
关于 ADXL 335 加速度计
什么是加速度和 ADXL 335 加速度计?加速度是速度随时间变化的过程,它是一个矢量。同样,速度是速度和方向。有两种方法可以解释任何事物的加速度:第一种是速度的变化,第二种是方向的变化。有时两者会同时更改。如果我们谈论 ADXL 335 加速度计,那么这个加速度计是一种用于测量任何物体加速度的设备。它以模拟输入的形式测量 X、Y 和 Z 等三维方向的加速度。它是低噪音和低功耗的设备。当它用于加速度测量目的时,它与任何类型的控制器(如微控制器或 Arduino 等)连接。它多用于建筑作业机械,如钻孔、打桩、拆迁等,人类活动机械如跑步、行走、跳舞和跳绳等。它很容易在市场上或网上商店买到。
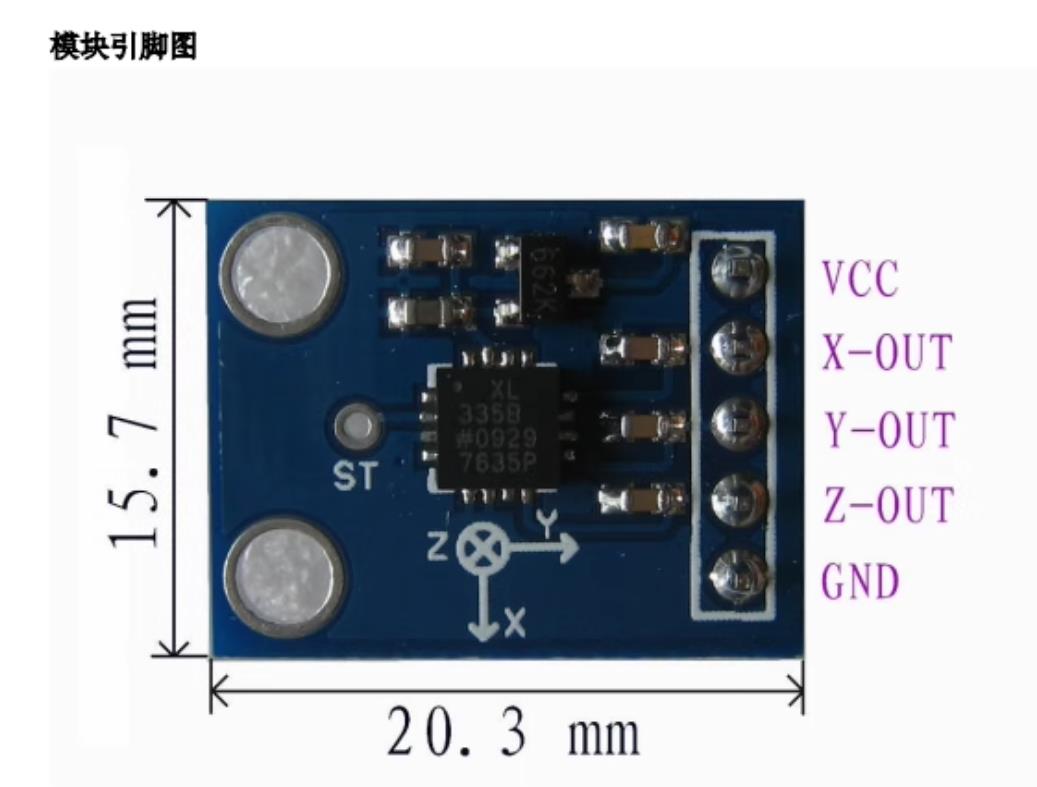
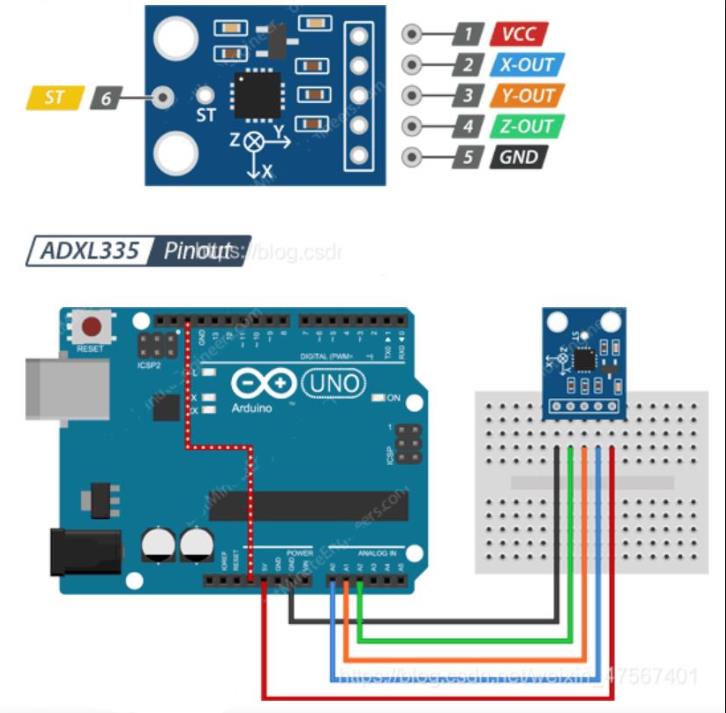
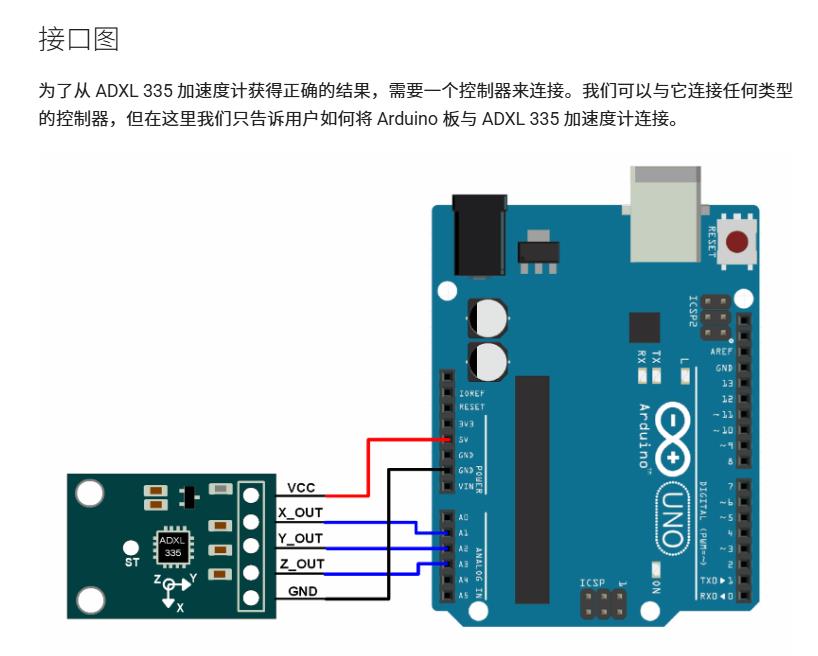
ADXL 335 加速度计的引脚配置

ADXL 335 加速度计的工作原理
目前市场上有不同类型的加速度计,用于不同的目的。有些工作原理是 MEMS(微机电传感器)的工作原理。它由一个小质量组成,该质量被蚀刻到硅表面,然后集成到一个小电路中。当力施加在这个质量上时,它会覆盖一些位移,因此根据牛顿第二运动定律 F= 马 在这个质量中产生加速度,由其传感器感应。同样,如果我们谈论模拟加速度计,那么它们的工作原理有两个原则,例如电容感应和压电感应。两者都有不同的优点和缺点。同样,ADXL335加速度计是一种模拟加速度计,因此它的工作原理是电容感应。在电容式感应加速度计中,当它向任何方向移动时,其电容都会发生变化。当该电容发生变化时,其模拟电压会发生变化,这由其接口控制器感应。
【Arduino】189种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验二百三十九:GY-61 ADXL335模拟量加速度模块 倾斜角度三轴加速度传感器
项目之三:使用模拟电压计算出设备的滚动和俯仰的数值
实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】189种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
实验二百三十九:GY-61 ADXL335模拟量加速度模块 倾斜角度三轴加速度传感器
项目之三:使用模拟电压计算出设备的滚动和俯仰的数值
*/
#include <math.h>
const int x_out = A0; /* connect x_out of module to A0 of UNO board */
const int y_out = A1; /* connect y_out of module to A1 of UNO board */
const int z_out = A2; /* connect z_out of module to A2 of UNO board */
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int x_adc_value, y_adc_value, z_adc_value;
double x_g_value, y_g_value, z_g_value;
double roll, pitch, yaw;
x_adc_value = analogRead(x_out); /* Digital value of voltage on x_out pin */
y_adc_value = analogRead(y_out); /* Digital value of voltage on y_out pin */
z_adc_value = analogRead(z_out); /* Digital value of voltage on z_out pin */
Serial.print("x = ");
Serial.print(x_adc_value);
Serial.print("\t\t");
Serial.print("y = ");
Serial.print(y_adc_value);
Serial.print("\t\t");
Serial.print("z = ");
Serial.print(z_adc_value);
Serial.print("\t\t");
//delay(100);
x_g_value = ( ( ( (double)(x_adc_value * 5)/1024) - 1.65 ) / 0.330 ); /* Acceleration in x-direction in g units */
y_g_value = ( ( ( (double)(y_adc_value * 5)/1024) - 1.65 ) / 0.330 ); /* Acceleration in y-direction in g units */
z_g_value = ( ( ( (double)(z_adc_value * 5)/1024) - 1.80 ) / 0.330 ); /* Acceleration in z-direction in g units */
roll = ( ( (atan2(y_g_value,z_g_value) * 180) / 3.14 ) + 180 ); /* Formula for roll */
pitch = ( ( (atan2(z_g_value,x_g_value) * 180) / 3.14 ) + 180 ); /* Formula for pitch */
//yaw = ( ( (atan2(x_g_value,y_g_value) * 180) / 3.14 ) + 180 ); /* Formula for yaw */
/* Not possible to measure yaw using accelerometer. Gyroscope must be used if yaw is also required */
Serial.print("Roll = ");
Serial.print(roll);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print("Pitch = ");
Serial.print(pitch);
Serial.print("\n\n");
delay(1000);
}代码解读
这段代码使用 加速度传感器 采集 X、Y、Z 轴的运动数据,并计算 倾斜角度(Roll 和 Pitch),核心逻辑如下:
1. 传感器连接
✅ const int x_out = A0; → X 轴信号连接到 A0
✅ const int y_out = A1; → Y 轴信号连接到 A1
✅ const int z_out = A2; → Z 轴信号连接到 A2
2. 读取加速度数据
✅ analogRead(x_out); → 读取 X 轴的电压信号
✅ analogRead(y_out); → 读取 Y 轴的电压信号
✅ analogRead(z_out); → 读取 Z 轴的电压信号
✅ 转换为加速度值(单位 G) → 计算公式:
cpp
x_g_value = ((x_adc_value * 5.0 / 1024) - 1.65) / 0.330;
⚠ 注意: 1.65V 是 零重力点,0.330V/G 是 灵敏度(不同传感器可能不同)
3. 计算倾斜角度
✅ atan2(y_g_value, z_g_value) → 计算 Roll(翻滚角度)
✅ atan2(z_g_value, x_g_value) → 计算 Pitch(俯仰角度)
✅ 转化为角度(度数) → * 180 / 3.14
4. 输出数据
✅ Serial.print("Roll = "); Serial.print(roll); → 打印 Roll 角度
✅ Serial.print("Pitch = "); Serial.print(pitch); → 打印 Pitch 角度
5. 采集间隔
✅ delay(1000); → 每秒采集一次数据,适合稳定读取
6. 为什么没有 Yaw?
⚠ Yaw(偏航角)无法直接从加速度计计算出来,因为加速度计只能检测线性加速度,而偏航角需要陀螺仪。
这个代码让加速度传感器不断采集 XYZ 运动数据,并计算设备的倾斜角度。
实验串口返回情况
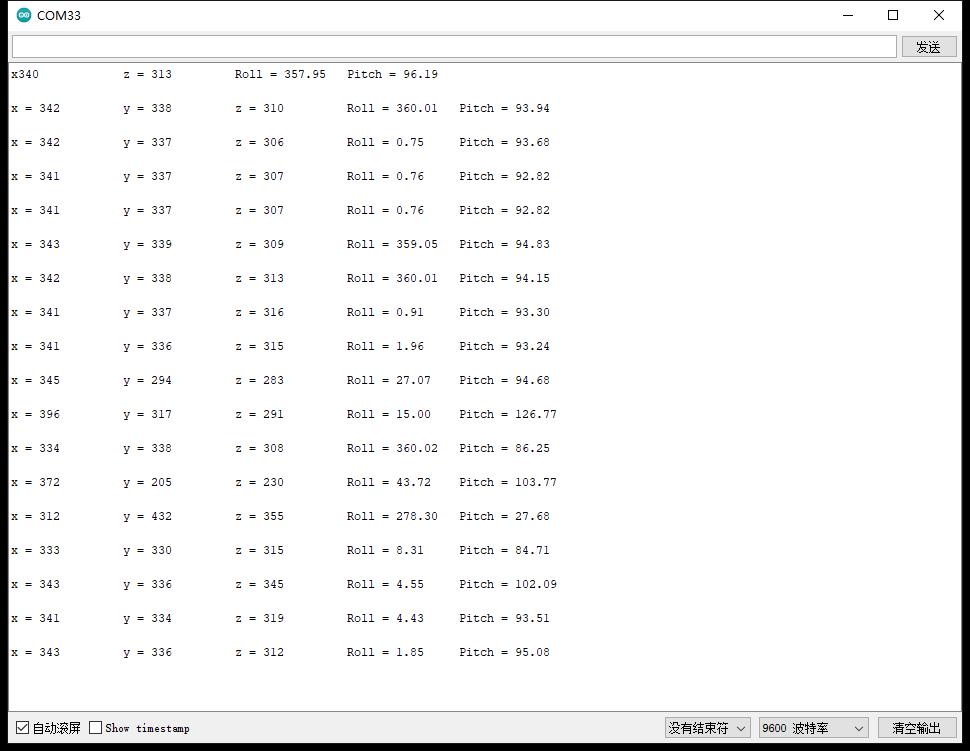
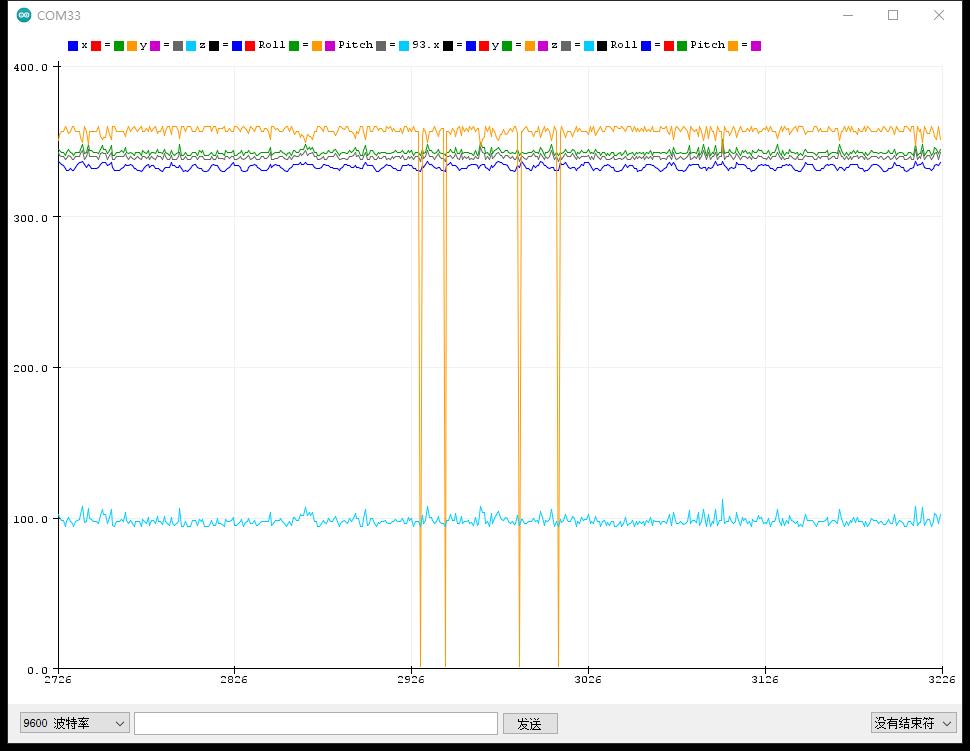
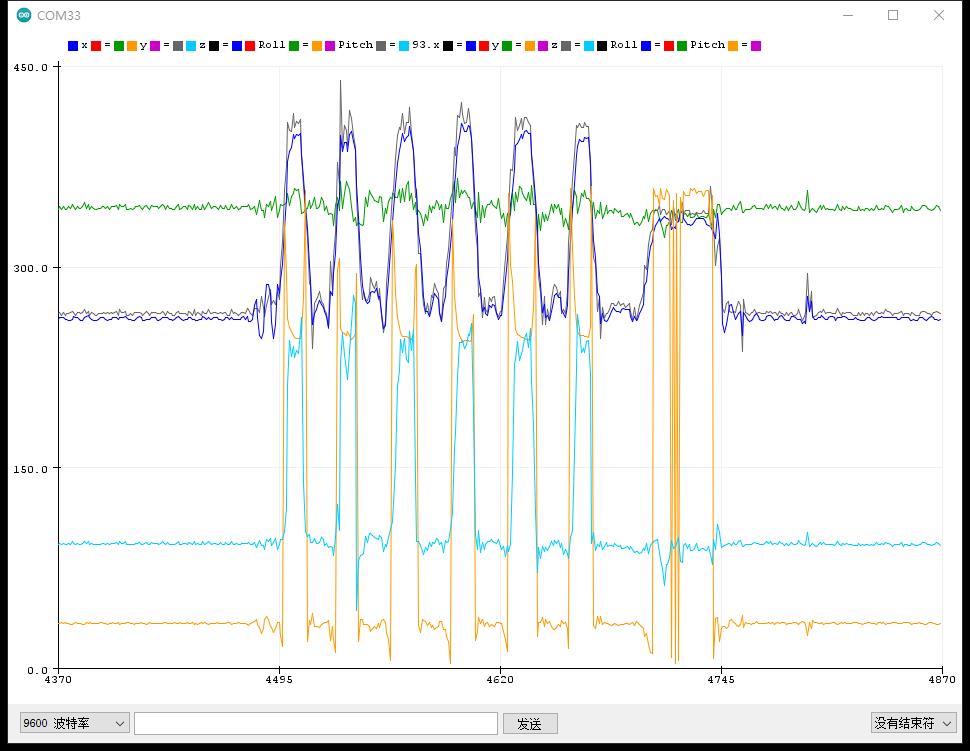
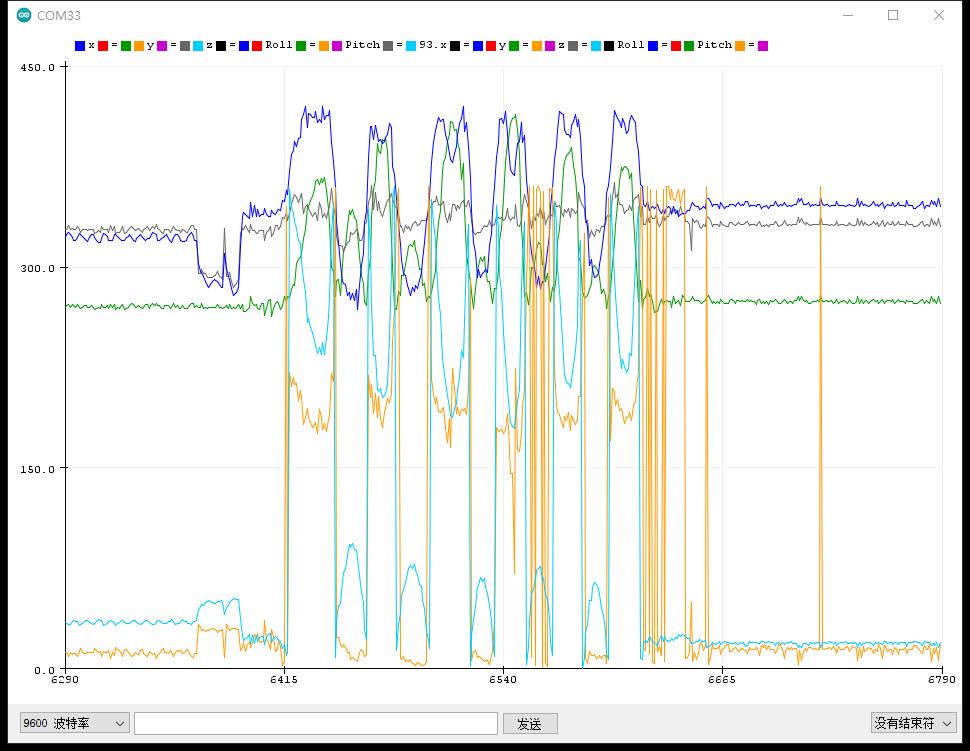
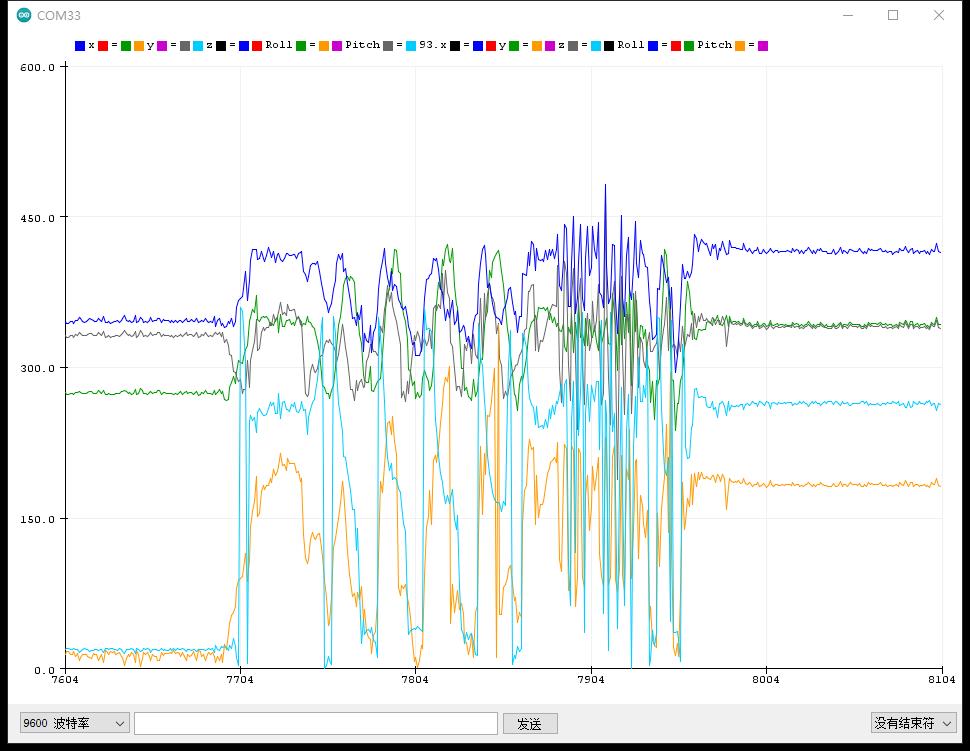
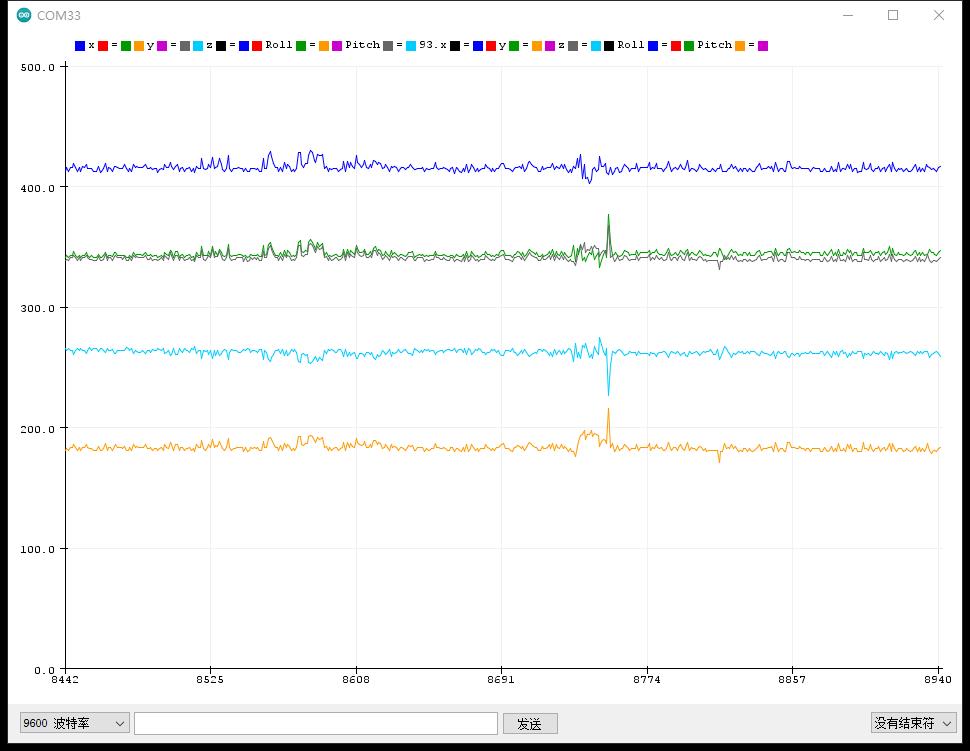
实验串口绘图器返回情况

 返回首页
返回首页
 回到顶部
回到顶部


评论