【项目背景】
随着智能家居和物联网技术的发展,语音交互已经成为人与设备沟通的重要方式之一。为了提供更加自然和便捷的用户体验,本项目旨在开发一个基于行空板的智能语音交互系统。该系统将集成先进的语音唤醒、人声检测、语音识别、对话处理和语音合成技术,以实现流畅的语音交互体验。
【项目设计】
语音唤醒:利用Snowboy库实现低功耗的语音唤醒功能,用户可以通过特定的唤醒词激活设备,而不需要手动操作。
人声检测:通过WebRTCVAD(Voice Activity Detection)技术进行人声检测,确保系统只在有人说话时开始录音,提高录音效率和准确性。
录音与暂停:当检测到人声时,系统开始录音;当语音停顿超过2秒时,系统自动停止录音,以减少无效录音。
语音识别:将录音文件发送给讯飞语音识别服务,将语音转换为文本,为后续的对话处理提供基础。
对话处理:将识别出的文本发送给Kimi进行对话处理,Kimi将根据文本内容生成合适的回复。
语音合成:将Kimi生成的文本回复发送给讯飞进行语音合成,转换成语音信号。
语音播放:利用行空板连接的蓝牙音箱播放合成的语音,为用户提供听觉反馈。
技术亮点:
- 低功耗语音唤醒:Snowboy库提供了高效的离线语音唤醒功能,减少了设备的能耗。
- 实时人声检测:WebRTCVAD能够实时检测人声活动,确保录音的准确性。
- 智能对话处理:Kimi的智能对话系统能够理解用户意图并生成合适的回复。
- 高质量的语音合成:讯飞的语音合成技术能够生成自然流畅的语音输出。
- 无线音频输出:通过蓝牙音箱播放语音,提供了便捷的无线音频解决方案。

【获取唤醒词】
1.windows系统上安装'snowboy"库:pip install snowboy
2.snowboy已停止运营了,可以使用第三方:https://snowboy.hahack.com/,录制自己的唤醒词,并下载训练好的模型文件。
3.行空板系统上安装Snowboy,打开
(1)获取Snowboy源码:
- 可以从GitHub上的Snowboy仓库克隆源代码:
- git clone https://github.com/Kitt-AI/snowboy.git
(2)编译Snowboy:
- 进入源码目录并编译Python wrapper:
- cd snowboy/swig/Python
- make
- 这将生成_snowboydetect.so文件和Python wrapper snowboydetect.py。
(3)测试Snowboy:
- 进入示例目录并运行demo:
- cd snowboy/examples/Python
- python demo.py resources/models/snowboy.umdl
- 按照提示说话,看是否能检测到唤醒词。
【唤醒词测试】
1.Mind+使用“终端“连接行空板,进入”行空板中的文件“——”snowboy“——”examples“——”Python3“,修改”demo.py“文件,并将下载的唤醒词文件yuntian.pmdl,上传至行空板当前目录。
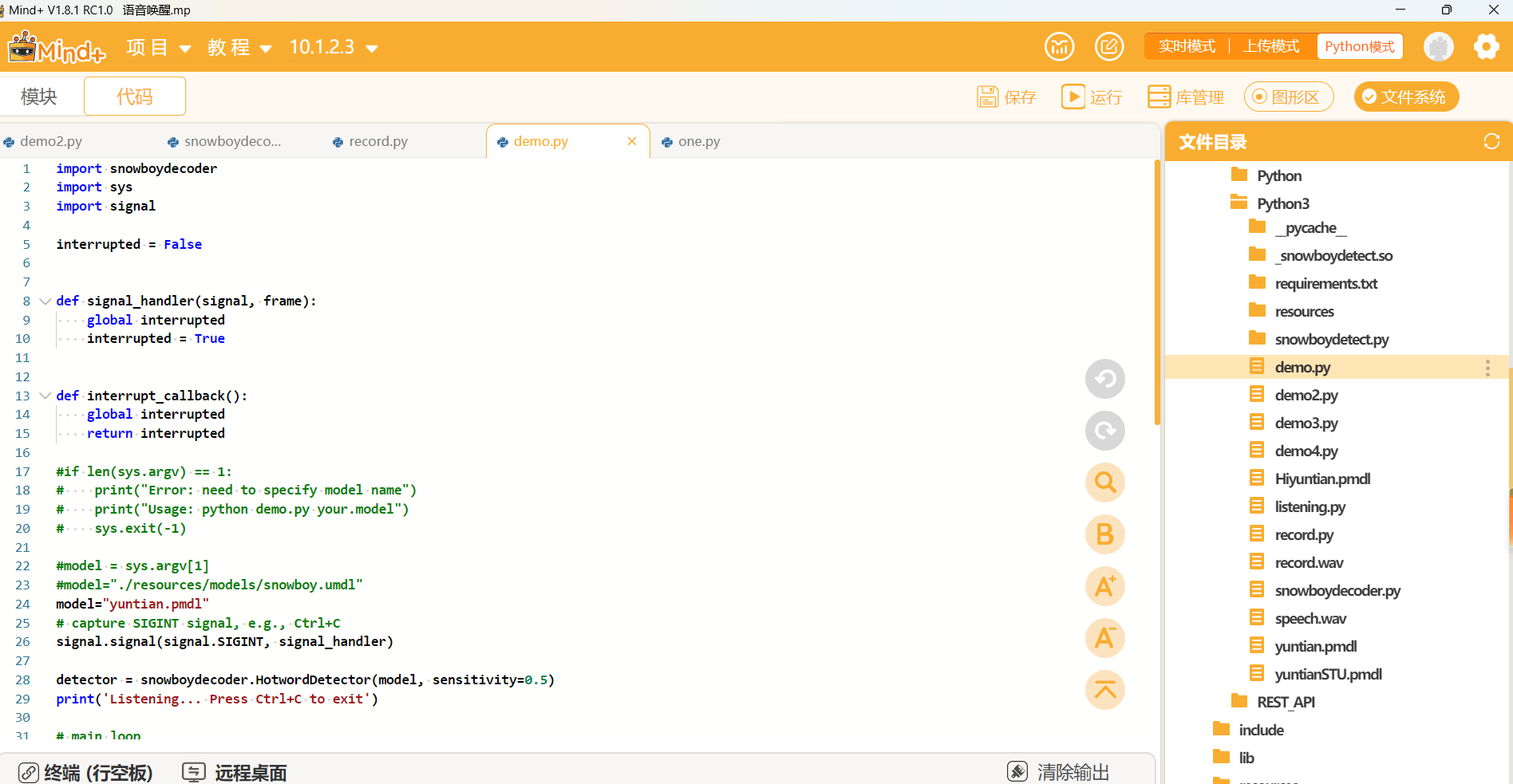
import snowboydecoder
import sys
import signal
interrupted = False
def signal_handler(signal, frame):
global interrupted
interrupted = True
def interrupt_callback():
global interrupted
return interrupted
#if len(sys.argv) == 1:
# print("Error: need to specify model name")
# print("Usage: python demo.py your.model")
# sys.exit(-1)
#model = sys.argv[1]
#model="./resources/models/snowboy.umdl"
model="yuntian.pmdl"
# capture SIGINT signal, e.g., Ctrl+C
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal_handler)
detector = snowboydecoder.HotwordDetector(model, sensitivity=0.5)
print('Listening... Press Ctrl+C to exit')
# main loop
detector.start(detected_callback=snowboydecoder.play_audio_file,
interrupt_check=interrupt_callback,
sleep_time=0.03)
detector.terminate()
【完整程序】
修改”snowboydecoder.py“文件,实现语音唤醒、人声检测、语音识别、对话处理和语音合成技术,以流畅的语音交互体验。
#!/usr/bin/env python
import collections
import pyaudio
import snowboydetect
import time
import wave
import os
import logging
from ctypes import *
from contextlib import contextmanager
import sys
sys.path.append("/root/mindplus/.lib/thirdExtension/liliang-xunfeiyuyin-thirdex")
sys.path.append("/root/mindplus/.lib/thirdExtension/mengchangfeng-kimi-thirdex")
import xunfeiasr
import openai
import json
from unihiker import Audio
from df_xfyun_speech import XfTts
from unihiker import GUI
import record
u_gui=GUI()
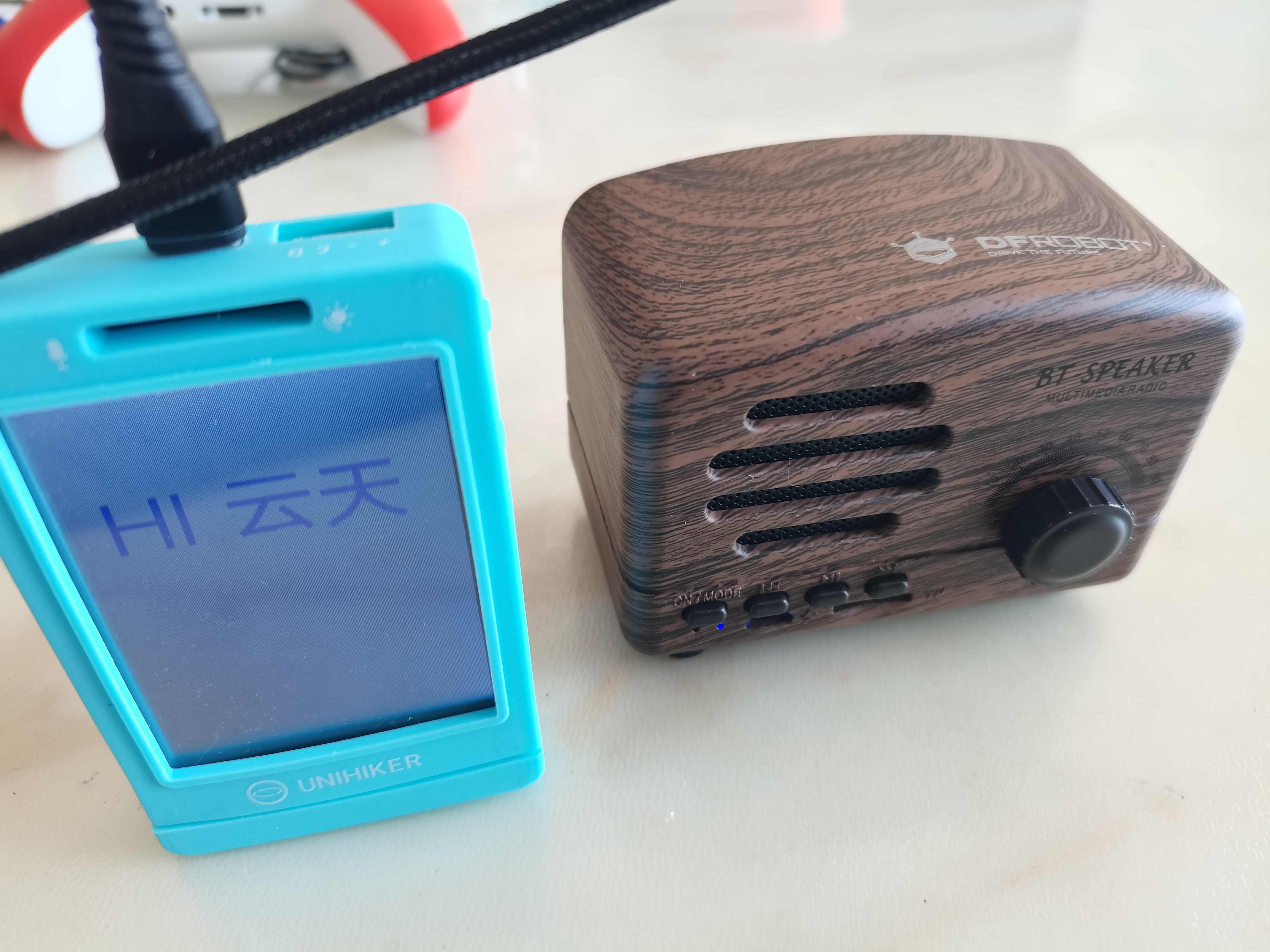
显示=u_gui.draw_text(text="Hi 云天",x=25,y=60,font_size=40, color="#0000FF")
appId = "5c7a6af2" #填写控制台中获取的 APPID 信息
apiSecret = "YTYwZjMwMDYwNDVjYTU0OTFhY2RmNjEx" #填写控制台中获取的 APISecret 信息
apiKey ="94932090baf7bb1eae2200ace714f424" #填写控制台中获取的 APIKey 信息
u_audio = Audio()
options = {}
tts = XfTts(appId, apiKey, apiSecret, options)
xunfeiasr.xunfeiasr_set(APPID=appId,APISecret=apiSecret,APIKey=apiKey)
client = openai.OpenAI(api_key="sk-7EuCue2dQIFOWzaBpeavzSNjxrTi0KXbKVKKbDiN7n1vR8Mz", base_url="https://api.moonshot.cn/v1")
kimi_model = "moonshot-v1-8k"
kimi_temperature = 0.3
kimi_history = [
{"role": "system", "content": """你是 Kimi,由 Moonshot AI 提供的人工智能助手,
你更擅长中文和英文的对话。你会为用户提供安全,有帮助,准确的回答。
回答问题的时候尽量精简词语,尽量将回答控制在100字以内。
也不需要在回答中添加关于时效性或者是请注意之类的额外说明"""}
]
def kimi_chat(query, kimi_history, kimi_model, kimi_temperature):
kimi_history.append({
"role": "user",
"content": query
})
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model=kimi_model,
messages=kimi_history,
temperature=kimi_temperature,
)
result = completion.choices[0].message.content
kimi_history.append({
"role": "assistant",
"content": result
})
return result
interrupted = False
logging.basicConfig()
logger = logging.getLogger("snowboy")
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
TOP_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
RESOURCE_FILE = os.path.join(TOP_DIR, "resources/common.res")
DETECT_DING = os.path.join(TOP_DIR, "resources/wzn.wav")
DETECT_DONG = os.path.join(TOP_DIR, "resources/dong.wav")
def py_error_handler(filename, line, function, err, fmt):
pass
ERROR_HANDLER_FUNC = CFUNCTYPE(None, c_char_p, c_int, c_char_p, c_int, c_char_p)
c_error_handler = ERROR_HANDLER_FUNC(py_error_handler)
@contextmanager
def no_alsa_error():
try:
asound = cdll.LoadLibrary('libasound.so')
asound.snd_lib_error_set_handler(c_error_handler)
yield
asound.snd_lib_error_set_handler(None)
except:
yield
pass
class RingBuffer(object):
"""Ring buffer to hold audio from PortAudio"""
def __init__(self, size=4096):
self._buf = collections.deque(maxlen=size)
def extend(self, data):
"""Adds data to the end of buffer"""
self._buf.extend(data)
def get(self):
"""Retrieves data from the beginning of buffer and clears it"""
tmp = bytes(bytearray(self._buf))
self._buf.clear()
return tmp
def play_audio_file(fname=DETECT_DING):
"""Simple callback function to play a wave file. By default it plays
a Ding sound.
:param str fname: wave file name
:return: None
"""
ding_wav = wave.open(fname, 'rb')
ding_data = ding_wav.readframes(ding_wav.getnframes())
with no_alsa_error():
audio = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream_out = audio.open(
format=audio.get_format_from_width(ding_wav.getsampwidth()),
channels=ding_wav.getnchannels(),
rate=ding_wav.getframerate(), input=False, output=True)
stream_out.start_stream()
stream_out.write(ding_data)
time.sleep(0.2)
stream_out.stop_stream()
stream_out.close()
audio.terminate()
class HotwordDetector(object):
"""
Snowboy decoder to detect whether a keyword specified by `decoder_model`
exists in a microphone input stream.
:param decoder_model: decoder model file path, a string or a list of strings
:param resource: resource file path.
:param sensitivity: decoder sensitivity, a float of a list of floats.
The bigger the value, the more senstive the
decoder. If an empty list is provided, then the
default sensitivity in the model will be used.
:param audio_gain: multiply input volume by this factor.
:param apply_frontend: applies the frontend processing algorithm if True.
"""
def __init__(self, decoder_model,
resource=RESOURCE_FILE,
sensitivity=[],
audio_gain=1,
apply_frontend=False):
tm = type(decoder_model)
ts = type(sensitivity)
if tm is not list:
decoder_model = [decoder_model]
if ts is not list:
sensitivity = [sensitivity]
model_str = ",".join(decoder_model)
self.detector = snowboydetect.SnowboyDetect(
resource_filename=resource.encode(), model_str=model_str.encode())
self.detector.SetAudioGain(audio_gain)
self.detector.ApplyFrontend(apply_frontend)
self.num_hotwords = self.detector.NumHotwords()
if len(decoder_model) > 1 and len(sensitivity) == 1:
sensitivity = sensitivity * self.num_hotwords
if len(sensitivity) != 0:
assert self.num_hotwords == len(sensitivity), \
"number of hotwords in decoder_model (%d) and sensitivity " \
"(%d) does not match" % (self.num_hotwords, len(sensitivity))
sensitivity_str = ",".join([str(t) for t in sensitivity])
if len(sensitivity) != 0:
self.detector.SetSensitivity(sensitivity_str.encode())
self.ring_buffer = RingBuffer(
self.detector.NumChannels() * self.detector.SampleRate() * 5)
def start(self, detected_callback=play_audio_file,
interrupt_check=lambda: False,
sleep_time=0.03,
audio_recorder_callback=None,
silent_count_threshold=15,
recording_timeout=100):
"""
Start the voice detector. For every `sleep_time` second it checks the
audio buffer for triggering keywords. If detected, then call
corresponding function in `detected_callback`, which can be a single
function (single model) or a list of callback functions (multiple
models). Every loop it also calls `interrupt_check` -- if it returns
True, then breaks from the loop and return.
:param detected_callback: a function or list of functions. The number of
items must match the number of models in
`decoder_model`.
:param interrupt_check: a function that returns True if the main loop
needs to stop.
:param float sleep_time: how much time in second every loop waits.
:param audio_recorder_callback: if specified, this will be called after
a keyword has been spoken and after the
phrase immediately after the keyword has
been recorded. The function will be
passed the name of the file where the
phrase was recorded.
:param silent_count_threshold: indicates how long silence must be heard
to mark the end of a phrase that is
being recorded.
:param recording_timeout: limits the maximum length of a recording.
:return: None
"""
self._running = True
def audio_callback(in_data, frame_count, time_info, status):
self.ring_buffer.extend(in_data)
play_data = chr(0) * len(in_data)
return play_data, pyaudio.paContinue
with no_alsa_error():
self.audio = pyaudio.PyAudio()
self.stream_in = self.audio.open(
input=True, output=False,
format=self.audio.get_format_from_width(
self.detector.BitsPerSample() / 8),
channels=self.detector.NumChannels(),
rate=self.detector.SampleRate(),
frames_per_buffer=2048,
stream_callback=audio_callback)
if interrupt_check():
logger.debug("detect voice return")
return
tc = type(detected_callback)
if tc is not list:
detected_callback = [detected_callback]
if len(detected_callback) == 1 and self.num_hotwords > 1:
detected_callback *= self.num_hotwords
assert self.num_hotwords == len(detected_callback), \
"Error: hotwords in your models (%d) do not match the number of " \
"callbacks (%d)" % (self.num_hotwords, len(detected_callback))
logger.debug("detecting...")
state = "PASSIVE"
while self._running is True:
if interrupt_check():
logger.debug("detect voice break")
break
data = self.ring_buffer.get()
if len(data) == 0:
time.sleep(sleep_time)
continue
status = self.detector.RunDetection(data)
if status == -1:
logger.warning("Error initializing streams or reading audio data")
#small state machine to handle recording of phrase after keyword
if state == "PASSIVE":
if status > 0: #key word found
self.recordedData = []
self.recordedData.append(data)
silentCount = 0
recordingCount = 0
message = "Keyword " + str(status) + " detected at time: "
message += time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",
time.localtime(time.time()))
logger.info(message)
callback = detected_callback[status-1]
if callback is not None:
callback()
显示.config(text="听你说")
record.record_audio()
#u_audio.record("record.wav",6)
text=xunfeiasr.xunfeiasr(r"record.wav")
print(text)
texts=""
if(len(text)>7):
num_lines = (len(text) + 6) // 7
for i in range(num_lines):
texts+=text[i*7:(i+1)*7]+"\n"
显示.config(text="你说:\n"+texts)
else:
显示.config(text="你说:\n"+text)
显示.config(font_size=20)
if(text):
text=kimi_chat(text,kimi_history, kimi_model, kimi_temperature)
显示.config(text="思考中")
显示.config(font_size=40)
tts.synthesis(text+"呢", "speech.wav")
显示.config(text="回答中")
u_audio.play("speech.wav")
显示.config(text="HI 云天")
if audio_recorder_callback is not None:
state = "ACTIVE"
continue
elif state == "ACTIVE":
stopRecording = False
if recordingCount > recording_timeout:
stopRecording = True
elif status == -2: #silence found
if silentCount > silent_count_threshold:
stopRecording = True
else:
silentCount = silentCount + 1
elif status == 0: #voice found
silentCount = 0
if stopRecording == True:
fname = self.saveMessage()
audio_recorder_callback(fname)
state = "PASSIVE"
continue
recordingCount = recordingCount + 1
self.recordedData.append(data)
logger.debug("finished.")
def saveMessage(self):
"""
Save the message stored in self.recordedData to a timestamped file.
"""
filename = 'output' + str(int(time.time())) + '.wav'
data = b''.join(self.recordedData)
#use wave to save data
wf = wave.open(filename, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(1)
wf.setsampwidth(self.audio.get_sample_size(
self.audio.get_format_from_width(
self.detector.BitsPerSample() / 8)))
wf.setframerate(self.detector.SampleRate())
wf.writeframes(data)
wf.close()
logger.debug("finished saving: " + filename)
return filename
def terminate(self):
"""
Terminate audio stream. Users can call start() again to detect.
:return: None
"""
self.stream_in.stop_stream()
self.stream_in.close()
self.audio.terminate()
self._running = False
【视频演示】
【应用场景】
本项目适用于家庭、办公室、服务机器人等多种场景,可以作为智能助手、语音控制中心或信息查询工具,为用户提供便捷的语音交互服务。
本项目的实施将推动语音交互技术在智能家居和物联网领域的应用,提高用户的操作便利性和体验满意度,同时也为未来智能设备的发展提供了新的方向。

 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部



评论