【LattePanda Mu 开发套件】AI 视觉应用开发——物体识别
本文介绍了 LattePanda Mu 开发套件实现 AI 视觉识别类相关应用——物体识别,包括模型训练、板端推理、摄像头实时检测和推理识别等。
项目介绍
基于 YOLO 模型实现常见的 80 种物体识别,包括
物体识别的板端推理:包括流程图、代码、效果演示;
物体识别的动态显示:包括流程图、代码、效果演示;
YOLO 模型
YOLO(You Only Look Once)是一种流行的物体检测和图像分割模型,由华盛顿大学的 Joseph Redmon 和 Ali Farhadi 开发。YOLO 于 2015 年推出,因其高速和高精度而广受欢迎。
Ultralytics YOLO 是 YOLO 系列中最新的技术,用于实时目标检测和图像分割。它在前几个版本的基础上,引入了新的功能和改进,以增强性能、灵活性和效率。YOLO支持各种视觉AI任务,如检测、分割、姿势估计、跟踪和分类。其最先进的架构确保了卓越的速度和准确性,使其适用于各种应用,包括边缘设备和云API。
详见:Ultralytics YOLO 文档 . GitHub - Ultralytics YOLO 🚀 .
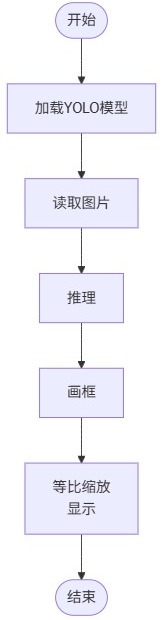
板端推理
实现本地物体图片的识别和推理,并弹窗显示识别结果。
流程图
代码
新建 objective_recognition.py 并添加如下代码
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import os
def detect_objects_in_image(image_path, model_path="model/yolov8n.pt"):
"""
对本地图片进行物体识别并显示结果
Args:
image_path (str): 图片文件路径
model_path (str): YOLO模型路径,默认为yolov8n.pt
"""
# 1. 检查图片文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print(f"错误: 图片文件 '{image_path}' 不存在")
return
# 2. 加载模型(如果不存在则自动下载)
try:
model = YOLO(model_path)
except Exception as e:
print(f"加载模型时出错: {e}")
return
# 3. 读取图片
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
if image is None:
print(f"错误: 无法读取图片 '{image_path}'")
return
# 4. 推理
results = model(image)
# 5. 绘制检测结果
annotated_image = results[0].plot() # 绘制边界框和标签
# 6. 显示结果
window_name = f"YOLOv8 检测结果: {os.path.basename(image_path)}"
cv2.imshow(window_name, annotated_image)
# 调整窗口大小以适应屏幕(可选)
height, width = annotated_image.shape[:2]
max_height = 800 # 最大窗口高度
if height > max_height:
scale = max_height / height
new_width = int(width * scale)
resized_image = cv2.resize(annotated_image, (new_width, max_height))
cv2.imshow(window_name, resized_image)
print("按任意键关闭窗口...")
cv2.waitKey(0) # 等待按键
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 设置图片路径(修改为您的图片路径)
image_path = "object_img/desktop.jpg" # 请替换为实际图片路径
# 执行物体识别
detect_objects_in_image(image_path)
右键该文件,选择使用 IDLE 编辑;
菜单栏选择 Run - Run Module 选项,运行程序;
或双击 *.py 文件运行。
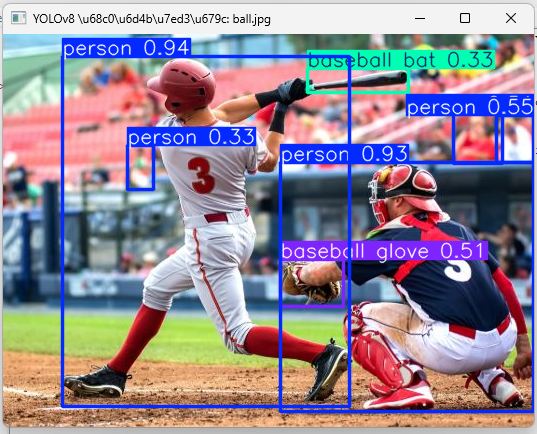
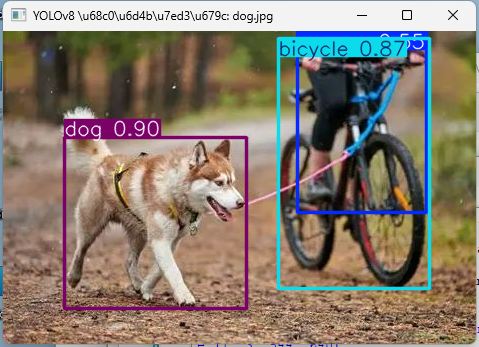
效果
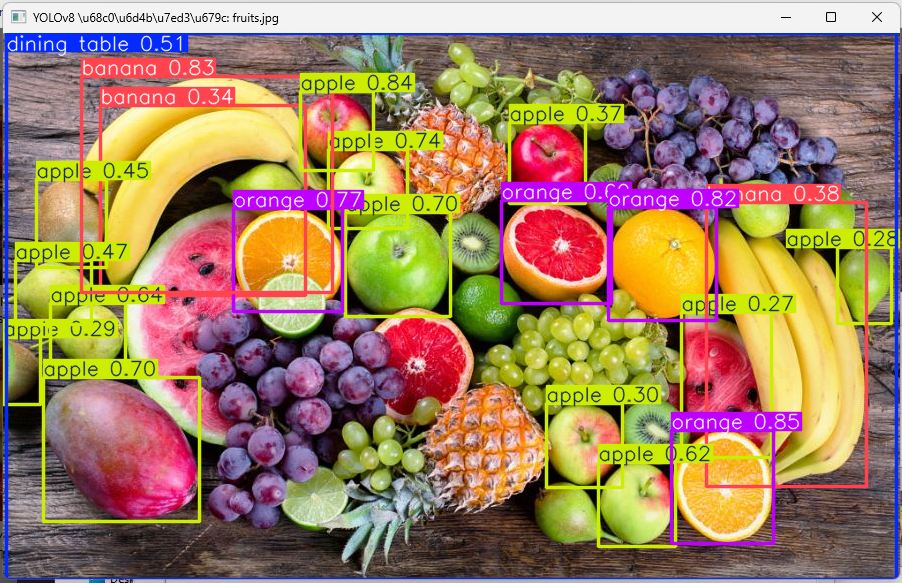
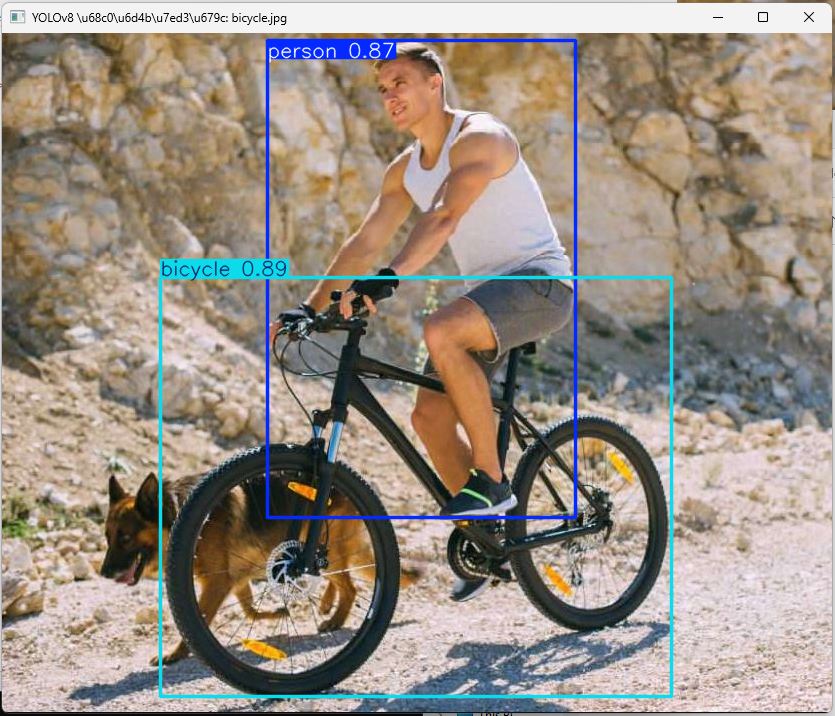
运行程序后弹出物体识别结果图片窗口;
标注物体识别选框、文字和置信度;
同时终端打印识别结果,包括物体类别、位置、置信度等信息;
更多场景举例
路口
运动
动物
水果
自行车
动态检测
使用 USB 摄像头实现动态实时物体识别,并标注和打印识别结果。
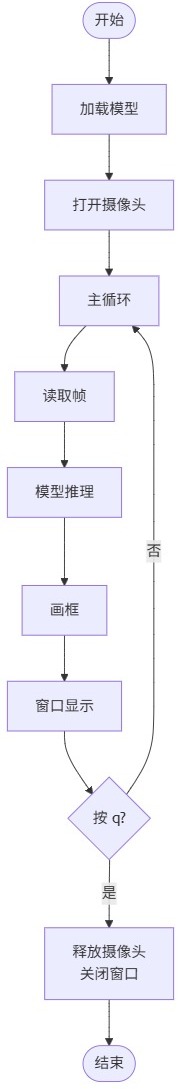
流程图
代码
新建 objective_recognition_CamUSB.py 并添加如下代码
# cam_yolo.py
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
# 1. 加载模型(6 MB,COCO 80 类)
model = YOLO("model/yolov8n.pt") # 不存在则自动下载
# 2. 打开摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not cap.isOpened():
raise RuntimeError("打不开摄像头")
print("按 q 退出")
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 3. 推理
results = model(frame, stream=True) # 返回生成器,逐帧推理
# 4. 画框+置信度(Ultralytics 自带 API)
annotated = results.__next__().plot() # BGR 数组
# 5. 显示
cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 USB Camera", annotated)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
右键该文件,选择使用 IDLE 编辑;
菜单栏选择 Run - Run Module 选项,运行程序;
或双击 *.py 文件运行。
效果
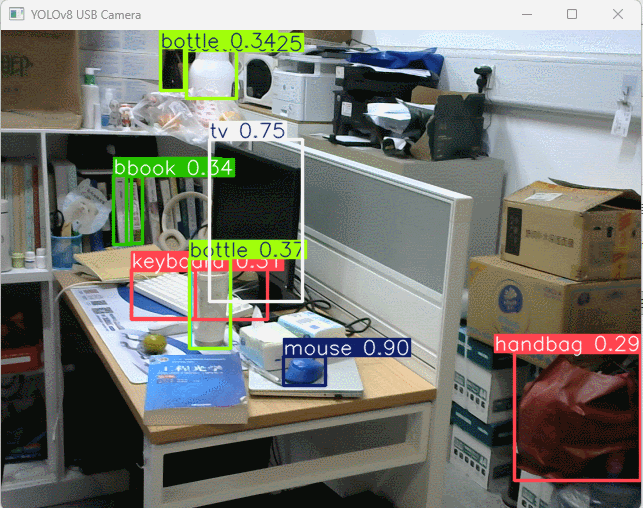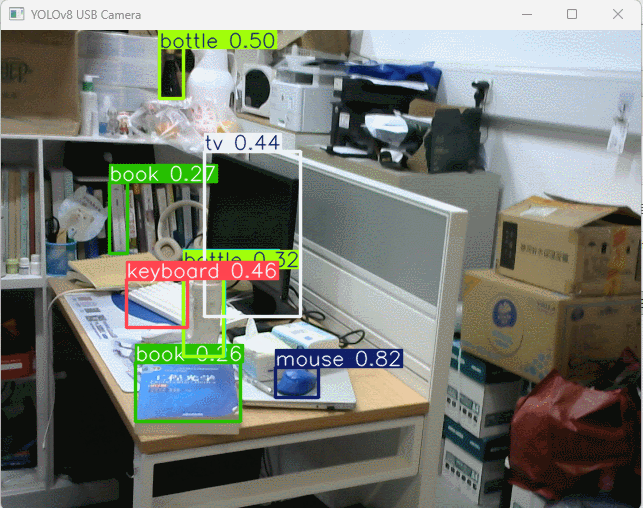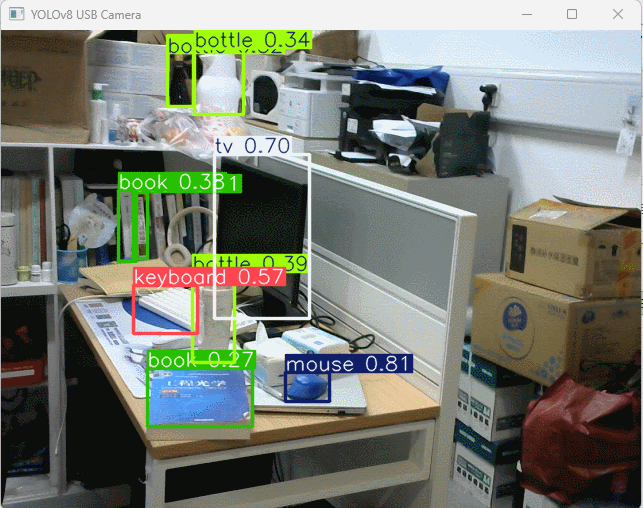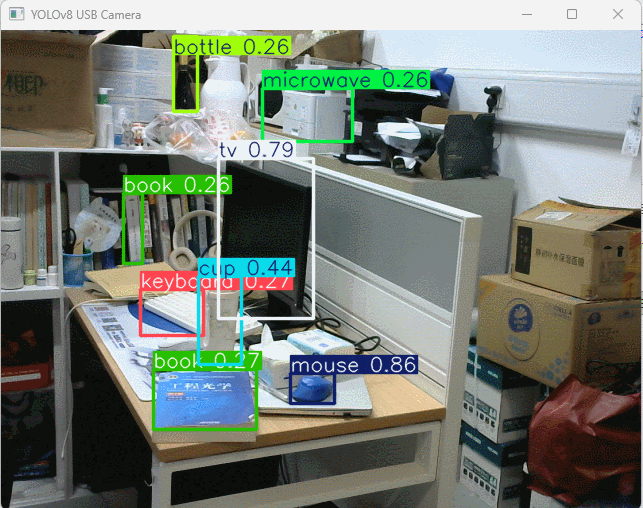
运行程序后弹出摄像头实时采集画面,自动标注物体识别选框、文字和置信度
总结
本文介绍了 LattePanda Mu 开发套件实现 AI 视觉识别类相关应用——物体识别,包括模型训练、板端推理、摄像头实时检测和推理识别等,为该产品在 AI 视觉领域的快速开发和应用提供了参考。

 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部




罗罗罗2025.11.27
666