Kitronik ARCADE 是一款由英国教育科技公司 Kitronik 精心打造的可编程游戏机开发板,专为编程教学与创客实践而设计。该设备原生支持微软的 MakeCode Arcade 平台,用户可通过图形化或 JavaScript 编程方式,轻松创建、下载并运行复古风格的街机游戏。
它集成了彩色 LCD 显示屏、方向控制键、功能按键、蜂鸣器和震动马达等交互组件,提供完整的游戏输入输出体验。无论是初学者进行编程启蒙,还是创客群体开发交互式作品,Kitronik ARCADE 都能作为理想的硬件载体,助力创意实现。
凭借其开源友好、易于上手、兼容性强等特点,该开发板广泛应用于中小学编程课程、创客工作坊、游戏开发教学以及个人项目原型设计,深受教育者与技术爱好者的喜爱。

作为学习、练习与尝试,这里创建一个Pi 蒙特卡洛的小游戏。
打开网页版:https://arcade.makecode.com/,设置项目名称:Pi 蒙特卡洛
MicroPython实验代码
@namespace
class SpriteKind:
Square = SpriteKind.create()
Circle = SpriteKind.create()
def on_on_destroyed(sprite):
game.reset()
sprites.on_destroyed(SpriteKind.Square, on_on_destroyed)
def on_b_pressed():
game.show_long_text("Pi: " + ("" + str(4 * circleDots / squareDots)) + " using " + ("" + str(circleDots)) + " dots",
DialogLayout.BOTTOM)
controller.B.on_event(ControllerButtonEvent.PRESSED, on_b_pressed)
def on_life_zero():
info.set_score(circleDots)
game.show_long_text("Pi: " + ("" + str(4 * circleDots / squareDots)),
DialogLayout.BOTTOM)
mCircle.say("Bye..")
mCircle.vx = 1000
mSquare.say("..we have Pi")
mSquare.ax = 50
info.on_life_zero(on_life_zero)
def drawCircle():
global xx, yy
# draw a circle outline using random dots!
for index in range(dots):
xx = randint(0, 2 * r) - r
yy = randint(0, 2 * r) - r
# test if the point will draw the circle
if xx * xx + yy * yy >= r ** 2 and xx * xx + yy * yy < (r + 1) ** 2:
cirImage.set_pixel(xx + r, yy + r, 1)
delay2 = 0
simulate = False
j = 0
yy = 0
xx = 0
squareDots = 0
circleDots = 0
mCircle: Sprite = None
mSquare: Sprite = None
cirImage: Image = None
dots = 0
r = 0
# set the radius and side length for the shapes
r = scene.screen_height() / 4
l = r * 2 + 1
# total dots (sample count)
dots = 1000000
# virtual radius length
r2 = 5000
# scale the actual radius from the virtual radius
scale = (r + 1) / r2
sqImage = image.create(l, l)
sqImage.fill(0)
sqImage.draw_rect(0, 0, l, l, 1)
cirImage = image.create(l, l)
cirImage.fill(0)
game.splash("Approximate Pi", "Monte Carlo Method")
mSquare = sprites.create(sqImage, SpriteKind.Square)
mSquare.set_flag(SpriteFlag.AUTO_DESTROY, True)
drawCircle()
mCircle = sprites.create(cirImage, SpriteKind.Circle)
def on_forever():
global xx, yy, squareDots, circleDots, j
# A simple Monte Carlo simulation to approximate Pi
while j < dots and simulate:
# generate a point within the square
xx = randint(0, 2 * r2) - r2
yy = randint(0, 2 * r2) - r2
sqImage.set_pixel(xx * scale + r, yy * scale + r, 7)
squareDots += 1
# test if the point is within the circle
# sqrt(x**2 + y**2) < r ==> x**2 + y**2 < r**2
if xx * xx + yy * yy <= r2 ** 2:
circleDots += 1
# scale to screen coordinates
xx = xx * scale
yy = yy * scale
# shift over the x or y == 0 position
if xx < 0:
xx += 1
if yy < 0:
yy += 1
cirImage.set_pixel(xx + r, yy + r, 2)
# after a little while just quickly finish the simulation
if squareDots < dots / 50 and squareDots % 100 == 0:
info.set_score(circleDots)
pause(100)
j += 1
if j >= dots:
info.set_score(circleDots)
info.set_life(0)
forever(on_forever)
def on_update_interval():
global simulate, delay2
if delay2 > 10:
# start simulation
simulate = True
if delay2 > 20:
# slide shape apart
if mCircle.x < scene.screen_width() - 3 * r / 2:
mSquare.x += -1
mCircle.x += 1
delay2 += 1
game.on_update_interval(100, on_update_interval)
ARCADE MakeCode Pi 蒙特卡洛游戏代码解读
这是一个使用蒙特卡洛方法估算π值的游戏程序。代码结构分析:
1. 自定义精灵类型
python
class SpriteKind:
Square = SpriteKind.create()
Circle = SpriteKind.create()
定义两种精灵类型:方形和圆形,用于表示蒙特卡洛模拟中的方形区域和圆形区域。
2. 全局变量初始化
python
# 各种变量初始化
delay2 = 0
simulate = False
j = 0
yy = 0
xx = 0
squareDots = 0 # 方形内的点数
circleDots = 0 # 圆形内的点数
mCircle: Sprite = None
mSquare: Sprite = None
cirImage: Image = None
dots = 0
r = 0
# 设置形状的半径和边长
r = scene.screen_height() / 4 # 半径为屏幕高度的1/4
l = r * 2 + 1 # 方形边长
# 总点数(样本数量)
dots = 1000000
# 虚拟半径长度(用于计算)
r2 = 5000
# 实际半径与虚拟半径的比例
scale = (r + 1) / r2
3. 图像和精灵创建
python
# 创建方形图像
sqImage = image.create(l, l)
sqImage.fill(0)
sqImage.draw_rect(0, 0, l, l, 1)
# 创建圆形图像
cirImage = image.create(l, l)
cirImage.fill(0)
# 显示游戏介绍
game.splash("Approximate Pi", "Monte Carlo Method")
# 创建方形精灵
mSquare = sprites.create(sqImage, SpriteKind.Square)
mSquare.set_flag(SpriteFlag.AUTO_DESTROY, True)
# 绘制圆形轮廓
drawCircle()
# 创建圆形精灵
mCircle = sprites.create(cirImage, SpriteKind.Circle)
4. 绘制圆形函数
python
def drawCircle():
global xx, yy
# 使用随机点绘制圆形轮廓
for index in range(dots):
xx = randint(0, 2 * r) - r
yy = randint(0, 2 * r) - r
# 测试点是否在圆形轮廓上
if xx * xx + yy * yy >= r ** 2 and xx * xx + yy * yy < (r + 1) ** 2:
cirImage.set_pixel(xx + r, yy + r, 1)
5. 蒙特卡洛模拟主循环
python
def on_forever():
global xx, yy, squareDots, circleDots, j
# 简单的蒙特卡洛模拟来估算π值
while j < dots and simulate:
# 在方形内生成随机点
xx = randint(0, 2 * r2) - r2
yy = randint(0, 2 * r2) - r2
sqImage.set_pixel(xx * scale + r, yy * scale + r, 7)
squareDots += 1
# 测试点是否在圆形内
if xx * xx + yy * yy <= r2 ** 2:
circleDots += 1
# 缩放到屏幕坐标
xx = xx * scale
yy = yy * scale
# 调整x或y为0的位置
if xx < 0:
xx += 1
if yy < 0:
yy += 1
cirImage.set_pixel(xx + r, yy + r, 2)
# 定期更新显示
if squareDots < dots / 50 and squareDots % 100 == 0:
info.set_score(circleDots)
pause(100)
j += 1
# 完成模拟
if j >= dots:
info.set_score(circleDots)
info.set_life(0)
6. 更新间隔函数
python
def on_update_interval():
global simulate, delay2
if delay2 > 10:
# 开始模拟
simulate = True
if delay2 > 20:
# 将形状分开
if mCircle.x < scene.screen_width() - 3 * r / 2:
mSquare.x += -1
mCircle.x += 1
delay2 += 1
7. 事件处理函数
python
# B按钮按下事件:显示π值估算结果
def on_b_pressed():
game.show_long_text("Pi: " + ("" + str(4 * circleDots / squareDots)) + " using " + ("" + str(circleDots)) + " dots",
DialogLayout.BOTTOM)
controller.B.on_event(ControllerButtonEvent.PRESSED, on_b_pressed)
# 生命值为零事件:显示最终结果
def on_life_zero():
info.set_score(circleDots)
game.show_long_text("Pi: " + ("" + str(4 * circleDots / squareDots)),
DialogLayout.BOTTOM)
mCircle.say("Bye..")
mCircle.vx = 1000
mSquare.say("..we have Pi")
mSquare.ax = 50
info.on_life_zero(on_life_zero)
# 方形精灵销毁事件:重置游戏
def on_on_destroyed(sprite):
game.reset()
sprites.on_destroyed(SpriteKind.Square, on_on_destroyed)
蒙特卡洛方法原理
这个程序使用蒙特卡洛方法估算π值,原理如下:
在一个正方形内随机生成大量点
统计落在内切圆内的点的数量
根据公式 π ≈ 4 × (圆内点数 / 总点数) 估算π值
这种方法通过随机抽样和概率统计来近似计算数学常数,是蒙特卡洛方法的经典应用。
这个程序通过可视化方式展示了这一过程,使抽象的数学概念变得更加直观和有趣。
图形编程参考实验程序
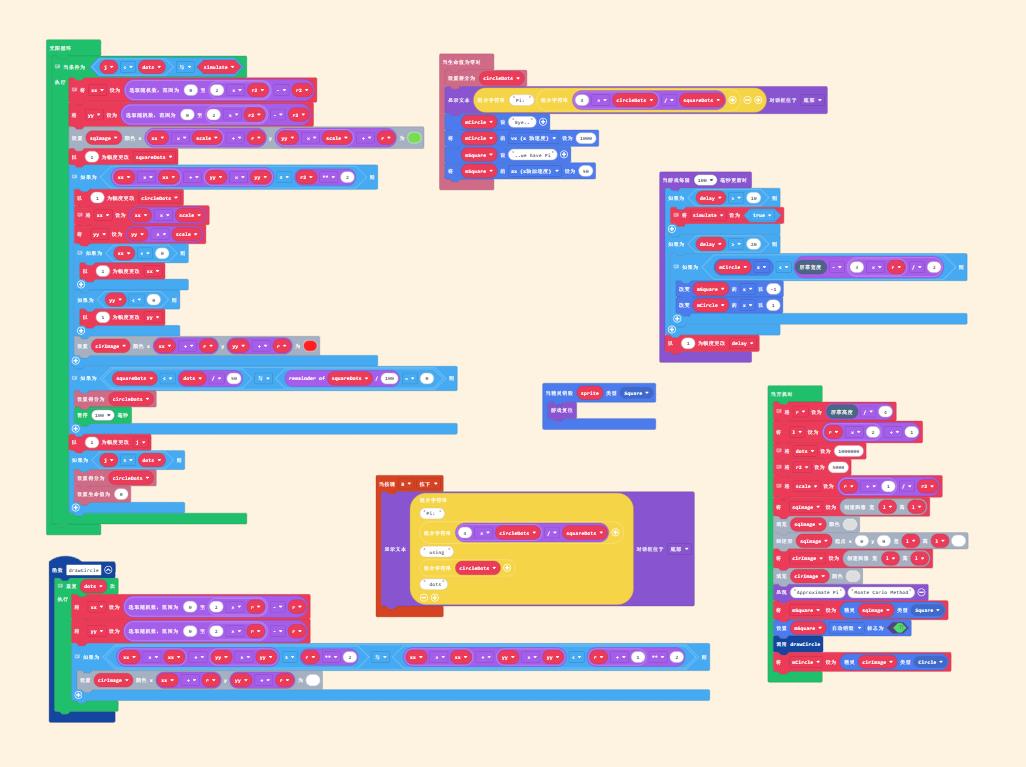
通过模拟器,调试与模拟运行
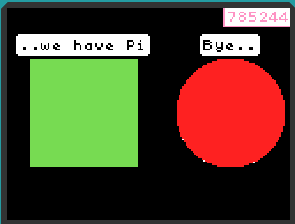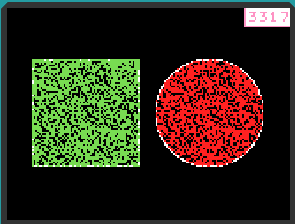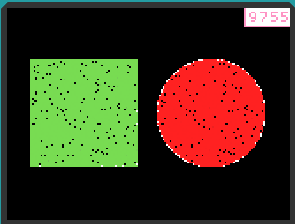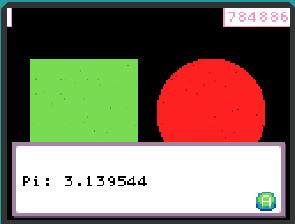
实验场景记录
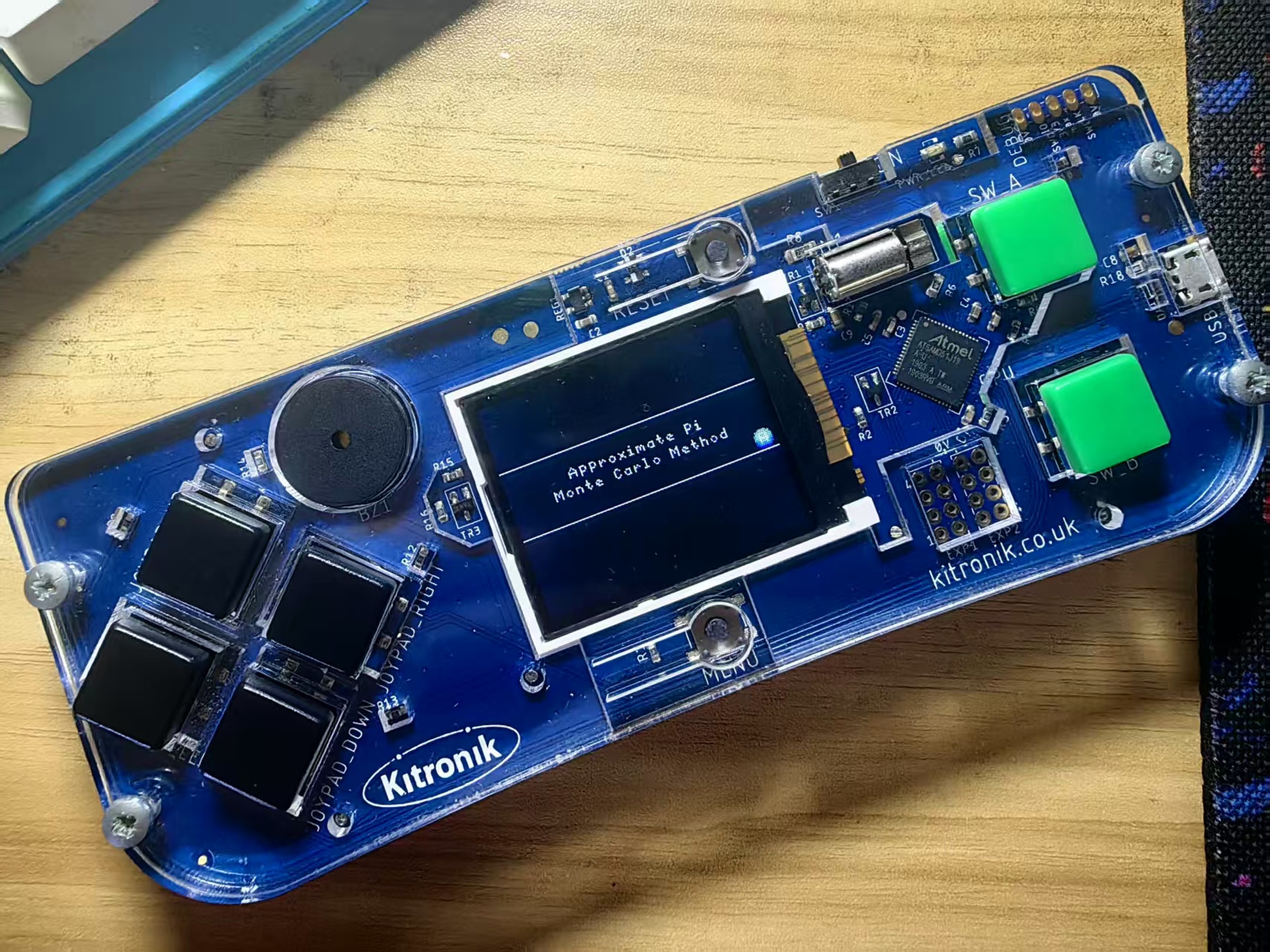
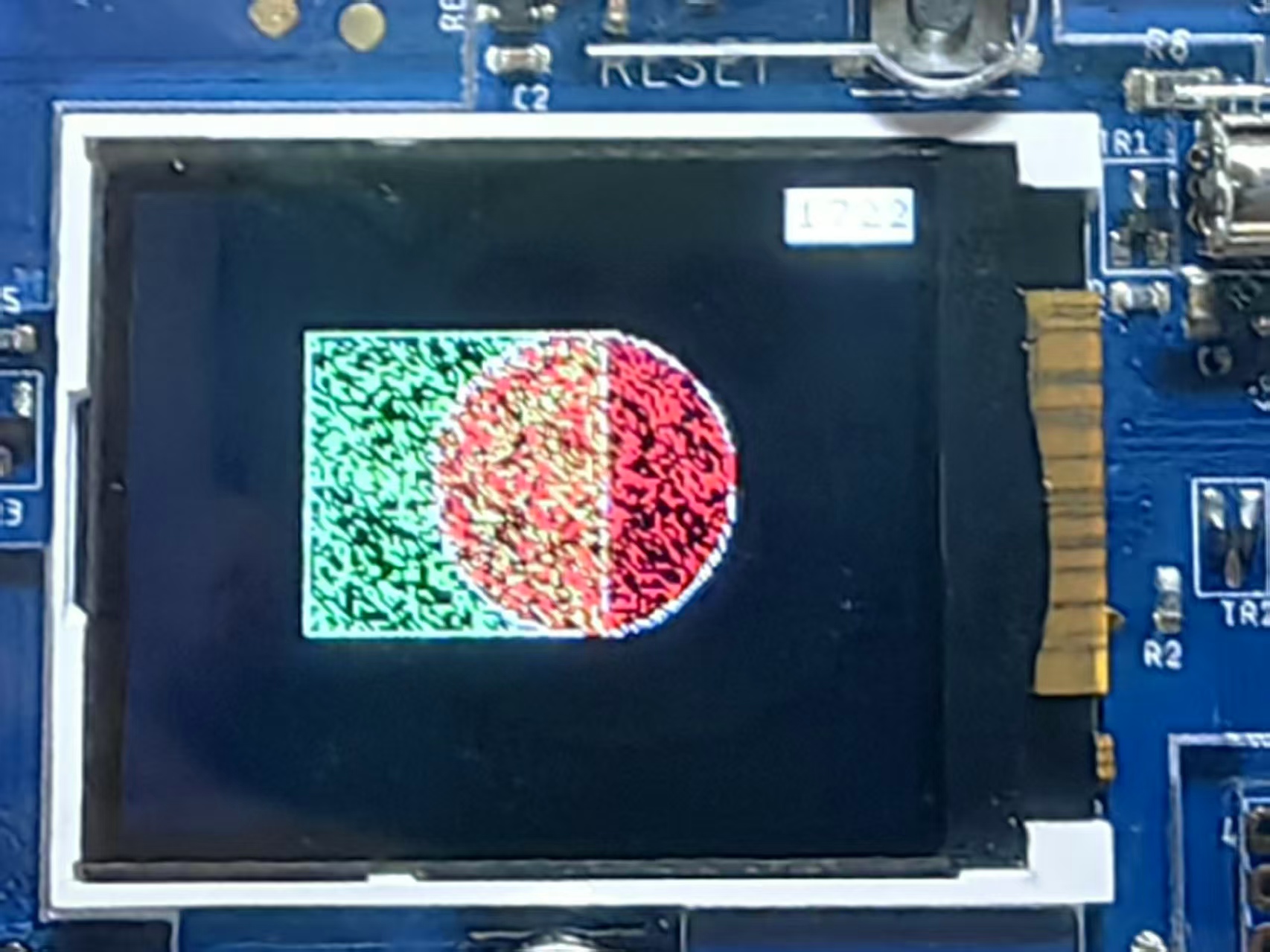

 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部


评论