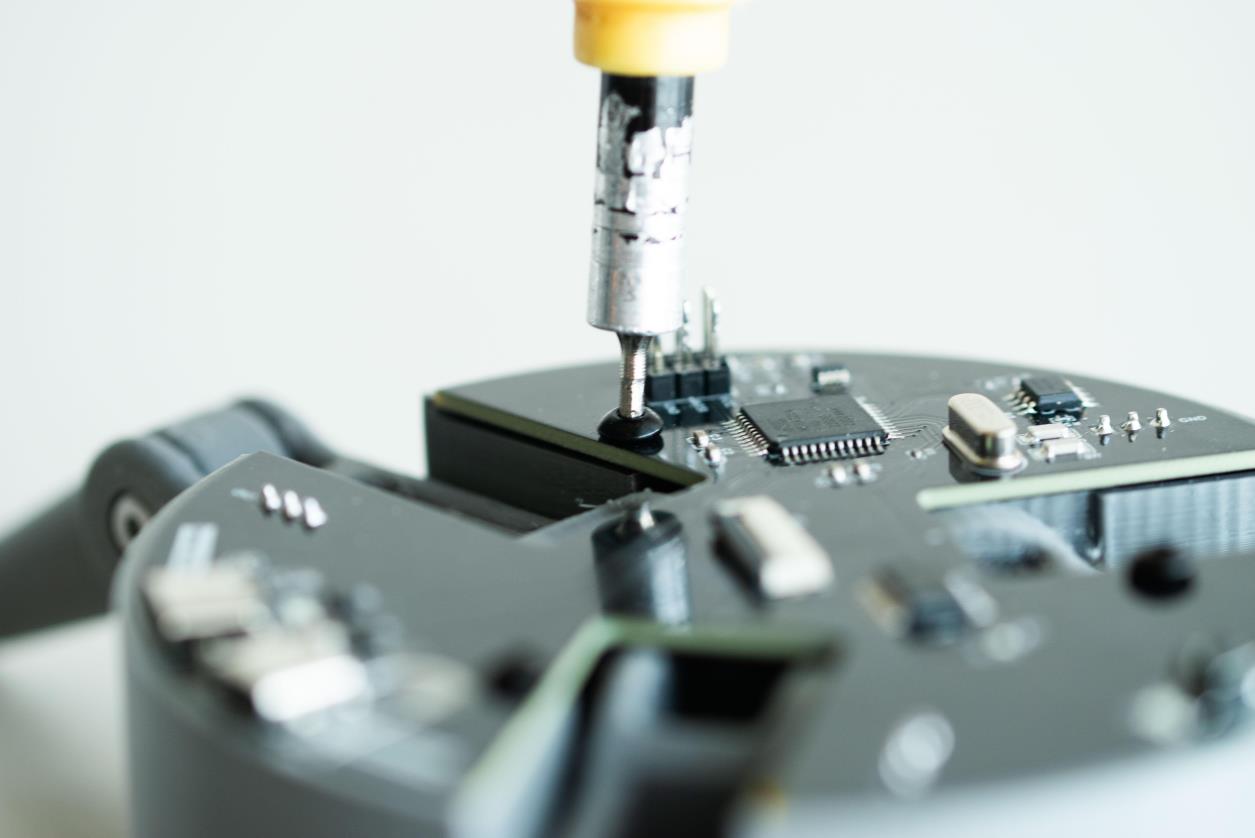
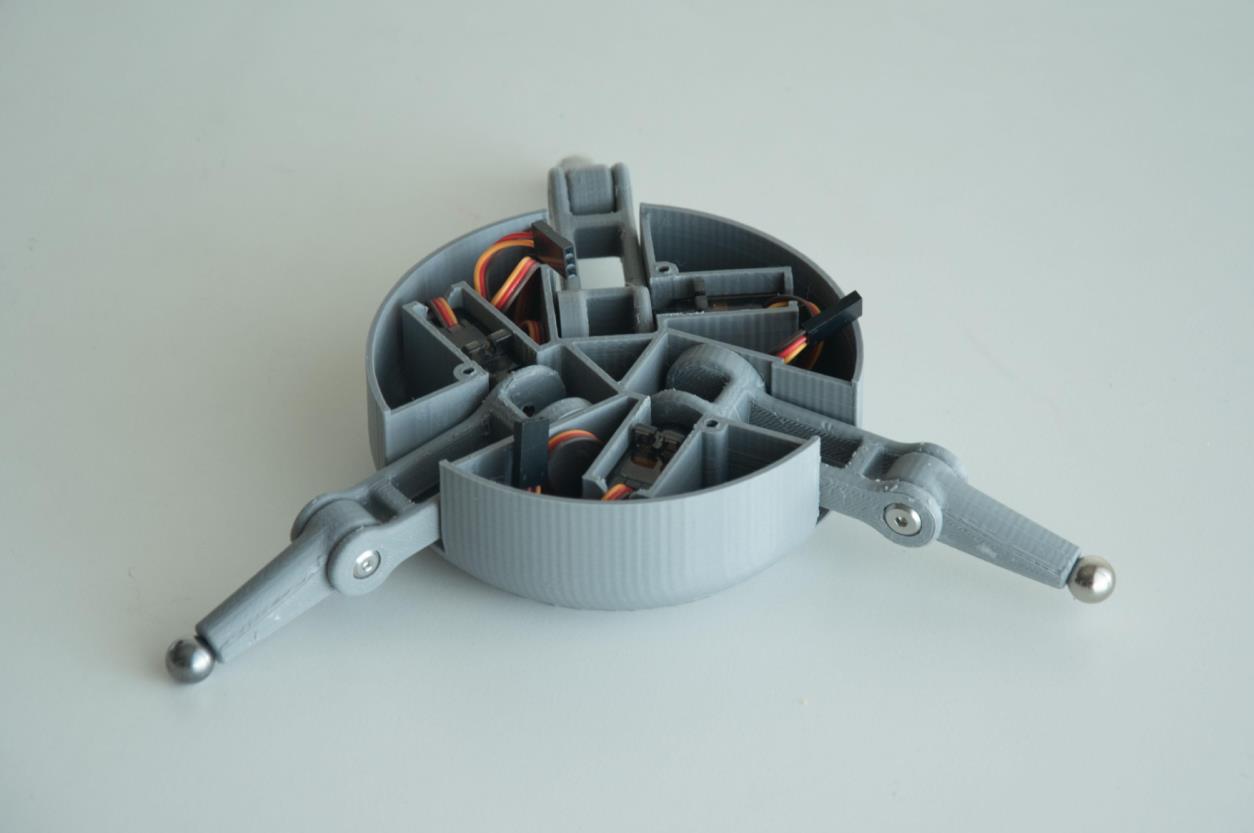
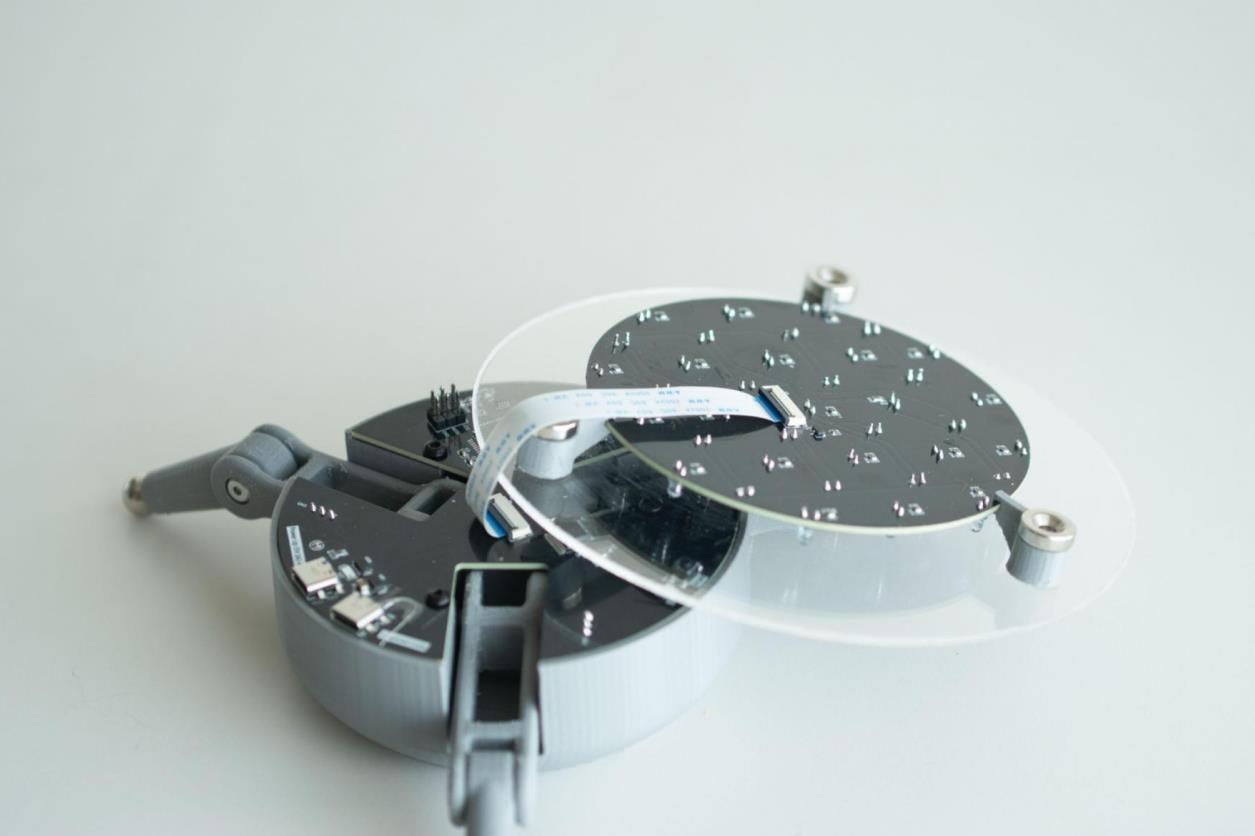
步骤5:安装顶板
现在将顶部丙烯酸板连接到第二个 PCB。

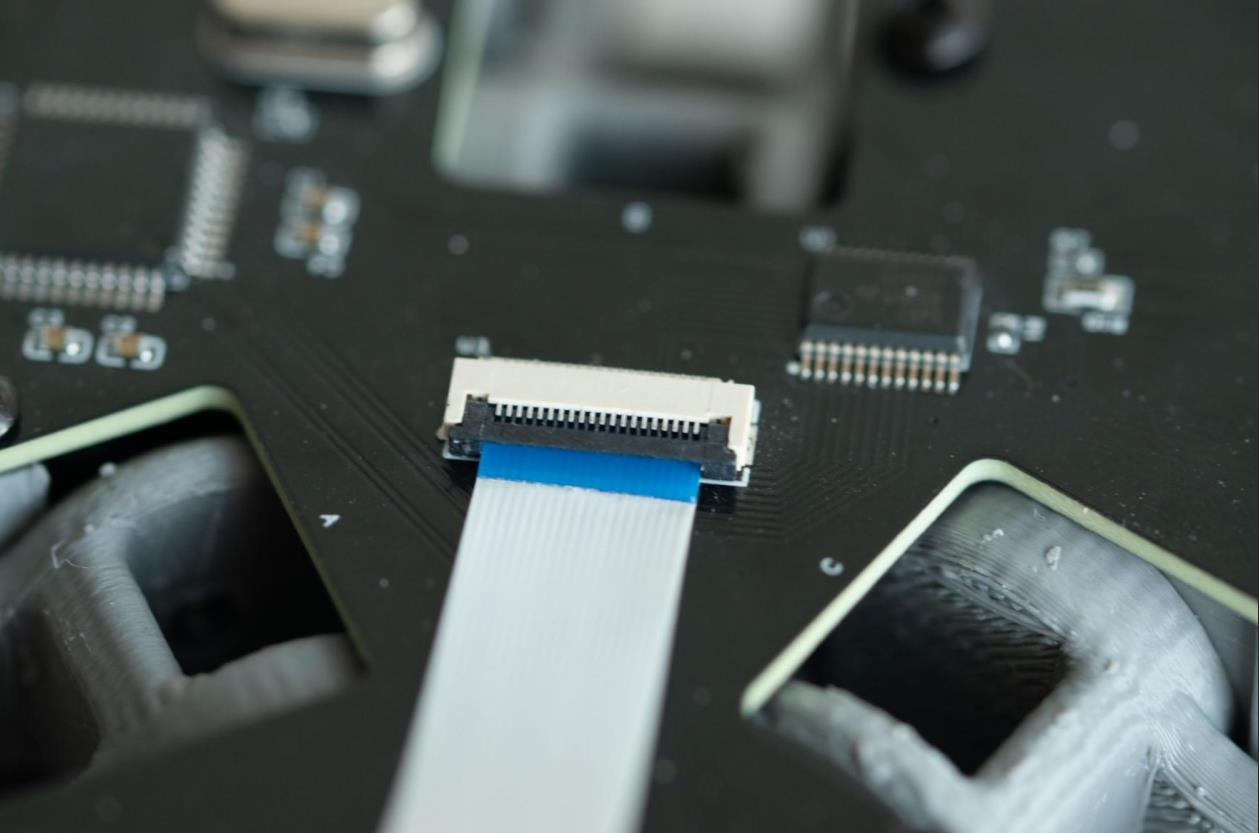
步骤6:上传代码
上传代码
使用 Arduino IDE 将固件上传到 PCB 上的 ATmega32U4 微控制器。代码是开源的,可在GitHub页面上获取。代码已添加注释,以帮助您理解其工作原理。项目最终完成后,我们将在 ba-bot.com 上发布更详细的说明。

#include <math.h>
// ---- PID Coefficients ----
const float P_GAIN = 2.0;
const float I_GAIN = 0.1;
const float D_GAIN = 30.0;
// ---- Smoothing Factors ----
const float EMA_ALPHA = 0.9; // Exponential moving average
const float IR_ALPHA = 0.5; // IR signal low-pass filter
// ---- Mechanical Constants ----
const float DEG2RAD = M_PI / 180.0;
const float RAD2DEG = 180.0 / M_PI;
const float R1 = 50.0; // Servo arm length [mm]
const float R2 = 39.2; // Passive link length [mm]
const float BASE_R = 32.9 / sqrt(3.0); // Base triangle radius [mm]
const float PLAT_R = 107.9 / sqrt(3.0); // Platform triangle radius [mm]
// ---- Pin Assignments ----
// Control
const int BUTTON_PIN = A1;
const int LED_PIN = 8;
// IR Sensor
const int IR_LED_PIN = 7;
const int IR_RECEIVER_PIN= A0;
// Digital Potentiometer (MCP42xx)
const int DIGIPOT_CS = 4;
const int DIGIPOT_DIN = 1;
const int DIGIPOT_SCLK = 0;
// Servo pins
const int SERVO_PIN_A = 10;
const int SERVO_PIN_B = 9;
const int SERVO_PIN_C = 11;
// Button press timings [ms]
const unsigned long SHORT_PRESS_TIME = 50;
const unsigned long LONG_PRESS_TIME = 1000;
const unsigned long DOUBLE_PRESS_TIME = 350;
// ---- Globals ----
// IR measurements and center tracking
int ambientLight[16] = {0};
int irLight[16] = {0};
float irSignal[16] = {0.0};
float centerX = 0.0;
float centerY = 0.0;
float setpointX = 0.0;
float setpointY = 0.0;
// PID state
float lastErrorX = 0.0;
float lastErrorY = 0.0;
float integralX = 0.0;
float integralY = 0.0;
// Ball tracking
bool ballWasOnPlate = false;
unsigned long ballLostTime = 0;
// Button state
bool buttonPressed = false;
unsigned long pressStart = 0;
unsigned long lastPress = 0;
bool singlePressFlag = false;
// Trajectory
float trajectoryAngle = 0.0;
// ---- Objects ----
CD74HC4067 mux(5, 13, 6, 12); // S0,S1 -> 13, S2->6, S3->12
Servo servoA, servoB, servoC;
// ---- Kalman Filter Definition ----
struct KalmanFilter {
float x = 0, v = 0, p = 1;
const float q = 0.3, r = 1.0;
void update(float z, float dt) {
// Prediction
x += v * dt;
p += q;
// Correction
float k = p / (p + r);
v += k * ((z - x) / dt);
x += k * (z - x);
p *= (1 - k);
}
};
KalmanFilter kfX, kfY;
// ---- Function Prototypes ----
void blinkLED(unsigned long interval);
void measureIR();
void setDigitalPot(byte value);
bool ballOnPlate();
void computeCenter(float rawX, float rawY);
void pidControl(float input, float setpoint, float &lastError, float &integral, float &output);
void movePlatform(float rollDeg, float pitchDeg, float height);
void moveServos(float a, float b, float c);
void checkButton();
void calculateWeightedCenter(const float ir[], float &x, float &y);
void sendSerialData();
void setTrajectory(float radius, float speed);
// ---- Arduino Setup ----
void setup() {
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IR_LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIGIPOT_CS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIGIPOT_DIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIGIPOT_SCLK, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(DIGIPOT_CS, HIGH);
servoA.attach(SERVO_PIN_A);
servoB.attach(SERVO_PIN_B);
servoC.attach(SERVO_PIN_C);
// Initialize platform to neutral
movePlatform(0, -20, 60);
delay(1000);
Serial.begin(115200);
}
// ---- Main Loop ----
void loop() {
static unsigned long lastTime = 0;
unsigned long now = millis();
float dt = (now - lastTime) / 1000.0;
blinkLED(300);
setDigitalPot(255);
measureIR();
checkButton();
sendSerialData();
if (ballOnPlate()) {
ballWasOnPlate = true;
ballLostTime = now;
// Raw center calculation
float rawX, rawY;
calculateWeightedCenter(irSignal, rawX, rawY);
// Kalman & EMA filters
kfX.update(rawX, dt);
kfY.update(rawY, dt);
centerX = EMA_ALPHA * rawX + (1 - EMA_ALPHA) * kfX.x;
centerY = EMA_ALPHA * rawY + (1 - EMA_ALPHA) * kfY.x;
// PID
float outputX, outputY;
pidControl(centerX, setpointX, lastErrorX, integralX, outputX);
pidControl(centerY, setpointY, lastErrorY, integralY, outputY);
movePlatform(outputX, outputY, 60);
}
else {
if (ballWasOnPlate && now - ballLostTime < 1000) {
// hold last
movePlatform(0, 0, 60);
} else {
ballWasOnPlate = false;
integralX = integralY = 0;
lastErrorX = lastErrorY = 0;
setpointX = setpointY = 0;
movePlatform(0, -20, 60);
}
}
lastTime = now;
}
// ---- Utility Functions ----
void blinkLED(unsigned long interval) {
static unsigned long lastToggle = 0;
if (millis() - lastToggle >= interval) {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN));
lastToggle = millis();
}
}
void setDigitalPot(byte val) {
digitalWrite(DIGIPOT_CS, LOW);
for (int i = 7; i >= 0; --i) {
digitalWrite(DIGIPOT_DIN, (val & (1 << i)) ? HIGH : LOW);
digitalWrite(DIGIPOT_SCLK, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(DIGIPOT_SCLK, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
}
digitalWrite(DIGIPOT_CS, HIGH);
}
void measureIR() {
// Ambient
digitalWrite(IR_LED_PIN, LOW);
delay(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
mux.channel(i);
delayMicroseconds(250);
ambientLight[i] = analogRead(IR_RECEIVER_PIN);
}
// IR On
digitalWrite(IR_LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
mux.channel(i);
delayMicroseconds(250);
irLight[i] = analogRead(IR_RECEIVER_PIN);
}
// Compute signal
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
float delta = irLight[i] - ambientLight[i];
irSignal[i] = IR_ALPHA * delta + (1 - IR_ALPHA) * irSignal[i];
}
}
bool ballOnPlate() {
long sum = 0;
int maxVal = irSignal[0];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
sum += irSignal[i];
maxVal = max(maxVal, int(irSignal[i]));
}
float avg = sum / 16.0;
return maxVal > 1.5 * avg;
}
void pidControl(float input, float target, float &lastErr, float &integ, float &out) {
float error = target - input;
integ += I_GAIN * error;
float deriv = D_GAIN * (error - lastErr);
out = P_GAIN * error + integ + deriv;
lastErr = error;
}
void movePlatform(float rollDeg, float pitchDeg, float height) {
float roll = -rollDeg * DEG2RAD;
float pitch = -pitchDeg * DEG2RAD;
float baseAngle[3] = {0, 120 * DEG2RAD, 240 * DEG2RAD};
float platX[3], platY[3], platZ[3], angles[3];
// Transform platform points
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
float a = baseAngle[i];
float px = PLAT_R * cos(a);
float py = PLAT_R * sin(a);
float pz = height;
// Pitch
float x1 = px * cos(pitch) + pz * sin(pitch);
float z1 = -px * sin(pitch) + pz * cos(pitch);
// Roll
float y1 = py * cos(roll) - z1 * sin(roll);
float z2 = py * sin(roll) + z1 * cos(roll);
platX[i] = x1; platY[i] = y1; platZ[i] = z2;
}
// Calculate servo angles
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
float a = baseAngle[i];
float bx = BASE_R * cos(a);
float by = BASE_R * sin(a);
float dx = platX[i] - bx;
float dy = platY[i] - by;
float dz = platZ[i];
float dxl = dx * cos(a) + dy * sin(a);
float dyl = dz;
float d = sqrt(dxl*dxl + dyl*dyl);
float theta = atan2(dyl, dxl) - acos(constrain((R1*R1 + d*d - R2*R2)/(2*R1*d), -1, 1));
angles[i] = theta * RAD2DEG;
}
moveServos(angles[0], angles[1], angles[2]);
}
void moveServos(float a, float b, float c) {
a = constrain(a, -10, 65);
b = constrain(b, -10, 65);
c = constrain(c, -10, 65);
servoA.write(100 - a);
servoB.write(100 - b);
servoC.write(100 - c);
}
void calculateWeightedCenter(const float arr[], float &x, float &y) {
// If insufficient contrast, return (0,0)
float minV = arr[0], maxV = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < 16; i++) {
minV = min(minV, arr[i]);
maxV = max(maxV, arr[i]);
}
if (maxV - minV < 150) { x = y = 0; return; }
const float coordsX[16] = {0,1,2,3, 0,1,2,3, 0,1,2,3, 0,1,2,3};
const float coordsY[16] = {0,0,0,0, 1,1,1,1, 2,2,2,2, 3,3,3,3};
float sumW=0, wx=0, wy=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
float norm = pow((arr[i] - minV)/(maxV - minV), 4);
wx += coordsX[i] * norm;
wy += coordsY[i] * norm;
sumW += norm;
}
x = wx/sumW - 1.5;
y = wy/sumW - 1.5;
}
void checkButton() {
bool state = digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN);
unsigned long now = millis();
static bool lastState = LOW;
if (state && !lastState) {
pressStart = now;
buttonPressed = true;
}
if (buttonPressed && state && (now - pressStart > LONG_PRESS_TIME)) {
Serial.println("Long Press Detected");
buttonPressed = false;
}
if (buttonPressed && !state) {
unsigned long dur = now - pressStart;
if (dur >= SHORT_PRESS_TIME && dur < LONG_PRESS_TIME) {
if (now - lastPress < DOUBLE_PRESS_TIME) {
Serial.println("Double Press Detected");
singlePressFlag = false;
} else {
singlePressFlag = true;
}
lastPress = now;
}
buttonPressed = false;
}
if (singlePressFlag && now - lastPress > DOUBLE_PRESS_TIME) {
Serial.println("Single Press Detected");
singlePressFlag = false;
}
lastState = state;
}
void sendSerialData() {
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
Serial.print(irSignal[i]);
Serial.print(',');
}
Serial.print(centerX); Serial.print(',');
Serial.print(centerY); Serial.print(',');
Serial.print(setpointX); Serial.print(',');
Serial.println(setpointY);
}
void setTrajectory(float radius, float speed) {
unsigned long now = millis();
static unsigned long lastT = 0;
float dt = (now - lastT)/2000.0;
trajectoryAngle += speed * dt;
setpointX = radius * cos(trajectoryAngle);
setpointY = radius * sin(trajectoryAngle);
lastT = now;
}步骤7:工作原理
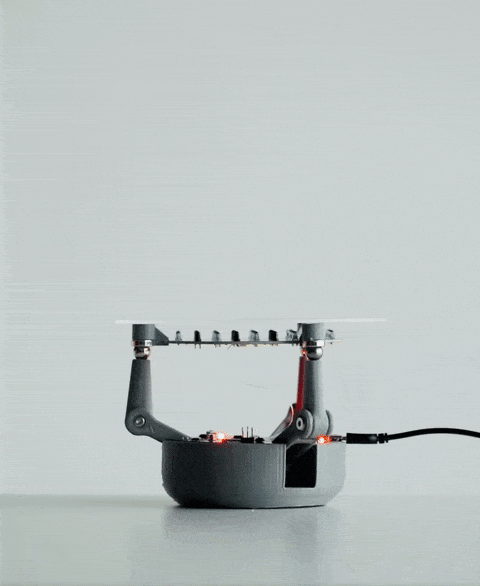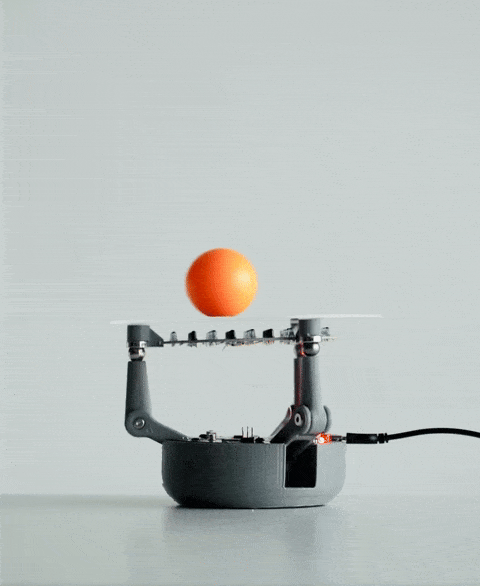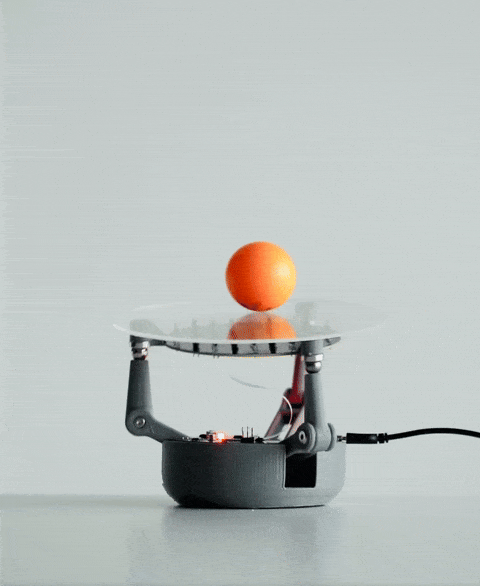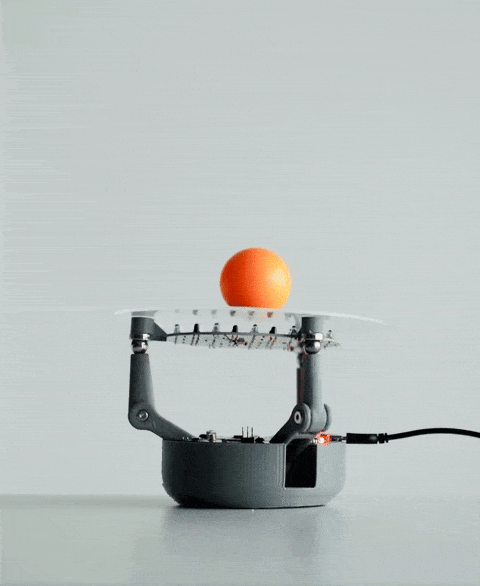
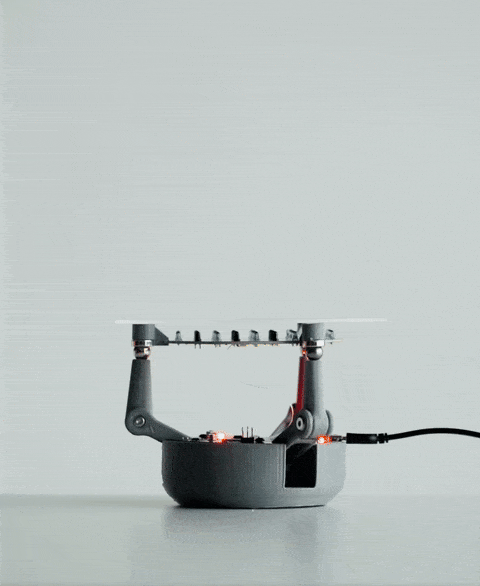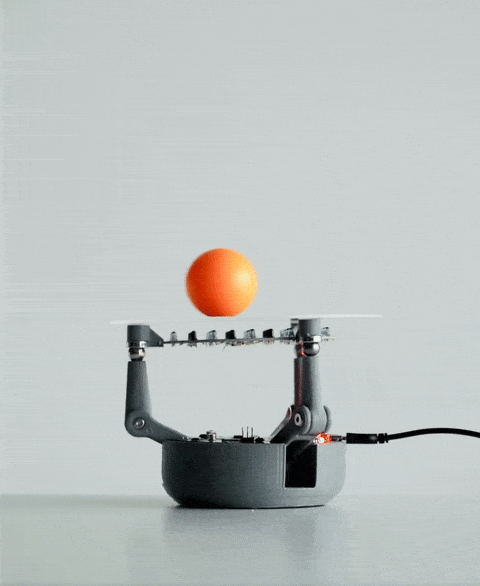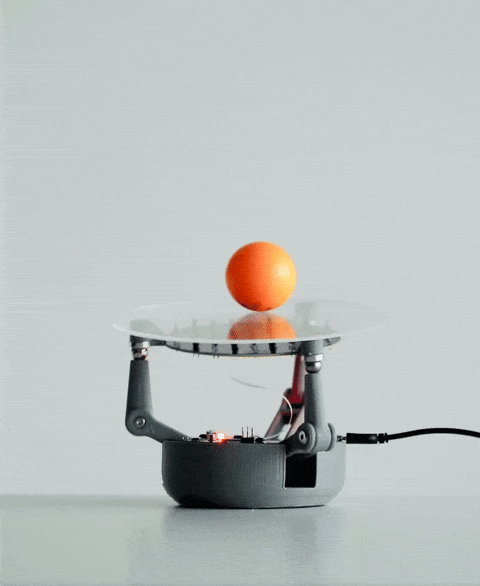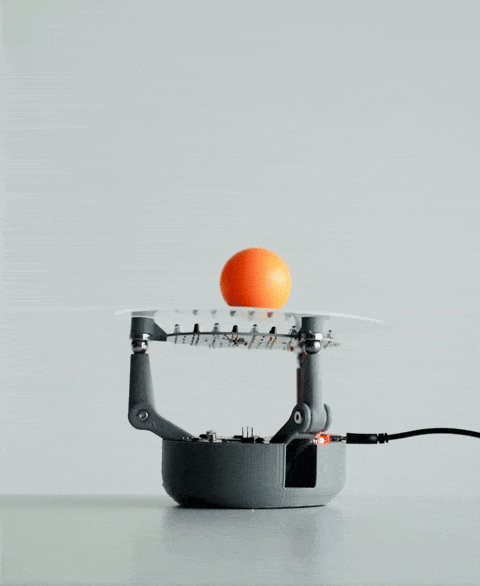
当你将球放在 BaBot 的透明板上时,会发生一系列事件:
红外探测:板下方是一块二级印刷电路板,内嵌多个红外 (IR) LED 和红外光电晶体管。这些红外 LED 向上发射光线,光线经球体底部反射后被光电晶体管捕获。这种设置使 BaBot 能够实时准确地确定球体在板上的位置。
数据处理:辅助 PCB 收集的位置数据传输到主 PCB,主 PCB 内置一个 ATmega32U4 微控制器,类似于 Arduino Leonardo 中的微控制器。该微控制器使用 PID(比例-积分-微分)算法处理数据。PID 算法计算球的当前位置与目标位置(通常是板的中心)之间的差值。
计算板倾斜度:为了校正球的位置,BaBot 必须适当倾斜板。这需要求解逆运动学方程,以确定三个伺服电机达到所需倾斜度所需的精确角度。
驱动运动:计算出的角度被发送到伺服电机,每个电机连接到铰接臂,铰接臂末端是金属球。这些金属球充当关节,并通过磁力吸附在板的底面上,从而实现平稳灵敏的运动。
持续反馈回路:调整板面方向后,系统会重新测量球的位置,并重复此过程。该反馈回路每秒运行约30次,确保球在板上保持平衡。
传感器、控制算法和机械部件的无缝集成使BaBot能够实时保持球平衡,从而提供机器人和控制系统的引人入胜的演示。
步骤8:在哪里获取你的BaBot?
哪里可以买到你的 BaBot?
BaBot提供构建和理解实时控制系统的实践经验。其开源设计鼓励实验和学习,使其成为初学者和经验丰富的创客的理想项目。
对于那些有兴趣进一步探索 BaBot 或获取套件的人,请访问ba-bot.com了解更多信息。
无论您是寻求引人入胜的课堂项目的老师,还是渴望深入研究机器人技术的学生,或者仅仅是欣赏创新小工具的人,BaBot 都旨在吸引和教育您。
无需任何经验,只需有好奇心和创造非凡事物的热情。
项目链接:https://www.ba-bot.com/
https://www.instructables.com/BaBot-Build-Your-Own-Ball-Balancing-Robot/
项目作者:瑞士 约翰·林克
项目视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1V3j9zYEcj/?share_source=copy_web&vd_source=371a292a55e5ca9be994cbb4a86cc987
原理图:https://content.instructables.com/FZK/JW2B/MAL3FTM5/FZKJW2BMAL3FTM5.pdf
3D文件:https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:7021268
项目代码:https://github.com/JohanLink/BABOT
项目动图:https://cdn.thingiverse.com/assets/d5/bb/a9/42/05/main-ezgif.com-optimize.gif
https://cdn.thingiverse.com/assets/0c/5e/ce/f3/c6/Sanstitre-ezgif.com-optimize_2.gif
https://cdn.thingiverse.com/assets/58/30/35/3d/6c/assemblyfinal-ezgif.com-optimize.gif

 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部

评论