【Beetle 树莓派RP2350】环境气体监测仪
本文介绍了 Beetle 树莓派 RP2350 结合 盛思锐SEN66 用 MicroPython 和 OLED 实现环境气体实时显示和监测的项目设计。
项目介绍
准备工作:硬件连接、软件库安装;
工程测试:根据官方手册实现 MicroPython 驱动设计,实现 SEN66 传感器数据的终端打印;
OLED 显示:结合 SSD1306 库,实现 OLED 驱动并显示实时传感器数据;
准备工作
包括硬件连接、开发环境搭建、驱动设计等。
硬件连接
将 SEN66 的 IIC 引脚对应连接至开发板;
| SEN66 | RP2350 | Note |
|---|---|---|
| SDA (green) | SDA (4) | Serial Data |
| SCL (yellow) | SCL (5) | Serial Clock |
| GND (black) | GND | Ground |
| VCC (red) | 3.3V | Power |
实物图
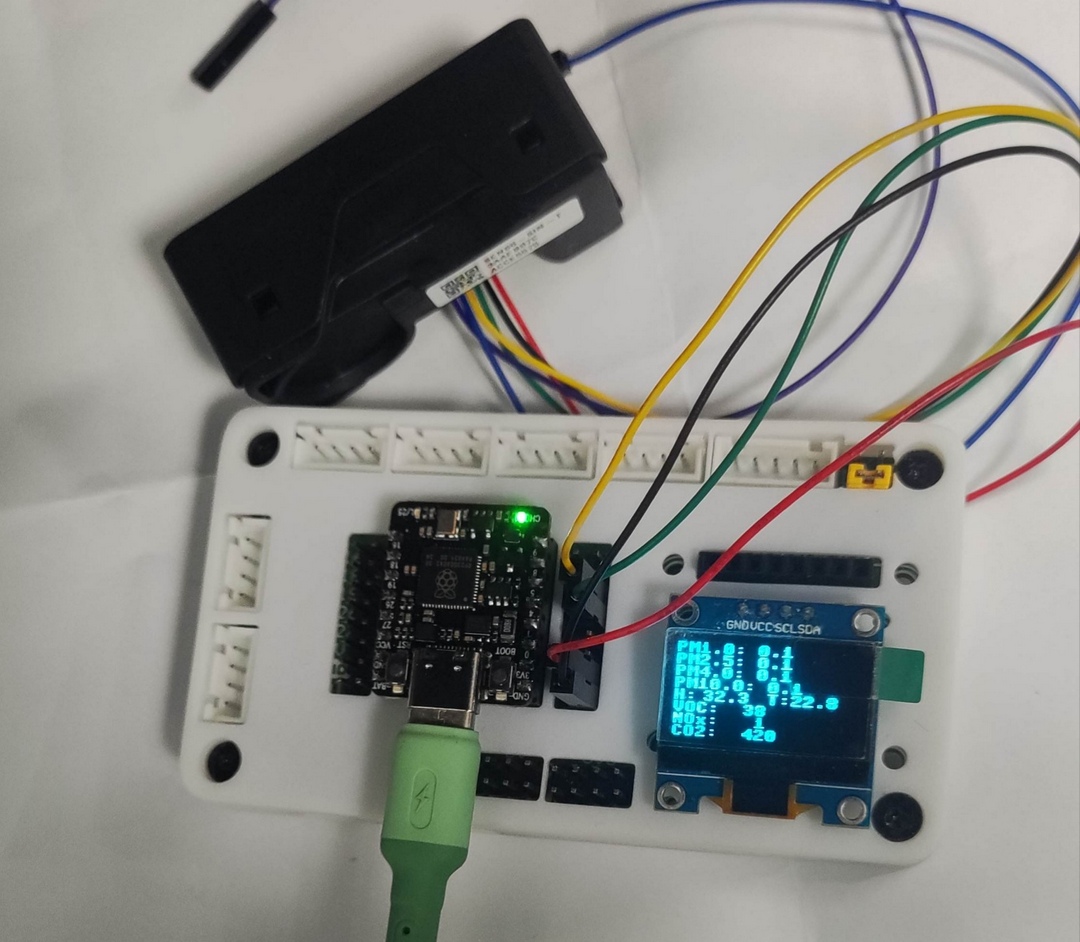
SEN66 引脚
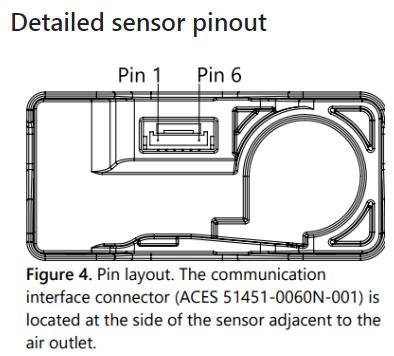
引脚定义及描述
| Pin | Color | Name | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | red | VDD | Supply Voltage | 3.3V ±5% |
| 2 | black | GND | Ground | |
| 3 | green | SDA | I2C: Serial data input / output | TTL 5V compatible |
| 4 | yellow | SCL | I2C: Serial clock input | TTL 5V compatible |
| 5 | NC | Do not connect | Ground (Pins 2 and 5 are connected internally) | |
| 6 | NC | Do not connect | Supply voltage (Pins 1 and 6 are connected internally) |
详见:https://github.com/Sensirion/arduino-i2c-sen66
OLED 连接
将 IIC OLED 连接至 RP2350 开发板;
| OLED | RP2350 | Note |
|---|---|---|
| SDA | SDA (4) | Serial Data |
| SCL | SCL (5) | Serial Clock |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| VCC | 3.3V | Power |
OLED 驱动代码 ssd1306.py 详见:https://oshwhub.com/jinleili/dht11-module
开发环境搭建
下载并安装 Thonny IDE;

驱动设计
运行 Thonny IDE,新建工程文件,添加如下 SEN66 驱动代码
import machine
from micropython import const
import time
import random
"""
Library for the Sensirion SEN66 multi-sensor module.
Hardware Connections:
- VCC: 3.3 V (only 1 wire has to be connected)
- Ground (only 1 wire has to be connected)
- I2C: @100 kHz
Code is not yet compleet. Working with default settings and able to read out
measurement values
"""
class SEN66:
address = 0x6b #107
clean_interval_bounds= (86400,2*86400) # clean every other day the fan
mode = 'idle'
commands = {
'activate_sht_heater': {'code': [0x67, 0x65], 'delay':20, 'length':0, 'mode': 'idle'},
'device_reset': {'code': [0xd3, 0x04], 'delay':1200, 'length':0, 'mode':'idle'},
'get_ambient_pressure':{'code': [0x67, 0x20], 'delay':20, 'length':3, 'mode': 'both'},
'get_data_ready': {'code': [0x02, 0x02], 'delay':20, 'length':3, 'mode': 'measurement'},
'get_product_name' : {'code': [0xd0, 0x14], 'delay':20, 'length':48, 'mode': 'both'},
'get_sensor_altitude': {'code': [0x67, 0x36], 'delay':20, 'length':3, 'mode': 'idle'},
'get_serial_number': {'code': [0xd0, 0x33], 'delay':20, 'length':48, 'mode': 'both'},
'get_sht_heater_measurement':{'code':[0x67,0x90], 'delay':20, 'length':6, 'mode': 'idle'},
'get_version': {'code': [0xd1, 0x00], 'delay':20, 'length':12, 'mode':'both'},
'start_fan_cleaning': {'code': [0x56, 0x07], 'delay':20, 'length':0, 'mode': 'idle'},
'start_measurement': {'code': [0x00,0x21], 'delay':50, 'length':0, 'mode': 'idle'},
'stop_measurement': {'code': [0x01, 0x04], 'delay':1000, 'length':0, 'mode': 'measurement'},
'read_and_clear_device_status': {'code': [0xd2, 0x10], 'delay':20, 'length':6, 'mode':'both'},
'read_device_status': {'code': [0xd2, 0x06], 'delay':20, 'length':6, 'mode':'both'},
'read_measured_raw' : {'code': [0x04, 0x05], 'delay':20, 'length':15, 'mode': 'measurement'},
'read_measured_values':{'code': [0x03, 0x00], 'delay':20, 'length':27, 'mode':'measurement'},
'read_number_concentration': {'code': [0x03, 0x16], 'delay':20, 'length':15, 'mode':'measurement'},
}
def __init__(self, i2c, address=None, wdt=None):
"""
Initialize the Sensirion SEN66 sensor
arguments:
i2c: i2c object connected to the bus where the sensor is connected.
address: (optional) I2C address of the sensor, default 0x6B
wdt: (optional) watchdog-timer object with a feed argument. Will feed every other second orso.
raises:
raises an error if the sensor can not be detected on the I2C bus.
"""
self.wdt = wdt
self.i2c = i2c
if address:
self.address = address
self.__I2C_scan()
self.wdt_feed()
self.get_id()
self.clean_interval = random.randint(self.clean_interval_bounds[0], self.clean_interval_bounds[1])
self.t0 = time.time()
self.wdt_feed()
def wdt_feed(self):
"""
Feed the watchdog.
"""
if self.wdt:
self.wdt.feed()
def print_string(self, data):
""" Creates a printable string from the data.
arguments:
data: list of bytes from the SEN66. Should be 2 bytes followed
by one CRC byte.
return:
data as string-object from the data where the CRC bytes are excluded.
Zero's (0x00) add the end of the string are removed.
"""
ll = sorted(list(range(0,len(data), 3))
+ list(range(1, len(data), 3)))
data = ''.join([chr(data[ii]) for ii in ll])
return data.replace('\x00', '') # replace empties...
def get_status(self, verbose=False):
""" Get the status from the sensor
Fills the status member of this object with the status bits (32 bit).
arguments:
verbose: (default False) if true prints the status bits of the sensor
"""
status = self.crc_all(self.__I2C_write('read_device_status'))
self.status = (status[0] << 24) + (status[1] << 16) + (status[3] << 8) + status[4]
if verbose:
print('Status bits:')
print('{0:016b}'.format(self.status))
def get_id(self, verbose=False):
""" Get the product name, serial number and firmware version of the sensor
arguments:
verbose: (default = False) also print all the information.
raises:
Error: if SEN66 string is not found in the product name.
"""
self.name = self.crc_all(self.__I2C_write('get_product_name'))
if self.name:
self.name = self.print_string(self.name)
if self.name != 'SEN66':
print(self.name)
raise Error('Something wrong with the sensorstring! Did you get an SEN66?')
firmware = self.crc_all(self.__I2C_write('get_version'))
self.firmware = float("%d.%d" %(firmware[0], firmware[1]))
self.serial = self.print_string(self.crc_all(self.__I2C_write('get_serial_number')))
if verbose:
print('Sensor: ',self.name)
print("Firmware version: %2.1f" %(self.firmware))
print("Serial: ", self.serial)
def crc_all(self, data):
crc = 0
for ii in range(len(data)//3):
item = ii*3
crc += self.__CRC([data[item], data[item+1]]) - data[item+2]
if crc == 0:
return data
else:
return None
def start(self):
self.__I2C_write('start_measurement')
self.mode = 'measurement'
def stop(self):
self.__I2C_write('stop_measurement')
self.mode = 'idle'
def get_data(self):
if self.mode != 'measurement':
raise Exception('device not in measurement mode!')
ready = self.__I2C_write('get_data_ready')
data = None
if ready[1] == 1:
data = self.__I2C_write('read_measured_values')
pm1p0 = self.parse_crc(data[0], data[1], data[2])/10
pm2p5 = self.parse_crc(data[3], data[4], data[5])/10
pm4p0 = self.parse_crc(data[6], data[7], data[8])/10
pm10p0 = self.parse_crc(data[9], data[10], data[11])/10
amb_hum = self.parse_crc(data[12], data[13], data[14])/100
amb_temp = self.parse_crc(data[15], data[16], data[17])/200
voc = self.parse_crc(data[18], data[19], data[20])/10
nox = self.parse_crc(data[21], data[22], data[23])/10
co2 = self.parse_crc(data[24], data[25], data[26])
data = (pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2)
self.clean()
return data
def clean(self, force=False):
now = time.time()
self.wdt_feed()
if force or ((now - self.t0) > self.clean_interval):
print('cleaning fan!')
# set new times
self.clean_interval = random.randint(self.clean_interval_bounds[0], self.clean_interval_bounds[1])
self.t0 = now
# stop measurement, clean, and start gain
self.__I2C_write('stop_measurement')
self.wdt_feed()
time.sleep(1)
self.__I2C_write('start_fan_cleaning')
for ii in range(5):
self.wdt_feed()
time.sleep(3)
self.__I2C_write('start_measurement')
def parse_crc(self, b1, b2, crc):
if self.__CRC([b1, b2]) != crc:
return None
return (b1 << 8) + b2
def __I2C_scan(self):
self.wdt_feed()
bus = self.i2c.scan()
if (len(bus) > 10) or (self.address not in bus):
print(bus, self.address)
raise OSError("device not found! Are the cables connected?")
def __I2C_write(self, command):
self.wdt_feed()
self.i2c.writeto(self.address, bytearray(self.commands[command]['code']))
time.sleep(self.commands[command]['delay']/1000)
self.wdt_feed()
data = None
if self.commands[command]['length'] > 0:
data = self.__I2C_read(command)
return data
def __I2C_read(self, command):
return self.i2c.readfrom(self.address, self.commands[command]['length'])
def __CRC(self, data):
poly = 0x31
init = 0xff
crc = init
for ii in range(len(data)):
crc ^= (data[ii])
crc &= 0xff
for _ in range(8):
if crc & 0x80:
crc = (crc << 1) ^ poly
else:
crc = (crc << 1)
crc &= 0xff
return crc
if __name__ == "__main__":
i2c0 = machine.I2C(1, sda=machine.Pin(18), scl=machine.Pin(19), freq=100000)
sen = SEN66(i2c0)
sen.start()
sen.clean(force=True) # force a cleanup of the sensor
#for ii in range(5):
running = True
while running:
try:
print(sen.get_data())
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
running = False
保存代码文件为 sen66.py ;
上传驱动文件 sen66.py 和 ssd1306.py 至板端根目录;
详见:https://github.com/ddland/mp_sen66
工程测试
结合 SEN66 驱动设计,实现环境气体数据的串口打印。
代码
新建 Thonny IDE 工程文件,添加如下代码
from sen66 import SEN66
from machine import Pin, I2C
import time
i2c0 = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=100_000)
sen = SEN66(i2c0)
sen.start()
for ii in range(5):
print(sen.get_data())
time.sleep(1)
保存并运行代码。
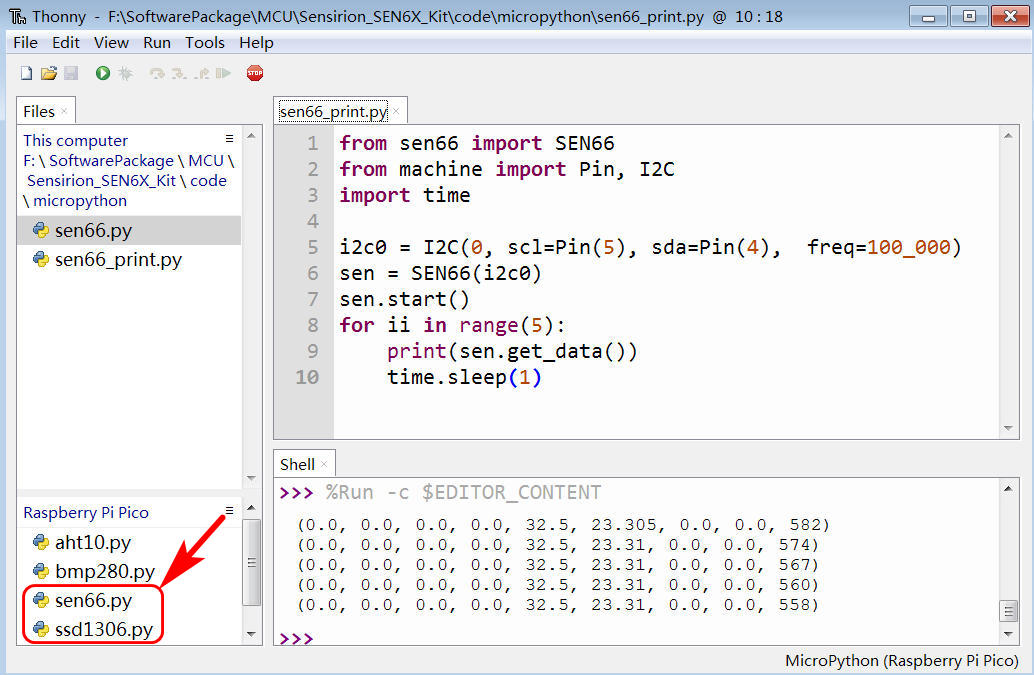
效果
终端打印传感器数据;

9 列数据分别为 PM1.0、PM2.5、PM4.0、PM10.0、湿度、温度、VOC系数、NOx系数、CO2 浓度;
即 pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2
OLED 实时显示
将 OLED 连接至开发板,使用 ssd1306.py 库驱动 IIC OLED 显示传感器数据。
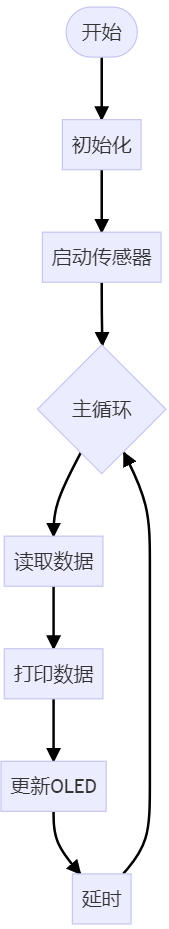
流程图
代码
打开 Thonny IDE 软件,新建工程文件,添加如下代码
from machine import Pin, I2C
from sen66 import SEN66
from ssd1306 import SSD1306_I2C
import time
# ==== Initialized IIC OLED ====
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=400000)
oled_width = 128
oled_height = 64
oled = SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c)
#i2c0 = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=100_000)
sen = SEN66(i2c)
sen.start()
def display_sen66(pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2):
oled.fill(0)
oled.text("PM1.0:", 0, 0)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm1p0), 56, 0)
oled.text("PM2.5:", 0, 8)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm2p5), 56, 8)
oled.text("PM4.0:", 0, 16)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm4p0), 56, 16)
oled.text("PM10.0:", 0, 24)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm10p0), 64, 24)
oled.text("H:", 0, 32)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(amb_hum), 20, 32)
oled.text("T:", 64, 32)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(amb_temp), 80, 32)
oled.text("VOC:", 0, 40)
oled.text("{:3d}".format(int(voc)), 40, 40)
oled.text("NOx:", 0, 48)
oled.text("{:3d}".format(int(nox)), 40, 48)
oled.text("CO2:", 0, 56)
oled.text("{:4d}".format(int(co2)), 40, 56)
oled.show()
while True:
pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2 = sen.get_data()
print("PM1.0={:.1f} PM2.5={:.1f} PM4.0={:.1f} PM10={:.1f} | "
"T={:.1f}°C H={:.1f}% | VOC={:.0f} NOx={:.0f} | CO2={:.0f} ppm"
.format(pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_temp, amb_hum, voc, nox, co2))
display_sen66(pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2)
time.sleep(2)
保存代码。
效果
运行程序,终端打印环境气体参数;
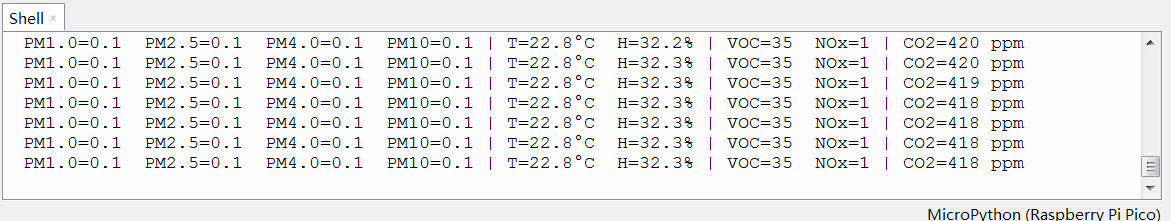
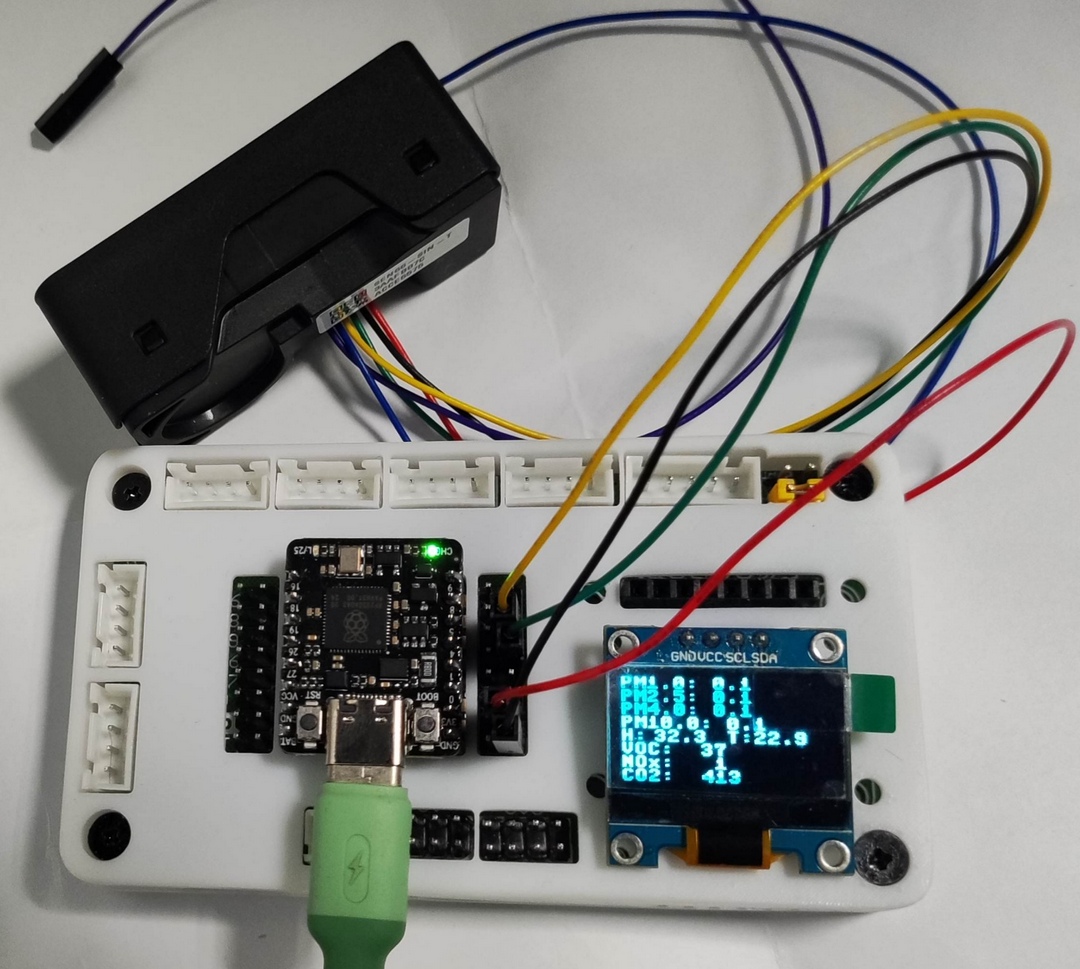
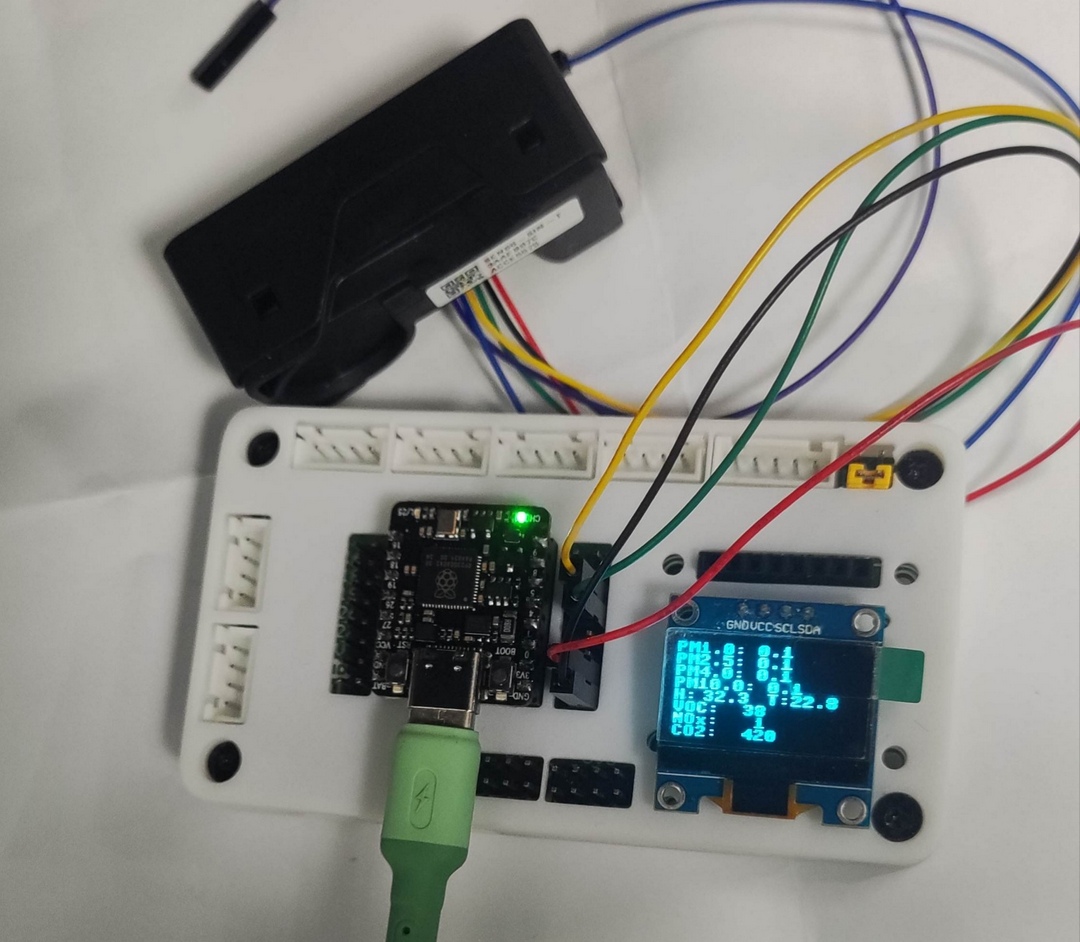
同时 OLED 显示实时环境气体指标信息;

显示数据每两秒更新一次;
总结
本文介绍了 Beetle 树莓派 RP2350 结合 盛思锐SEN66 用 MicroPython 和 OLED 实现环境气体实时显示和监测的项目设计,为相关产品在工业数据采集、智慧家庭、消费电子等领域的快速开发和应用设计提供了参考。
from machine import Pin, I2C
from sen66 import SEN66
from ssd1306 import SSD1306_I2C
import time
# ==== Initialized IIC OLED ====
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=400000)
oled_width = 128
oled_height = 64
oled = SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c)
#i2c0 = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=100_000)
sen = SEN66(i2c)
sen.start()
def display_sen66(pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2):
oled.fill(0)
oled.text("PM1.0:", 0, 0)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm1p0), 56, 0)
oled.text("PM2.5:", 0, 8)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm2p5), 56, 8)
oled.text("PM4.0:", 0, 16)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm4p0), 56, 16)
oled.text("PM10.0:", 0, 24)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(pm10p0), 64, 24)
oled.text("H:", 0, 32)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(amb_hum), 20, 32)
oled.text("T:", 64, 32)
oled.text("{:.1f}".format(amb_temp), 80, 32)
oled.text("VOC:", 0, 40)
oled.text("{:3d}".format(int(voc)), 40, 40)
oled.text("NOx:", 0, 48)
oled.text("{:3d}".format(int(nox)), 40, 48)
oled.text("CO2:", 0, 56)
oled.text("{:4d}".format(int(co2)), 40, 56)
oled.show()
while True:
pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2 = sen.get_data()
print("PM1.0={:.1f} PM2.5={:.1f} PM4.0={:.1f} PM10={:.1f} | "
"T={:.1f}°C H={:.1f}% | VOC={:.0f} NOx={:.0f} | CO2={:.0f} ppm"
.format(pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_temp, amb_hum, voc, nox, co2))
display_sen66(pm1p0, pm2p5, pm4p0, pm10p0, amb_hum, amb_temp, voc, nox, co2)
time.sleep(2)

 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部




评论