37款传感器与执行器的提法,在网络上广泛流传,其实Arduino能够兼容的传感器模块肯定是不止这37种的。鉴于本人手头积累了一些传感器和执行器模块,依照实践出真知(一定要动手做)的理念,以学习和交流为目的,这里准备逐一动手尝试系列实验,不管成功(程序走通)与否,都会记录下来—小小的进步或是搞不掂的问题,希望能够抛砖引玉。
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
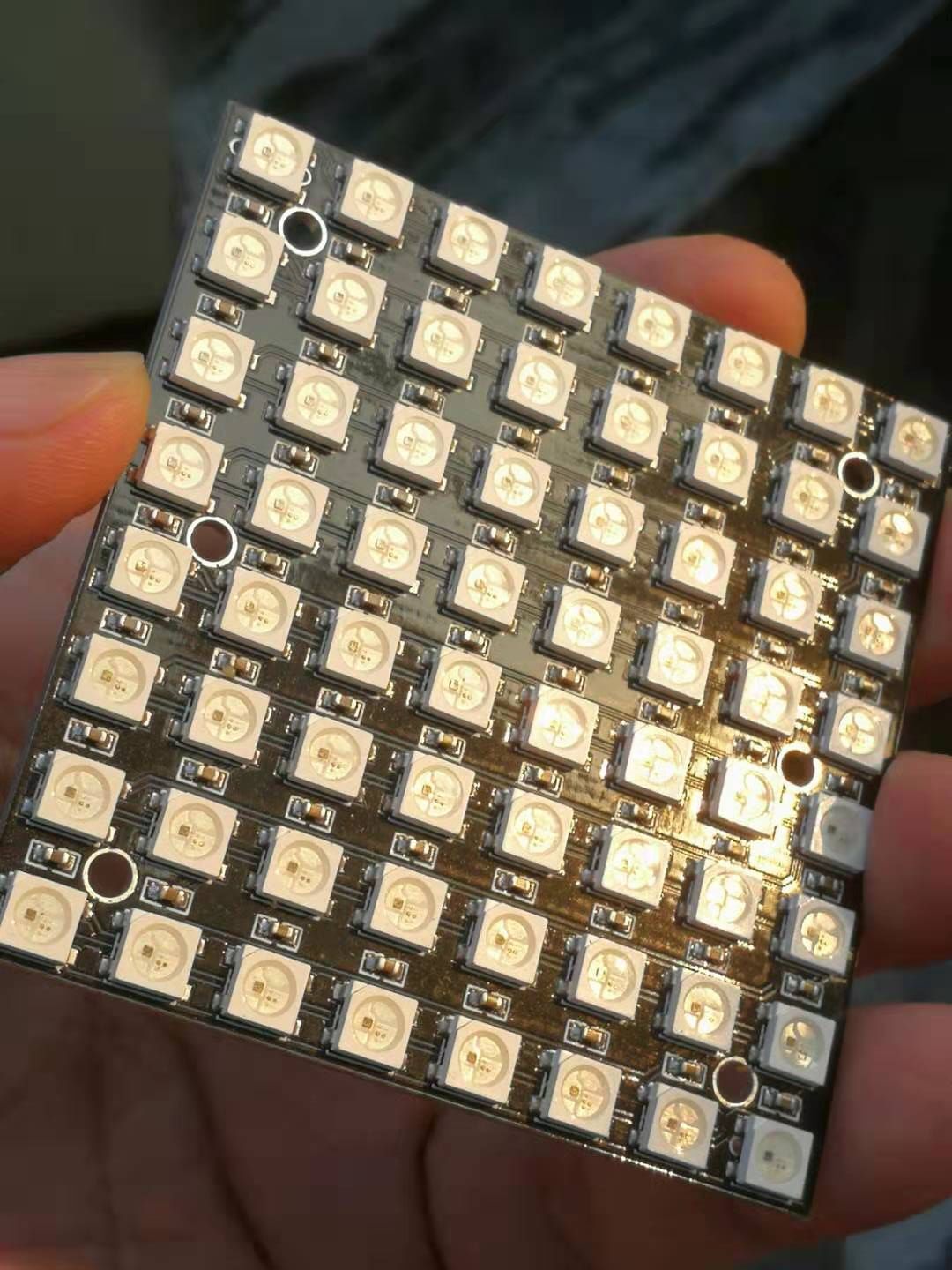
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十四:快速淡入淡出循环变色
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十四:快速淡入淡出循环变色
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <FastLED.h>
// How many leds in your strip?
#define NUM_LEDS 64
// For led chips like Neopixels, which have a data line, ground, and power, you just
// need to define DATA_PIN. For led chipsets that are SPI based (four wires - data, clock,
// ground, and power), like the LPD8806, define both DATA_PIN and CLOCK_PIN
#define DATA_PIN 6
//#define CLOCK_PIN 13
// Define the array of leds
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
Serial.println("resetting");
FastLED.addLeds<WS2812,DATA_PIN,RGB>(leds,NUM_LEDS);
FastLED.setBrightness(24);
}
void fadeall() { for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) { leds[i].nscale8(250); } }
void loop() {
static uint8_t hue = 0;
Serial.print("x");
// First slide the led in one direction
for(int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
// Set the i'th led to red
leds[i] = CHSV(hue++, 255, 255);
// Show the leds
FastLED.show();
// now that we've shown the leds, reset the i'th led to black
// leds[i] = CRGB::Black;
fadeall();
// Wait a little bit before we loop around and do it again
delay(10);
}
Serial.print("x");
// Now go in the other direction.
for(int i = (NUM_LEDS)-1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Set the i'th led to red
leds[i] = CHSV(hue++, 255, 255);
// Show the leds
FastLED.show();
// now that we've shown the leds, reset the i'th led to black
// leds[i] = CRGB::Black;
fadeall();
// Wait a little bit before we loop around and do it again
delay(10);
}
}【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十五:每个 LED 灯条的颜色校正设置,以及总输出'色温'的总控制
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料+代码+图形+仿真)
实验一百四十六:64位WS2812B 8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十五:每个 LED 灯条的颜色校正设置,以及总输出'色温'的总控制
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <FastLED.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
// Information about the LED strip itself
#define NUM_LEDS 64
#define CHIPSET WS2811
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define BRIGHTNESS 26
// FastLED v2.1 provides two color-management controls:
// (1) color correction settings for each LED strip, and
// (2) master control of the overall output 'color temperature'
//
// THIS EXAMPLE demonstrates the second, "color temperature" control.
// It shows a simple rainbow animation first with one temperature profile,
// and a few seconds later, with a different temperature profile.
//
// The first pixel of the strip will show the color temperature.
//
// HELPFUL HINTS for "seeing" the effect in this demo:
// * Don't look directly at the LED pixels. Shine the LEDs aganst
// a white wall, table, or piece of paper, and look at the reflected light.
//
// * If you watch it for a bit, and then walk away, and then come back
// to it, you'll probably be able to "see" whether it's currently using
// the 'redder' or the 'bluer' temperature profile, even not counting
// the lowest 'indicator' pixel.
//
//
// FastLED provides these pre-conigured incandescent color profiles:
// Candle, Tungsten40W, Tungsten100W, Halogen, CarbonArc,
// HighNoonSun, DirectSunlight, OvercastSky, ClearBlueSky,
// FastLED provides these pre-configured gaseous-light color profiles:
// WarmFluorescent, StandardFluorescent, CoolWhiteFluorescent,
// FullSpectrumFluorescent, GrowLightFluorescent, BlackLightFluorescent,
// MercuryVapor, SodiumVapor, MetalHalide, HighPressureSodium,
// FastLED also provides an "Uncorrected temperature" profile
// UncorrectedTemperature;
#define TEMPERATURE_1 Tungsten100W
#define TEMPERATURE_2 OvercastSky
// How many seconds to show each temperature before switching
#define DISPLAYTIME 20
// How many seconds to show black between switches
#define BLACKTIME 3
void loop()
{
// draw a generic, no-name rainbow
static uint8_t starthue = 0;
fill_rainbow( leds + 5, NUM_LEDS - 5, --starthue, 20);
// Choose which 'color temperature' profile to enable.
uint8_t secs = (millis() / 1000) % (DISPLAYTIME * 2);
if( secs < DISPLAYTIME) {
FastLED.setTemperature( TEMPERATURE_1 ); // first temperature
leds[0] = TEMPERATURE_1; // show indicator pixel
} else {
FastLED.setTemperature( TEMPERATURE_2 ); // second temperature
leds[0] = TEMPERATURE_2; // show indicator pixel
}
// Black out the LEDs for a few secnds between color changes
// to let the eyes and brains adjust
if( (secs % DISPLAYTIME) < BLACKTIME) {
memset8( leds, 0, NUM_LEDS * sizeof(CRGB));
}
FastLED.show();
FastLED.delay(8);
}
void setup() {
delay( 3000 ); // power-up safety delay
// It's important to set the color correction for your LED strip here,
// so that colors can be more accurately rendered through the 'temperature' profiles
FastLED.addLeds<CHIPSET, LED_PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection( TypicalSMD5050 );
FastLED.setBrightness( BRIGHTNESS );
}【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十六:FastLED“100行代码”演示卷轴动画效果
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十六:FastLED“100行代码”演示卷轴动画效果
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <FastLED.h>
FASTLED_USING_NAMESPACE
// FastLED "100-lines-of-code" demo reel, showing just a few
// of the kinds of animation patterns you can quickly and easily
// compose using FastLED.
//
// This example also shows one easy way to define multiple
// animations patterns and have them automatically rotate.
//
// -Mark Kriegsman, December 2014
#define DATA_PIN 6
//#define CLK_PIN 4
#define LED_TYPE WS2811
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
#define NUM_LEDS 64
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define BRIGHTNESS 26
#define FRAMES_PER_SECOND 120
void setup() {
delay(3000); // 3 second delay for recovery
// tell FastLED about the LED strip configuration
FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE,DATA_PIN,COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection(TypicalLEDStrip);
//FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE,DATA_PIN,CLK_PIN,COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection(TypicalLEDStrip);
// set master brightness control
FastLED.setBrightness(BRIGHTNESS);
}
// List of patterns to cycle through. Each is defined as a separate function below.
typedef void (*SimplePatternList[])();
SimplePatternList gPatterns = { rainbow, rainbowWithGlitter, confetti, sinelon, juggle, bpm };
uint8_t gCurrentPatternNumber = 0; // Index number of which pattern is current
uint8_t gHue = 0; // rotating "base color" used by many of the patterns
void loop()
{
// Call the current pattern function once, updating the 'leds' array
gPatterns[gCurrentPatternNumber]();
// send the 'leds' array out to the actual LED strip
FastLED.show();
// insert a delay to keep the framerate modest
FastLED.delay(1000/FRAMES_PER_SECOND);
// do some periodic updates
EVERY_N_MILLISECONDS( 20 ) { gHue++; } // slowly cycle the "base color" through the rainbow
EVERY_N_SECONDS( 10 ) { nextPattern(); } // change patterns periodically
}
#define ARRAY_SIZE(A) (sizeof(A) / sizeof((A)[0]))
void nextPattern()
{
// add one to the current pattern number, and wrap around at the end
gCurrentPatternNumber = (gCurrentPatternNumber + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE( gPatterns);
}
void rainbow()
{
// FastLED's built-in rainbow generator
fill_rainbow( leds, NUM_LEDS, gHue, 7);
}
void rainbowWithGlitter()
{
// built-in FastLED rainbow, plus some random sparkly glitter
rainbow();
addGlitter(80);
}
void addGlitter( fract8 chanceOfGlitter)
{
if( random8() < chanceOfGlitter) {
leds[ random16(NUM_LEDS) ] += CRGB::White;
}
}
void confetti()
{
// random colored speckles that blink in and fade smoothly
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 10);
int pos = random16(NUM_LEDS);
leds[pos] += CHSV( gHue + random8(64), 200, 255);
}
void sinelon()
{
// a colored dot sweeping back and forth, with fading trails
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 20);
int pos = beatsin16( 13, 0, NUM_LEDS-1 );
leds[pos] += CHSV( gHue, 255, 192);
}
void bpm()
{
// colored stripes pulsing at a defined Beats-Per-Minute (BPM)
uint8_t BeatsPerMinute = 62;
CRGBPalette16 palette = PartyColors_p;
uint8_t beat = beatsin8( BeatsPerMinute, 64, 255);
for( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) { //9948
leds[i] = ColorFromPalette(palette, gHue+(i*2), beat-gHue+(i*10));
}
}
void juggle() {
// eight colored dots, weaving in and out of sync with each other
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 20);
uint8_t dothue = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
leds[beatsin16( i+7, 0, NUM_LEDS-1 )] |= CHSV(dothue, 200, 255);
dothue += 32;
}
}【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十七:随机60帧火焰花
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十七:随机60帧火焰花
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <FastLED.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
#define CHIPSET WS2811
#define NUM_LEDS 64
#define BRIGHTNESS 22
#define FRAMES_PER_SECOND 60
bool gReverseDirection = false;
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
void setup() {
delay(3000); // sanity delay
FastLED.addLeds<CHIPSET, LED_PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection( TypicalLEDStrip );
FastLED.setBrightness( BRIGHTNESS );
}
void loop()
{
// Add entropy to random number generator; we use a lot of it.
// random16_add_entropy( random());
Fire2012(); // run simulation frame
FastLED.show(); // display this frame
FastLED.delay(1000 / FRAMES_PER_SECOND);
}
// Fire2012 by Mark Kriegsman, July 2012
// as part of "Five Elements" shown here: http://youtu.be/knWiGsmgycY
////
// This basic one-dimensional 'fire' simulation works roughly as follows:
// There's a underlying array of 'heat' cells, that model the temperature
// at each point along the line. Every cycle through the simulation,
// four steps are performed:
// 1) All cells cool down a little bit, losing heat to the air
// 2) The heat from each cell drifts 'up' and diffuses a little
// 3) Sometimes randomly new 'sparks' of heat are added at the bottom
// 4) The heat from each cell is rendered as a color into the leds array
// The heat-to-color mapping uses a black-body radiation approximation.
//
// Temperature is in arbitrary units from 0 (cold black) to 255 (white hot).
//
// This simulation scales it self a bit depending on NUM_LEDS; it should look
// "OK" on anywhere from 20 to 100 LEDs without too much tweaking.
//
// I recommend running this simulation at anywhere from 30-100 frames per second,
// meaning an interframe delay of about 10-35 milliseconds.
//
// Looks best on a high-density LED setup (60+ pixels/meter).
//
//
// There are two main parameters you can play with to control the look and
// feel of your fire: COOLING (used in step 1 above), and SPARKING (used
// in step 3 above).
//
// COOLING: How much does the air cool as it rises?
// Less cooling = taller flames. More cooling = shorter flames.
// Default 50, suggested range 20-100
#define COOLING 55
// SPARKING: What chance (out of 255) is there that a new spark will be lit?
// Higher chance = more roaring fire. Lower chance = more flickery fire.
// Default 120, suggested range 50-200.
#define SPARKING 120
void Fire2012()
{
// Array of temperature readings at each simulation cell
static uint8_t heat[NUM_LEDS];
// Step 1. Cool down every cell a little
for ( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
heat[i] = qsub8( heat[i], random8(0, ((COOLING * 10) / NUM_LEDS) + 2));
}
// Step 2. Heat from each cell drifts 'up' and diffuses a little
for ( int k = NUM_LEDS - 1; k >= 2; k--) {
heat[k] = (heat[k - 1] + heat[k - 2] + heat[k - 2] ) / 3;
}
// Step 3. Randomly ignite new 'sparks' of heat near the bottom
if ( random8() < SPARKING ) {
int y = random8(7);
heat[y] = qadd8( heat[y], random8(160, 255) );
}
// Step 4. Map from heat cells to LED colors
for ( int j = 0; j < NUM_LEDS; j++) {
CRGB color = HeatColor( heat[j]);
int pixelnumber;
if ( gReverseDirection ) {
pixelnumber = (NUM_LEDS - 1) - j;
} else {
pixelnumber = j;
}
leds[pixelnumber] = color;
}
}【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十八:带有可编程调色板的 Fire2012 火灾模拟
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验一百三十八:64位 WS2812B8*8 xRGB 5050 LED模块 ws2812s像素点阵屏
项目十八:带有可编程调色板的 Fire2012 火灾模拟
实验接线
Module UNO
VCC —— 3.3V
GND —— GND
DI —— D6
*/
#include <FastLED.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
#define CHIPSET WS2811
#define NUM_LEDS 64
#define BRIGHTNESS 22
#define FRAMES_PER_SECOND 60
bool gReverseDirection = false;
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
// Fire2012 with programmable Color Palette
//
// This code is the same fire simulation as the original "Fire2012",
// but each heat cell's temperature is translated to color through a FastLED
// programmable color palette, instead of through the "HeatColor(...)" function.
//
// Four different static color palettes are provided here, plus one dynamic one.
//
// The three static ones are:
// 1. the FastLED built-in HeatColors_p -- this is the default, and it looks
// pretty much exactly like the original Fire2012.
//
// To use any of the other palettes below, just "uncomment" the corresponding code.
//
// 2. a gradient from black to red to yellow to white, which is
// visually similar to the HeatColors_p, and helps to illustrate
// what the 'heat colors' palette is actually doing,
// 3. a similar gradient, but in blue colors rather than red ones,
// i.e. from black to blue to aqua to white, which results in
// an "icy blue" fire effect,
// 4. a simplified three-step gradient, from black to red to white, just to show
// that these gradients need not have four components; two or
// three are possible, too, even if they don't look quite as nice for fire.
//
// The dynamic palette shows how you can change the basic 'hue' of the
// color palette every time through the loop, producing "rainbow fire".
CRGBPalette16 gPal;
void setup() {
delay(3000); // sanity delay
FastLED.addLeds<CHIPSET, LED_PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection( TypicalLEDStrip );
FastLED.setBrightness( BRIGHTNESS );
// This first palette is the basic 'black body radiation' colors,
// which run from black to red to bright yellow to white.
gPal = HeatColors_p;
// These are other ways to set up the color palette for the 'fire'.
// First, a gradient from black to red to yellow to white -- similar to HeatColors_p
// gPal = CRGBPalette16( CRGB::Black, CRGB::Red, CRGB::Yellow, CRGB::White);
// Second, this palette is like the heat colors, but blue/aqua instead of red/yellow
// gPal = CRGBPalette16( CRGB::Black, CRGB::Blue, CRGB::Aqua, CRGB::White);
// Third, here's a simpler, three-step gradient, from black to red to white
// gPal = CRGBPalette16( CRGB::Black, CRGB::Red, CRGB::White);
}
void loop()
{
// Add entropy to random number generator; we use a lot of it.
random16_add_entropy( random());
// Fourth, the most sophisticated: this one sets up a new palette every
// time through the loop, based on a hue that changes every time.
// The palette is a gradient from black, to a dark color based on the hue,
// to a light color based on the hue, to white.
//
// static uint8_t hue = 0;
// hue++;
// CRGB darkcolor = CHSV(hue,255,192); // pure hue, three-quarters brightness
// CRGB lightcolor = CHSV(hue,128,255); // half 'whitened', full brightness
// gPal = CRGBPalette16( CRGB::Black, darkcolor, lightcolor, CRGB::White);
Fire2012WithPalette(); // run simulation frame, using palette colors
FastLED.show(); // display this frame
FastLED.delay(1000 / FRAMES_PER_SECOND);
}
// Fire2012 by Mark Kriegsman, July 2012
// as part of "Five Elements" shown here: http://youtu.be/knWiGsmgycY
////
// This basic one-dimensional 'fire' simulation works roughly as follows:
// There's a underlying array of 'heat' cells, that model the temperature
// at each point along the line. Every cycle through the simulation,
// four steps are performed:
// 1) All cells cool down a little bit, losing heat to the air
// 2) The heat from each cell drifts 'up' and diffuses a little
// 3) Sometimes randomly new 'sparks' of heat are added at the bottom
// 4) The heat from each cell is rendered as a color into the leds array
// The heat-to-color mapping uses a black-body radiation approximation.
//
// Temperature is in arbitrary units from 0 (cold black) to 255 (white hot).
//
// This simulation scales it self a bit depending on NUM_LEDS; it should look
// "OK" on anywhere from 20 to 100 LEDs without too much tweaking.
//
// I recommend running this simulation at anywhere from 30-100 frames per second,
// meaning an interframe delay of about 10-35 milliseconds.
//
// Looks best on a high-density LED setup (60+ pixels/meter).
//
//
// There are two main parameters you can play with to control the look and
// feel of your fire: COOLING (used in step 1 above), and SPARKING (used
// in step 3 above).
//
// COOLING: How much does the air cool as it rises?
// Less cooling = taller flames. More cooling = shorter flames.
// Default 55, suggested range 20-100
#define COOLING 55
// SPARKING: What chance (out of 255) is there that a new spark will be lit?
// Higher chance = more roaring fire. Lower chance = more flickery fire.
// Default 120, suggested range 50-200.
#define SPARKING 120
void Fire2012WithPalette()
{
// Array of temperature readings at each simulation cell
static uint8_t heat[NUM_LEDS];
// Step 1. Cool down every cell a little
for( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
heat[i] = qsub8( heat[i], random8(0, ((COOLING * 10) / NUM_LEDS) + 2));
}
// Step 2. Heat from each cell drifts 'up' and diffuses a little
for( int k= NUM_LEDS - 1; k >= 2; k--) {
heat[k] = (heat[k - 1] + heat[k - 2] + heat[k - 2] ) / 3;
}
// Step 3. Randomly ignite new 'sparks' of heat near the bottom
if( random8() < SPARKING ) {
int y = random8(7);
heat[y] = qadd8( heat[y], random8(160,255) );
}
// Step 4. Map from heat cells to LED colors
for( int j = 0; j < NUM_LEDS; j++) {
// Scale the heat value from 0-255 down to 0-240
// for best results with color palettes.
uint8_t colorindex = scale8( heat[j], 240);
CRGB color = ColorFromPalette( gPal, colorindex);
int pixelnumber;
if( gReverseDirection ) {
pixelnumber = (NUM_LEDS-1) - j;
} else {
pixelnumber = j;
}
leds[pixelnumber] = color;
}
}
 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部


9mm2023.08.17
666